β-GLUCURONIDASE from Escherichia coli (Lot 120502b)
... One Unit of β-D-glucuronosidase activity is defined as the amount of enzyme required to release one μg of phenolphthalein per hour from phenolphthalein-β-D-glucuronide (0.5 mM) in sodium phosphate buffer (100 mM) at pH 6.8 and 37°C. ...
... One Unit of β-D-glucuronosidase activity is defined as the amount of enzyme required to release one μg of phenolphthalein per hour from phenolphthalein-β-D-glucuronide (0.5 mM) in sodium phosphate buffer (100 mM) at pH 6.8 and 37°C. ...
Biochemistry Vocabulary Review
... nucleotides that contain C, H, O, N, S and P are called… Nucleic acids ...
... nucleotides that contain C, H, O, N, S and P are called… Nucleic acids ...
Chapter 8 PPT
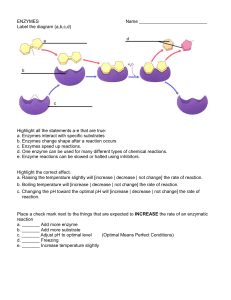
... Substrate binds to the active site of the enzyme forming an enzyme substrate complex Induced fit of the active site around the substrate Product departs active site and the enzyme emerges in its original form ...
... Substrate binds to the active site of the enzyme forming an enzyme substrate complex Induced fit of the active site around the substrate Product departs active site and the enzyme emerges in its original form ...
BY 330 Spring 2015Worksheet 3 Draw a protein made up of two
... 3. List and describe the two main types of protein secondary structure. Are R groups involved in secondary structure? (Include examples and drawings.) ...
... 3. List and describe the two main types of protein secondary structure. Are R groups involved in secondary structure? (Include examples and drawings.) ...
Enzyme catalysis

Enzyme catalysis is the increase in the rate of a chemical reaction by the active site of a protein. The protein catalyst (enzyme) may be part of a multi-subunit complex, and/or may transiently or permanently associate with a Cofactor (e.g. adenosine triphosphate). Catalysis of biochemical reactions in the cell is vital due to the very low reaction rates of the uncatalysed reactions. A key driver of protein evolution is the optimization of such catalytic activities via protein dynamics.The mechanism of enzyme catalysis is similar in principle to other types of chemical catalysis. By providing an alternative reaction route the enzyme reduces the energy required to reach the highest energy transition state of the reaction. The reduction of activation energy (Ea) increases the amount of reactant molecules that achieve a sufficient level of energy, such that they reach the activation energy and form the product. As with other catalysts, the enzyme is not consumed during the reaction (as a substrate is) but is recycled such that a single enzyme performs many rounds of catalysis.