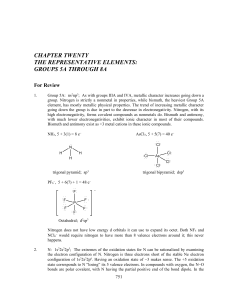
SYNTHESIS OF HIGH MOLECULAR WEIGHT POLY (METHYL
... molecular weight polyethylene glycol (PEG) (600 g/mol) as solvent significantly increased the reaction rate and provides molecular weight as high as 96 kDa within 2h reaction, Đ as low as 1.2. PEG can stabilize the catalyst by complexing to avoid the side reactions such as the reactions between cata ...
... molecular weight polyethylene glycol (PEG) (600 g/mol) as solvent significantly increased the reaction rate and provides molecular weight as high as 96 kDa within 2h reaction, Đ as low as 1.2. PEG can stabilize the catalyst by complexing to avoid the side reactions such as the reactions between cata ...
An Analogy for an Equilibrium Reaction
... row. We use the balanced equation to determine the values in the middle ‘change’ row. In this example, for every two moles of HI that are used up, one mole of H2 and one mole of I2 are created. We let the change in concentration equal x. To find the values in the bottom ‘equilibrium’ row you add the ...
... row. We use the balanced equation to determine the values in the middle ‘change’ row. In this example, for every two moles of HI that are used up, one mole of H2 and one mole of I2 are created. We let the change in concentration equal x. To find the values in the bottom ‘equilibrium’ row you add the ...
equilibrium - TeacherWeb
... Le Chatelier’s Principle – If a system at equilibrium is disturbed by a change in temperature, pressure or the concentration of one of the components, the system will shift its equilibrium position so as to counteract the effect of the ...
... Le Chatelier’s Principle – If a system at equilibrium is disturbed by a change in temperature, pressure or the concentration of one of the components, the system will shift its equilibrium position so as to counteract the effect of the ...
3.Redox
... 1. Solution = homogeneous mixture of two or more components. 2. Solvent = component present to largest extent. Phase of solution is same as the phase of the solvent. a. In some cases the solvent is not a pure substance . Mixed solvents are used in many reactions . b. In a few cases a minor component ...
... 1. Solution = homogeneous mixture of two or more components. 2. Solvent = component present to largest extent. Phase of solution is same as the phase of the solvent. a. In some cases the solvent is not a pure substance . Mixed solvents are used in many reactions . b. In a few cases a minor component ...
Physiological and phylogenetic studies of thermophilic
... The present study is based on two earlier projects. One, supervised by Ólafur Friðjónsson at Prokaria ehf, was based on the study of three mesophilic hydrogen oxidizing (HOX) bacteria, Wautersia eutropha, Hydrogenomonas pseudoflava and Acidovorax facilis. This research emphasised on genetic engineer ...
... The present study is based on two earlier projects. One, supervised by Ólafur Friðjónsson at Prokaria ehf, was based on the study of three mesophilic hydrogen oxidizing (HOX) bacteria, Wautersia eutropha, Hydrogenomonas pseudoflava and Acidovorax facilis. This research emphasised on genetic engineer ...
Specification – AS/A Level Chemistry A
... Other students without formal qualifications may have acquired sufficient knowledge of chemistry to enable progression onto the course. Recommended prior learning for the AS units is shown in the introduction to each AS unit. The A2 units build upon the knowledge and understanding acquired at AS. Re ...
... Other students without formal qualifications may have acquired sufficient knowledge of chemistry to enable progression onto the course. Recommended prior learning for the AS units is shown in the introduction to each AS unit. The A2 units build upon the knowledge and understanding acquired at AS. Re ...
Amidine: Structure, Reactivity and Complexation Behaviour
... disruption and formation of chemical bonds, being essential, to establish databases with experimental reliable data of bond dissociation energies (BDEs) as a direct information of the strength of chemical bonds[26]. Chemical species containing the N-H bond form an important class of compounds with a ...
... disruption and formation of chemical bonds, being essential, to establish databases with experimental reliable data of bond dissociation energies (BDEs) as a direct information of the strength of chemical bonds[26]. Chemical species containing the N-H bond form an important class of compounds with a ...
The Equilibrium Constant
... • Chemical equilibrium is the point at which the rate of the forward reaction is equal to the rate of the reverse reaction. At that point, the concentrations of all species are constant. • Using the collision model: – as the amount of NO2 builds up, there is a chance that two NO2 molecules will coll ...
... • Chemical equilibrium is the point at which the rate of the forward reaction is equal to the rate of the reverse reaction. At that point, the concentrations of all species are constant. • Using the collision model: – as the amount of NO2 builds up, there is a chance that two NO2 molecules will coll ...
Equilibrium - AP Chemistry
... • Chemical equilibrium is the point at which the rate of the forward reaction is equal to the rate of the reverse reaction. At that point, the concentrations of all species are constant. • Using the collision model: – as the amount of NO2 builds up, there is a chance that two NO2 molecules will coll ...
... • Chemical equilibrium is the point at which the rate of the forward reaction is equal to the rate of the reverse reaction. At that point, the concentrations of all species are constant. • Using the collision model: – as the amount of NO2 builds up, there is a chance that two NO2 molecules will coll ...
Wafer-Level Artificial Photosynthesis for CO2 Reduction into CH4
... mechanism is debatable among researchers6-8. With the input energy from photons in CO2 photoreduction, the bond C=O can be broken to form C-H bonds, which leads to the formation of different fuels such as methane (CH4). H2 formation is a very competitive process in CO2 photochemical and photoelectro ...
... mechanism is debatable among researchers6-8. With the input energy from photons in CO2 photoreduction, the bond C=O can be broken to form C-H bonds, which leads to the formation of different fuels such as methane (CH4). H2 formation is a very competitive process in CO2 photochemical and photoelectro ...
Equilibrium - Tenafly High School
... • Chemical equilibrium is the point at which the rate of the forward reaction is equal to the rate of the reverse reaction. At that point, the concentrations of all species are constant. • Using the collision model: – as the amount of NO2 builds up, there is a chance that two NO2 molecules will coll ...
... • Chemical equilibrium is the point at which the rate of the forward reaction is equal to the rate of the reverse reaction. At that point, the concentrations of all species are constant. • Using the collision model: – as the amount of NO2 builds up, there is a chance that two NO2 molecules will coll ...
Tro Chemistry a Molecular Approach, 3E
... The balanced equation shows that 16 CO2 molecules are produced for every 2 molecules of octane burned. We can extend this numerical relationship between molecules to the amounts in moles as follows: The coefficients in a chemical equation specify the relative amounts in moles of each of the substanc ...
... The balanced equation shows that 16 CO2 molecules are produced for every 2 molecules of octane burned. We can extend this numerical relationship between molecules to the amounts in moles as follows: The coefficients in a chemical equation specify the relative amounts in moles of each of the substanc ...
GCE Chemistry Specification (From 2015 - WALES ONLY
... Learners should be prepared to apply the knowledge, understanding and skills specified in a range of theoretical, practical, industrial and environmental contexts. It is a requirement of all A level specifications that learners must demonstrate a holistic understanding of the links between different ...
... Learners should be prepared to apply the knowledge, understanding and skills specified in a range of theoretical, practical, industrial and environmental contexts. It is a requirement of all A level specifications that learners must demonstrate a holistic understanding of the links between different ...
Laboratory Manual
... Playing a game is more enjoyable than just watching or reading about it. This is also true about learning chemistry. Getting to actually do experiments is a lot of fun. But chemistry can also be dangerous, and getting hurt is definitely not fun! For this reason there are safety rules to follow and p ...
... Playing a game is more enjoyable than just watching or reading about it. This is also true about learning chemistry. Getting to actually do experiments is a lot of fun. But chemistry can also be dangerous, and getting hurt is definitely not fun! For this reason there are safety rules to follow and p ...
Rubidium
... It occurs naturally in the minerals leucite, pollucite, and zinnwaldite, which contains traces of up to 1% of its oxide. Lepidolite contains 1.5% rubidium and this is the commercial source of the element. Some potassium minerals and potassium chlorides also contain the element in commercially signif ...
... It occurs naturally in the minerals leucite, pollucite, and zinnwaldite, which contains traces of up to 1% of its oxide. Lepidolite contains 1.5% rubidium and this is the commercial source of the element. Some potassium minerals and potassium chlorides also contain the element in commercially signif ...
Ans:- (i) Gluconic acid - Kendriya Vidyalaya No.2, Kribhco, Surat
... Ans-.a) one b) two c) four Q-3.What type of semiconductors are when Si doped with – a) Phosphorous and b) Gallium. Ans. a) n-type and b) p-type Q-4. What is the coordination no. of an octahedral void and tetrahedral void? A-. Six(6) and Four(4) Q-5. Which of the two will show the Schottky defect whe ...
... Ans-.a) one b) two c) four Q-3.What type of semiconductors are when Si doped with – a) Phosphorous and b) Gallium. Ans. a) n-type and b) p-type Q-4. What is the coordination no. of an octahedral void and tetrahedral void? A-. Six(6) and Four(4) Q-5. Which of the two will show the Schottky defect whe ...
Now! - Soojeede.com
... A great number of people associate a strong acid with its ability to react with skin, essentially “melting´ it away from bone. It was only recently on a popular crime show that this very acid chemistry know-how was ...
... A great number of people associate a strong acid with its ability to react with skin, essentially “melting´ it away from bone. It was only recently on a popular crime show that this very acid chemistry know-how was ...
Chemistry
... JOHN MCMURRY, educated at Harvard and Columbia, has taught approximately 17,000 students in general and organic chemistry over a 30-year period. A Professor of Chemistry at Cornell University since 1980, Dr. McMurry previously spent 13 years on the faculty at the University of California at Santa Cr ...
... JOHN MCMURRY, educated at Harvard and Columbia, has taught approximately 17,000 students in general and organic chemistry over a 30-year period. A Professor of Chemistry at Cornell University since 1980, Dr. McMurry previously spent 13 years on the faculty at the University of California at Santa Cr ...
File
... production; HNO3: important industrial chemical, used to form nitrogen-based explosives, strong acid and a very strong oxidizing agent. ...
... production; HNO3: important industrial chemical, used to form nitrogen-based explosives, strong acid and a very strong oxidizing agent. ...
OCR Gateway Science
... When molten lead iodide is electrolysed using a current of 12 A for 50 minutes, approximately 39 g of lead is deposited. (a) What mass of lead is produced using a current of 12 A for 25 minutes? (b) What mass of lead is produced using a current of 3 A for 50 minutes? (c) What charge in coulombs is t ...
... When molten lead iodide is electrolysed using a current of 12 A for 50 minutes, approximately 39 g of lead is deposited. (a) What mass of lead is produced using a current of 12 A for 25 minutes? (b) What mass of lead is produced using a current of 3 A for 50 minutes? (c) What charge in coulombs is t ...
Stoichiometery
... I have 1.6 mol of hydrogen. How much water can I make? A. 1.6 mol H2O B. 0.8 mol etc. C. 3.2 mol D. 4.8 mol E. None of the above ...
... I have 1.6 mol of hydrogen. How much water can I make? A. 1.6 mol H2O B. 0.8 mol etc. C. 3.2 mol D. 4.8 mol E. None of the above ...
15.0 EquilibriumIHS2014
... increasing the container volume. Then the equilibrium shifts to the left (the side with more moles of gas) • At B, the temperature is increased. Then the equilibrium shifts to left. • At C, C2H6(g) is added to the system. Then the equilibrium shifts to the left. • At D, no shift in equilibrium posit ...
... increasing the container volume. Then the equilibrium shifts to the left (the side with more moles of gas) • At B, the temperature is increased. Then the equilibrium shifts to left. • At C, C2H6(g) is added to the system. Then the equilibrium shifts to the left. • At D, no shift in equilibrium posit ...
Chapter 4 Classifying Reactions: Chemicals in Balance
... The name and state of each reactant and product are given. Plan Your Strategy A skeleton equation lists the chemical formula of each reactant on the left, separated by a + sign if more than one reactant is present, followed by →. The chemical formula of each product is listed on the right, separated ...
... The name and state of each reactant and product are given. Plan Your Strategy A skeleton equation lists the chemical formula of each reactant on the left, separated by a + sign if more than one reactant is present, followed by →. The chemical formula of each product is listed on the right, separated ...
File
... Answers to the chapter summary worksheets (see the textbook CD-ROM) are given at the end of each chapter of this Teacher Guide. The answers to the practice unit tests are model answers that include all that examiners look for when awarding marks, together with some extra explanation. Each marking po ...
... Answers to the chapter summary worksheets (see the textbook CD-ROM) are given at the end of each chapter of this Teacher Guide. The answers to the practice unit tests are model answers that include all that examiners look for when awarding marks, together with some extra explanation. Each marking po ...
Chapter 1 Chirality in clinical analysis 1.1. Introduction
... Stereoisomers are compounds made up of the same atoms connected by the same sequence of bonds, but having different 3-D structures (Figure 1.1). Chiral phenomena are common in living systems. Amino acids, nucleic acids, lipids, carbohydrates, metabolic intermediates, and many other biomolecules are ...
... Stereoisomers are compounds made up of the same atoms connected by the same sequence of bonds, but having different 3-D structures (Figure 1.1). Chiral phenomena are common in living systems. Amino acids, nucleic acids, lipids, carbohydrates, metabolic intermediates, and many other biomolecules are ...