Chapter 6 Notes
... • The reagents can be added above the arrow, most important one is usually first. • The solvent is often omitted from the equation; however, most organic reactions take place in a liquid solvent. • The symbols “D” and “hn ” are used for reactions that require ...
... • The reagents can be added above the arrow, most important one is usually first. • The solvent is often omitted from the equation; however, most organic reactions take place in a liquid solvent. • The symbols “D” and “hn ” are used for reactions that require ...
Population Analysis
... as belonging to the atom in question we see that all three components of ρ (r ) will contribute to the "atomic density". This conflict between our intuitively sensible notion that when charge is near an atom it "belongs" to that atom and the mathematically convenient population analysis has spawned ...
... as belonging to the atom in question we see that all three components of ρ (r ) will contribute to the "atomic density". This conflict between our intuitively sensible notion that when charge is near an atom it "belongs" to that atom and the mathematically convenient population analysis has spawned ...
General Chemistry (II) Chapter 1: Chemical Kinetic 1
... Chapter 6: Organic Chemistry, Polymers and Biochemistry 6-1 Hydrocarbons 6-1-1 Saturated Hydrocarbon 6-1-2 Nomenclature of Alkanes 6-1-3 Properties and Reaction of Alkanes 6-1-4 Cycloalkanes 6-1-5 Optical Isomerism in organic compounds 6-2 Unsaturated Hydrocarbons 6-2-1 Alkenes and Alkynes 6-2-2 Nom ...
... Chapter 6: Organic Chemistry, Polymers and Biochemistry 6-1 Hydrocarbons 6-1-1 Saturated Hydrocarbon 6-1-2 Nomenclature of Alkanes 6-1-3 Properties and Reaction of Alkanes 6-1-4 Cycloalkanes 6-1-5 Optical Isomerism in organic compounds 6-2 Unsaturated Hydrocarbons 6-2-1 Alkenes and Alkynes 6-2-2 Nom ...
CHM222A: Basic Physical Chemistry
... Elucidation of the mechanism : Gerhard Ertl (Nobel Prize 2007) ...
... Elucidation of the mechanism : Gerhard Ertl (Nobel Prize 2007) ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034 PART-A
... 12. State and explain the Hammond postulate to the bromination of n-propane. 13. How will you determine the reaction mechanism of hydrolysis of an ester using isotoping labeling method? 14. Write and explain the Steven’s rearrangement. 15. Predict the product and explain the mechanism of the followi ...
... 12. State and explain the Hammond postulate to the bromination of n-propane. 13. How will you determine the reaction mechanism of hydrolysis of an ester using isotoping labeling method? 14. Write and explain the Steven’s rearrangement. 15. Predict the product and explain the mechanism of the followi ...
Reaction Rates
... 3. H2O + SO3 H2SO4 4. O2 + C3H8 H2O + CO2 5. CaSO4 + Mg(OH)2 Ca(OH)2 + MgSO4 ...
... 3. H2O + SO3 H2SO4 4. O2 + C3H8 H2O + CO2 5. CaSO4 + Mg(OH)2 Ca(OH)2 + MgSO4 ...
Grade XII Foreign SET 2 Chemistry (Theory)
... (i) Nitrogen is chemically less reactive. This is because of the high stability of its molecule, N2. In N2, the two nitrogen atoms form a triple bond. This triple bond has very high bond strength, which is very difficult to break. It is because of nitrogen’s small size that it is able to form p– p ...
... (i) Nitrogen is chemically less reactive. This is because of the high stability of its molecule, N2. In N2, the two nitrogen atoms form a triple bond. This triple bond has very high bond strength, which is very difficult to break. It is because of nitrogen’s small size that it is able to form p– p ...
Ch 7: Reactions
... Why does a reaction occur? What causes a reaction to “want” to form products? • Scientists have recognized several tendencies in reactants the DRIVE them to form products. ...
... Why does a reaction occur? What causes a reaction to “want” to form products? • Scientists have recognized several tendencies in reactants the DRIVE them to form products. ...
Excercises 6-10
... Chimie Organique, Paul Arnaud, Dunod Editeur, 2009: pp. 609–618, 305–312, and 217–232. ...
... Chimie Organique, Paul Arnaud, Dunod Editeur, 2009: pp. 609–618, 305–312, and 217–232. ...
Lecture6-Organometallic Chemistry
... more specific) than an uncatalyzed version of the same reaction because the catalyst provide a different reaction pathway with a lower activation energy Catalyst efficiency • Turnover frequency : Commonly called the turnover number, N, and defined as molecules reacting per active site in unit time. ...
... more specific) than an uncatalyzed version of the same reaction because the catalyst provide a different reaction pathway with a lower activation energy Catalyst efficiency • Turnover frequency : Commonly called the turnover number, N, and defined as molecules reacting per active site in unit time. ...
Chem 30B Spring 2004 QUIZ #1 KEY Weds April 14th / 30
... BONUS QUESTION: What is the product of the Pinacol rearrangement shown below? Write your answer (just the structure) clearly in the box provided on the cover sheet to this quiz. There will be NO partial credit – either your structure is right or wrong. The next blank page can be used for working thr ...
... BONUS QUESTION: What is the product of the Pinacol rearrangement shown below? Write your answer (just the structure) clearly in the box provided on the cover sheet to this quiz. There will be NO partial credit – either your structure is right or wrong. The next blank page can be used for working thr ...
First Midterm Answer Key
... sp2 - makes a σ-bond to hydrogen O sp2 - makes a σ-bond to carbon sp2 - holds the non-bonding pair of electrons p - makes a π-bond to carbon Question 6 (20 pts.) ON TOP OF the structures of acetone and acetonitrile shown below, draw the molecular dipole moments (you should show the direction only, y ...
... sp2 - makes a σ-bond to hydrogen O sp2 - makes a σ-bond to carbon sp2 - holds the non-bonding pair of electrons p - makes a π-bond to carbon Question 6 (20 pts.) ON TOP OF the structures of acetone and acetonitrile shown below, draw the molecular dipole moments (you should show the direction only, y ...
NCEA Level 2 Chemistry (91165) 2012 Assessment Schedule
... No; for a molecule to exist as geometric isomers, it must contain a double bond, and each carbon (involved in the double bond) must have two different atoms / groups attached to it. Compound A has a double bond, but the atoms attached to one carbon are both the same (two hydrogen atoms) so it does n ...
... No; for a molecule to exist as geometric isomers, it must contain a double bond, and each carbon (involved in the double bond) must have two different atoms / groups attached to it. Compound A has a double bond, but the atoms attached to one carbon are both the same (two hydrogen atoms) so it does n ...
NCEA Level 2 Chemistry (91165) 2012
... No; for a molecule to exist as geometric isomers, it must contain a double bond, and each carbon (involved in the double bond) must have two different atoms / groups attached to it. Compound A has a double bond, but the atoms attached to one carbon are both the same (two hydrogen atoms) so it does n ...
... No; for a molecule to exist as geometric isomers, it must contain a double bond, and each carbon (involved in the double bond) must have two different atoms / groups attached to it. Compound A has a double bond, but the atoms attached to one carbon are both the same (two hydrogen atoms) so it does n ...
Regulations of the International Chemistry Olympiad (IChO)
... Laboratory skills Heating in the laboratory, heating under reflux; Mass and volume measurement (with electronic balance, measuring cylinder, pipette and burette, volumetric flask); Preparation and dilution of solutions and standard solutions; Operation of a magnetic stirrer; Carrying out of test tub ...
... Laboratory skills Heating in the laboratory, heating under reflux; Mass and volume measurement (with electronic balance, measuring cylinder, pipette and burette, volumetric flask); Preparation and dilution of solutions and standard solutions; Operation of a magnetic stirrer; Carrying out of test tub ...
Organic Reactions Worksheet
... iv) Write the balanced equation for each oxidizing reaction, use [O] convention c. Using any secondary alcohol: i) Give the displayed (structural formula) which it could be oxidized to ii) State which homologous series the products are part of iii) Write the balanced equation for each oxidizing reac ...
... iv) Write the balanced equation for each oxidizing reaction, use [O] convention c. Using any secondary alcohol: i) Give the displayed (structural formula) which it could be oxidized to ii) State which homologous series the products are part of iii) Write the balanced equation for each oxidizing reac ...
syllabus chemical science - SLET-NE
... deductive and inductive reasoning, weighing the evidence with special reference to analogical arguments and inductive generalization, evaluating, classification and definition, avoiding logical inconsistency arising out of failure to see logical relevance due to ambiguity and vagueness in language. ...
... deductive and inductive reasoning, weighing the evidence with special reference to analogical arguments and inductive generalization, evaluating, classification and definition, avoiding logical inconsistency arising out of failure to see logical relevance due to ambiguity and vagueness in language. ...
Organic Chemistry (HL) Revision Questions
... 2-bromo-2-methylbutane gives two different organic products. State the type of reaction taking place and suggest the identity (name or structure) of these two products. Explain whether or not they can exist as geometrical isomers. ...
... 2-bromo-2-methylbutane gives two different organic products. State the type of reaction taking place and suggest the identity (name or structure) of these two products. Explain whether or not they can exist as geometrical isomers. ...
1 - contentextra
... Nomenclature A precise means of naming entities so that they can be communicated nonambiguously. Organic chemistry uses the system of IUPAC nomenclature. Nucleophile An electron-rich species that is therefore attracted to parts of molecules that are electron deficient. Nucleophiles have a lone pair ...
... Nomenclature A precise means of naming entities so that they can be communicated nonambiguously. Organic chemistry uses the system of IUPAC nomenclature. Nucleophile An electron-rich species that is therefore attracted to parts of molecules that are electron deficient. Nucleophiles have a lone pair ...
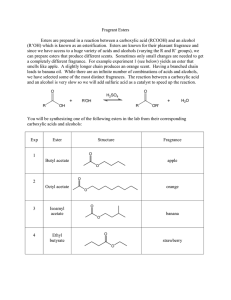
Fragrant Esters Esters are prepared in a reaction between a
... can prepare esters that produce different scents. Sometimes only small changes are needed to get a completely different fragrance. For example experiment 1 (see below) yields an ester that smells like apple. A slightly longer chain produces an orange scent. Having a branched chain leads to banana oi ...
... can prepare esters that produce different scents. Sometimes only small changes are needed to get a completely different fragrance. For example experiment 1 (see below) yields an ester that smells like apple. A slightly longer chain produces an orange scent. Having a branched chain leads to banana oi ...
Dr. Baxley`s Thermodynamics Worksheet
... you would look at how many bonds are formed vs how many break) b. Using ∆G°f, I get −1226 kJ. Using ∆H°f and S°f, then ∆G° = ∆H°–T∆S°, I get –1227 kJ 6. Since formation of a bond has − ∆H° and − ∆S°, breaking of bonds has + ∆H° and + ∆S°. Putting this into the equation ∆G° = ∆H° − T∆S°, you get sign ...
... you would look at how many bonds are formed vs how many break) b. Using ∆G°f, I get −1226 kJ. Using ∆H°f and S°f, then ∆G° = ∆H°–T∆S°, I get –1227 kJ 6. Since formation of a bond has − ∆H° and − ∆S°, breaking of bonds has + ∆H° and + ∆S°. Putting this into the equation ∆G° = ∆H° − T∆S°, you get sign ...
Woodward–Hoffmann rules

The Woodward–Hoffmann rules, devised by Robert Burns Woodward and Roald Hoffmann, are a set of rules in organic chemistry predicting the barrier heights of pericyclic reactions based upon conservation of orbital symmetry. The Woodward–Hoffmann rules can be applied to understand electrocyclic reactions, cycloadditions (including cheletropic reactions), sigmatropic reactions, and group transfer reactions. Reactions are classified as allowed if the electronic barrier is low, and forbidden if the barrier is high. Forbidden reactions can still take place but require significantly more energy.The Woodward–Hoffmann rules were first formulated to explain the striking stereospecificity of electrocyclic reactions under thermal and photochemical control. Thermolysis of the substituted cyclobutene trans-1,2,3,4-tetramethylcyclobutene (1) gave only one diastereomer, the (E,E)-3,4-dimethyl-2,4-hexadiene (2) as shown below; the (Z,Z) and the (E,Z) diastereomers were not detected in the reaction. Similarly, thermolysis of cis-1,2,3,4-tetramethylcyclobutene (3) gave only the (E,Z) diastereomer (4).Due to their elegance and simplicity, the Woodward–Hoffmann rules are credited with first exemplifying the power of molecular orbital theory to experimental chemists. Hoffmann was awarded the 1981 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for this work, shared with Kenichi Fukui who developed a similar model using frontier molecular orbital (FMO) theory; because Woodward had died two years before, he was not eligible to win what would have been his second Nobel Prize for Chemistry.