Chemical Equilibrium is reached when
... Increasing the pressure will increase the concentration of both N2O4 and NO2, and because the concentration of NO2 is squared, the increase in the numerator more than the denominator. The system is no longer at equilibrium, so we write Qc = [NO2]o2/[N2O4]o Thus Qc > Kc and the net reaction will shif ...
... Increasing the pressure will increase the concentration of both N2O4 and NO2, and because the concentration of NO2 is squared, the increase in the numerator more than the denominator. The system is no longer at equilibrium, so we write Qc = [NO2]o2/[N2O4]o Thus Qc > Kc and the net reaction will shif ...
Aromatic Chemistry - heckgrammar.co.uk
... most reactions occur in several steps (this is exemplified by organic reaction mechanisms) each step will take place at a different rate the slowest step will determine the overall rate of the reaction and is known as the rate determining step the order of the reaction regarding each reagent can pro ...
... most reactions occur in several steps (this is exemplified by organic reaction mechanisms) each step will take place at a different rate the slowest step will determine the overall rate of the reaction and is known as the rate determining step the order of the reaction regarding each reagent can pro ...
Revised (12 Sept 2009) Topic: Chemical Equilibrium
... above reaction quotient expression. If the new ratio, V2/nN2, in the Qc expression is greater than the original ratio in the Kc expression, then Qc is greater than Kc and the position of equilibrium must shift to the left. If the new ratio is less than the original ratio, then Qc is less than Kc and ...
... above reaction quotient expression. If the new ratio, V2/nN2, in the Qc expression is greater than the original ratio in the Kc expression, then Qc is greater than Kc and the position of equilibrium must shift to the left. If the new ratio is less than the original ratio, then Qc is less than Kc and ...
Side Chain Chemistry Mediates Backbone Fragmentation in
... A crown ether based, photolabile radical precursor which forms noncovalent complexes with peptides has been prepared. The peptide/precursor complexes can be electrosprayed, isolated in an ion trap, and then subjected to laser photolysis and collision induced dissociation to generate hydrogen deficie ...
... A crown ether based, photolabile radical precursor which forms noncovalent complexes with peptides has been prepared. The peptide/precursor complexes can be electrosprayed, isolated in an ion trap, and then subjected to laser photolysis and collision induced dissociation to generate hydrogen deficie ...
4Chemical Quantities and Aqueous Reactions
... The balanced chemical equation shows that 16 CO2 molecules are produced for every 2 molecules of octane burned. We can extend this numerical relationship between molecules to the amounts in moles as follows: The coefficients in a chemical reaction specify the relative amounts in moles of each of the ...
... The balanced chemical equation shows that 16 CO2 molecules are produced for every 2 molecules of octane burned. We can extend this numerical relationship between molecules to the amounts in moles as follows: The coefficients in a chemical reaction specify the relative amounts in moles of each of the ...
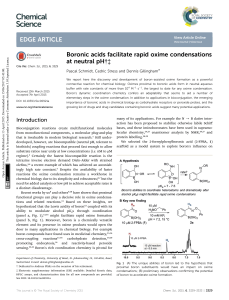
Boronic acids facilitate rapid oxime condensations at neutral pH
... condensation is the size of required 2-FBPA motif. Although for most applications this should present no difficulties, examples where the compactness of the oxime is critical (such as, for example, as a functional isostere of peptide bonds)37 would not be possible. The ability to run conjugations at 1 ...
... condensation is the size of required 2-FBPA motif. Although for most applications this should present no difficulties, examples where the compactness of the oxime is critical (such as, for example, as a functional isostere of peptide bonds)37 would not be possible. The ability to run conjugations at 1 ...
Ch 10 - Enrico Fermi High School
... 1. What fraction of the SO2Cl2 remains after 1 hour? [0.6 ] 2. How long (in seconds) will it take for 10% of the SO2Cl2 to decompose? [742 sec] H. It takes 2 hrs for the concentration of a reactant to drop to 17.1% of its initial value of 0.560 M in a second order reaction. 1. What is the rate const ...
... 1. What fraction of the SO2Cl2 remains after 1 hour? [0.6 ] 2. How long (in seconds) will it take for 10% of the SO2Cl2 to decompose? [742 sec] H. It takes 2 hrs for the concentration of a reactant to drop to 17.1% of its initial value of 0.560 M in a second order reaction. 1. What is the rate const ...
Chapter 14 Review
... A. Increasing the system volume shifts the equilibrium to the right. B. Increasing the temperature shifts the equilibrium to the right. C. A catalyst speeds up the approach to equilibrium and shifts the position of equilibrium to the right. D. Decreasing the total pressure of the system shifts the e ...
... A. Increasing the system volume shifts the equilibrium to the right. B. Increasing the temperature shifts the equilibrium to the right. C. A catalyst speeds up the approach to equilibrium and shifts the position of equilibrium to the right. D. Decreasing the total pressure of the system shifts the e ...
THESE DOCTORAT DE L`UNIVERSITE DE TOULOUSE ET
... The chemistry of molybdenum and tungsten cyclopentadienyl complexes in higher oxidation states with oxo, imido and sulfide ligands has increased in significance. Interest in Cp* oxo molybdenum and tungsten complexes is particularly motivated by their potential in oxidation catalysis. Most advances i ...
... The chemistry of molybdenum and tungsten cyclopentadienyl complexes in higher oxidation states with oxo, imido and sulfide ligands has increased in significance. Interest in Cp* oxo molybdenum and tungsten complexes is particularly motivated by their potential in oxidation catalysis. Most advances i ...
Answer
... If Step 2 is assumed to be very slow compared to the equilibrium of Step 1, derive the overall rate equation you would expect to see for this mechanism. If step 1 is at equilibrium, with equilibrium constant, K: K = [N2O2(g)]/[NO(g)]2 [N2O2(g)] = K [NO(g)]2 Step 2 involves the bimolecular reaction o ...
... If Step 2 is assumed to be very slow compared to the equilibrium of Step 1, derive the overall rate equation you would expect to see for this mechanism. If step 1 is at equilibrium, with equilibrium constant, K: K = [N2O2(g)]/[NO(g)]2 [N2O2(g)] = K [NO(g)]2 Step 2 involves the bimolecular reaction o ...
CHEM 1411 – STUDY-GUIDE-for-TEST-2
... 31. Which of the following statements is consistent with Boyle's Law concerning an ideal gas? A) At constant temperature and moles, a plot of volume versus pressure is linear. B) At constant pressure and volume, a plot of temperature versus moles is linear. C) At constant pressure and moles, a plot ...
... 31. Which of the following statements is consistent with Boyle's Law concerning an ideal gas? A) At constant temperature and moles, a plot of volume versus pressure is linear. B) At constant pressure and volume, a plot of temperature versus moles is linear. C) At constant pressure and moles, a plot ...
Spring 2005
... 18. (6 pts) In lab the class is running a series of reactions that use several potentially hazardous chemicals. Groups are working on the lab benches and are scattered throughout the lab (typical situation for our lab). Your group has finished the experiment earlier than those groups around you. Is ...
... 18. (6 pts) In lab the class is running a series of reactions that use several potentially hazardous chemicals. Groups are working on the lab benches and are scattered throughout the lab (typical situation for our lab). Your group has finished the experiment earlier than those groups around you. Is ...
Stoichiometry worksheet KEY
... Mass of reactants = mass of products (52.0 g C2H2 + 160 g O2) = (176 g CO2 + 36.0 g H2O) 212 g reactants = 212 g products ...
... Mass of reactants = mass of products (52.0 g C2H2 + 160 g O2) = (176 g CO2 + 36.0 g H2O) 212 g reactants = 212 g products ...
1.4 Enthalpy
... Enthalpy, H, is the heat energy that is stored in a chemical system, as reactants or products. It is impossible to measure the enthalpy content of a system directly but we can measure the differences in enthalpy contents. The difference in enthalpy contents is the energy either given out or absorbed ...
... Enthalpy, H, is the heat energy that is stored in a chemical system, as reactants or products. It is impossible to measure the enthalpy content of a system directly but we can measure the differences in enthalpy contents. The difference in enthalpy contents is the energy either given out or absorbed ...
ppt
... concentration. Therefore does not cause a shift. I.e. only applies to gases and aqueous solutions. ...
... concentration. Therefore does not cause a shift. I.e. only applies to gases and aqueous solutions. ...
Rates of Reaction
... – Although reaction orders frequently have whole number values (particularly 1 and 2), they can be fractional. – Zero and negative orders are also possible. – The concentration of a reactant with a zeroorder dependence has no effect on the rate of the reaction. ...
... – Although reaction orders frequently have whole number values (particularly 1 and 2), they can be fractional. – Zero and negative orders are also possible. – The concentration of a reactant with a zeroorder dependence has no effect on the rate of the reaction. ...
Table of Contents - slccscience`s Home Page
... and its compounds. Organic chemistry is the study of carbon and its compounds. Since there are 117 known elements, it often seems odd that an entire branch of chemistry is devoted to a single element and its compounds while the other 116 elements and their compounds are all lumped together in a sepa ...
... and its compounds. Organic chemistry is the study of carbon and its compounds. Since there are 117 known elements, it often seems odd that an entire branch of chemistry is devoted to a single element and its compounds while the other 116 elements and their compounds are all lumped together in a sepa ...
TERMS AND DEFINITIONS IN THERMOCHEMISTRY
... This is the law on which the whole of thermochemistry is based. It states that the enthalpy change for a process does not depend on the nature of any intermediate steps involved in bringing the process about. That is, the enthalpy change does not depend on the path chosen to accomplish the process, ...
... This is the law on which the whole of thermochemistry is based. It states that the enthalpy change for a process does not depend on the nature of any intermediate steps involved in bringing the process about. That is, the enthalpy change does not depend on the path chosen to accomplish the process, ...
M.Sc. Chemistry - Periyar University
... Thermodynamic and kinetic requirements for reactions, thermodynamic and kinetic control reactions, Hammonds postulate, Microscopic reversibility. Potential energy diagrams, transition states and intermediates, methods of determining mechanisms – identification of products and determination of the pr ...
... Thermodynamic and kinetic requirements for reactions, thermodynamic and kinetic control reactions, Hammonds postulate, Microscopic reversibility. Potential energy diagrams, transition states and intermediates, methods of determining mechanisms – identification of products and determination of the pr ...
Document
... Learning objective 3.3 The student is able to use stoichiometric calculations to predict the results of performing a reaction in the laboratory and/or to analyze deviations from the expected results. [See SP 2.2, 5.1; Essential knowledge 3.A.2] Learning objective 3.4 The student is able to relate qu ...
... Learning objective 3.3 The student is able to use stoichiometric calculations to predict the results of performing a reaction in the laboratory and/or to analyze deviations from the expected results. [See SP 2.2, 5.1; Essential knowledge 3.A.2] Learning objective 3.4 The student is able to relate qu ...
Document
... Learning objective 3.3 The student is able to use stoichiometric calculations to predict the results of performing a reaction in the laboratory and/or to analyze deviations from the expected results. [See SP 2.2, 5.1; Essential knowledge 3.A.2] Learning objective 3.4 The student is able to relate qu ...
... Learning objective 3.3 The student is able to use stoichiometric calculations to predict the results of performing a reaction in the laboratory and/or to analyze deviations from the expected results. [See SP 2.2, 5.1; Essential knowledge 3.A.2] Learning objective 3.4 The student is able to relate qu ...