Document
... • C, H, O, N (sometimes Sulfer) • Monomer – amino acid • Amino acids link together via PEPTIDE bonds to form a polypeptide chain • This chain folds up to form a functional protein ...
... • C, H, O, N (sometimes Sulfer) • Monomer – amino acid • Amino acids link together via PEPTIDE bonds to form a polypeptide chain • This chain folds up to form a functional protein ...
Unit1-KA4-Revision
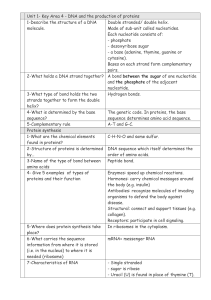
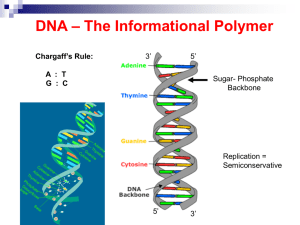
... - a base (adenine, thymine, guanine or cytosine). Bases on each strand form complementary pairs. 2-What holds a DNA strand together? A bond between the sugar of one nucleotide and the phosphate of the adjacent nucleotide. 3-What type of bond holds the two Hydrogen bonds. strands together to form the ...
... - a base (adenine, thymine, guanine or cytosine). Bases on each strand form complementary pairs. 2-What holds a DNA strand together? A bond between the sugar of one nucleotide and the phosphate of the adjacent nucleotide. 3-What type of bond holds the two Hydrogen bonds. strands together to form the ...
AASK Additional Activities
... Some students will randomly generate a sequence of side chains that is very difficult to fold into a shape that simultaneously satisfies all the 4 principles of chemistry. This is a good teaching moment in that the teacher can use these examples to emphasize that such proteins would not be selected ...
... Some students will randomly generate a sequence of side chains that is very difficult to fold into a shape that simultaneously satisfies all the 4 principles of chemistry. This is a good teaching moment in that the teacher can use these examples to emphasize that such proteins would not be selected ...
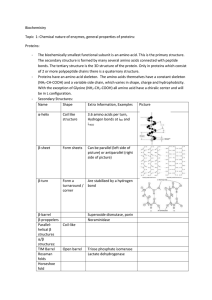
secstruct
... (Ca), an amino group (NH2), a carboxyl group (COOH), a hydrogen atom (H), a side chain (R). There are 20 amino acids The peptide bond is formed as the cacboxyl group of an aa bind to the amino group of the adjacent aa. The primary structure of a protein is simply the linear arrangement, or sequence, ...
... (Ca), an amino group (NH2), a carboxyl group (COOH), a hydrogen atom (H), a side chain (R). There are 20 amino acids The peptide bond is formed as the cacboxyl group of an aa bind to the amino group of the adjacent aa. The primary structure of a protein is simply the linear arrangement, or sequence, ...
Four Levels of Protein Structure
... Four Levels of Protein Structure • Primary Structure: Linear Sequence of Amino Acids Each amino acid has central carbon liked to ---hydrogen (H) ---amino group (NH2) ...
... Four Levels of Protein Structure • Primary Structure: Linear Sequence of Amino Acids Each amino acid has central carbon liked to ---hydrogen (H) ---amino group (NH2) ...
Self Test Quiz-1 Given below are some questions related to protein
... Given below are some questions related to protein and enzymes in general. Each statement is followed by 4 choices. Choose a single correct answer for each question. 1. How many different types of amino acid are used to make proteins? a. 4 b. 20 c. 23 d. 38 2. Amino acids contain carbon, hydrogen, ox ...
... Given below are some questions related to protein and enzymes in general. Each statement is followed by 4 choices. Choose a single correct answer for each question. 1. How many different types of amino acid are used to make proteins? a. 4 b. 20 c. 23 d. 38 2. Amino acids contain carbon, hydrogen, ox ...
1. Protein Interactions
... amino acids have a oneletter symbol. A sequence of three symbols, as shown for RNA (right) is called a Amino acids have a central codon carbon atom attached to a hydrogen, a carboxyl group (COOH) and an amine group (NH2) MSE-536 ...
... amino acids have a oneletter symbol. A sequence of three symbols, as shown for RNA (right) is called a Amino acids have a central codon carbon atom attached to a hydrogen, a carboxyl group (COOH) and an amine group (NH2) MSE-536 ...
File
... • The interaction between the variable side chains is what determines the structure. • These interactions may include hydrogen bonds, disulphide bridges, ionic interactions, polar associations, etc. • The affinity or repulsion of side chains will affect the overall shape of the polypeptide chain and ...
... • The interaction between the variable side chains is what determines the structure. • These interactions may include hydrogen bonds, disulphide bridges, ionic interactions, polar associations, etc. • The affinity or repulsion of side chains will affect the overall shape of the polypeptide chain and ...
Supplementary Material
... The secondary structure definitions of amino acids were generated with DSSP [1] considering only three groups: helical (H), extended (E) and coil (C). Based on this 7 types of protein interfaces can be defined taking into consideration the amount of each of the three basic secondary structural eleme ...
... The secondary structure definitions of amino acids were generated with DSSP [1] considering only three groups: helical (H), extended (E) and coil (C). Based on this 7 types of protein interfaces can be defined taking into consideration the amount of each of the three basic secondary structural eleme ...
BB 450/500 Lecture 5 Highlights
... protein. The word polypeptide refers to a polymer of amino acids. A protein may contain one or more polypeptides and is folded and may be covalently modified. 11. Hemoglobin (and many other proteins) have multiple polypeptide subunits. Interactions between the subunits include disulfide bonds, ionic ...
... protein. The word polypeptide refers to a polymer of amino acids. A protein may contain one or more polypeptides and is folded and may be covalently modified. 11. Hemoglobin (and many other proteins) have multiple polypeptide subunits. Interactions between the subunits include disulfide bonds, ionic ...
Amino Acids - Chemistry Courses: About
... of helices, loops, and sheets • Match – Helix-loophelix – Helix bundle – Hairpin – b-sandwich ...
... of helices, loops, and sheets • Match – Helix-loophelix – Helix bundle – Hairpin – b-sandwich ...
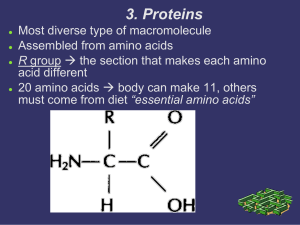
3. Proteins
... R group the section that makes each amino acid different 20 amino acids body can make 11, others must come from diet “essential amino acids” ...
... R group the section that makes each amino acid different 20 amino acids body can make 11, others must come from diet “essential amino acids” ...
Lecture 1
... hydrogen bonds with Ala residues located in an ahelix? A. Residues in a neighbouring a-helix. ...
... hydrogen bonds with Ala residues located in an ahelix? A. Residues in a neighbouring a-helix. ...
The Living World
... One of the three fatty acids is replaced by a phosphate and a small polar functional group ...
... One of the three fatty acids is replaced by a phosphate and a small polar functional group ...
Center for Structural Biology
... Secondary- local Supersecondary (motifs)- intermediate Domains- independent folding units Tertiary- organization of a complete chain Quaternary- organization of multiple chains ...
... Secondary- local Supersecondary (motifs)- intermediate Domains- independent folding units Tertiary- organization of a complete chain Quaternary- organization of multiple chains ...
Protein structure prediction

Protein structure prediction is the prediction of the three-dimensional structure of a protein from its amino acid sequence — that is, the prediction of its folding and its secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structure from its primary structure. Structure prediction is fundamentally different from the inverse problem of protein design. Protein structure prediction is one of the most important goals pursued by bioinformatics and theoretical chemistry; it is highly important in medicine (for example, in drug design) and biotechnology (for example, in the design of novel enzymes). Every two years, the performance of current methods is assessed in the CASP experiment (Critical Assessment of Techniques for Protein Structure Prediction). A continuous evaluation of protein structure prediction web servers is performed by the community project CAMEO3D.