Enzymes
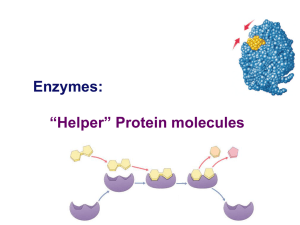
... Enzymes aren’t used up • Enzymes are not changed by the reaction – used only temporarily – re-used again for the same reaction with other molecules – very little enzyme needed to help in many reactions substrate active site ...
... Enzymes aren’t used up • Enzymes are not changed by the reaction – used only temporarily – re-used again for the same reaction with other molecules – very little enzyme needed to help in many reactions substrate active site ...
Enzymes - Chautauqua Lake Central SD
... Enzymes aren’t used up • Enzymes are not changed by the reaction – used only temporarily – re-used again for the same reaction with other molecules – very little enzyme needed to help in many reactions substrate active site ...
... Enzymes aren’t used up • Enzymes are not changed by the reaction – used only temporarily – re-used again for the same reaction with other molecules – very little enzyme needed to help in many reactions substrate active site ...
Microbial Metabolism
... 2. Nitrobacter bacteria use CO2 for their carbon source and nitrate ions as an energy source. This organism is a: A. Chemoautotroph B. Chemoheterotroph ...
... 2. Nitrobacter bacteria use CO2 for their carbon source and nitrate ions as an energy source. This organism is a: A. Chemoautotroph B. Chemoheterotroph ...
Enzymes: “Helper” Protein molecules
... Enzymes aren’t used up Enzymes are not changed by the reaction used only temporarily re-used again for the same reaction with other molecules very little enzyme needed to help in many reactions ...
... Enzymes aren’t used up Enzymes are not changed by the reaction used only temporarily re-used again for the same reaction with other molecules very little enzyme needed to help in many reactions ...
2.4 Chemical Reactions and Enzymes
... Energy needed to get a reaction going is the activation ...
... Energy needed to get a reaction going is the activation ...
Enzymes: “Helper” Protein molecules
... sucrase breaks down sucrose proteases breakdown proteins lipases breakdown lipids DNA polymerase builds DNA ...
... sucrase breaks down sucrose proteases breakdown proteins lipases breakdown lipids DNA polymerase builds DNA ...
Enzymes and Temperature
... will gain kinetic energy (move faster). collisons This will increase the rate of ____________ The rate of formation of enzyme-substrate complexes increases (and hence the product). This happens up to a particular temperature, called the enzyme’s ___________ Optimum________________. temperature ...
... will gain kinetic energy (move faster). collisons This will increase the rate of ____________ The rate of formation of enzyme-substrate complexes increases (and hence the product). This happens up to a particular temperature, called the enzyme’s ___________ Optimum________________. temperature ...
Biochem (Test 1)
... remains stable. For an enzyme to be a productive catalyst for reactions, which of the following is required? ...
... remains stable. For an enzyme to be a productive catalyst for reactions, which of the following is required? ...
StudyGuide_Biochemistry
... 37. What is the body’s primary source of energy? If that is not available, what will the body use? If both of those are not available, what will the body turn to for energy? 38. What is the purpose of a chemical reaction? 39. Define the terms “reactant” and “product” in reference to chemical reactio ...
... 37. What is the body’s primary source of energy? If that is not available, what will the body use? If both of those are not available, what will the body turn to for energy? 38. What is the purpose of a chemical reaction? 39. Define the terms “reactant” and “product” in reference to chemical reactio ...
do not
... pressure (LOW) 3)Without catalysts reactions would be too slow 4)Needed to sustain life ...
... pressure (LOW) 3)Without catalysts reactions would be too slow 4)Needed to sustain life ...
Enzyme catalysis

Enzyme catalysis is the increase in the rate of a chemical reaction by the active site of a protein. The protein catalyst (enzyme) may be part of a multi-subunit complex, and/or may transiently or permanently associate with a Cofactor (e.g. adenosine triphosphate). Catalysis of biochemical reactions in the cell is vital due to the very low reaction rates of the uncatalysed reactions. A key driver of protein evolution is the optimization of such catalytic activities via protein dynamics.The mechanism of enzyme catalysis is similar in principle to other types of chemical catalysis. By providing an alternative reaction route the enzyme reduces the energy required to reach the highest energy transition state of the reaction. The reduction of activation energy (Ea) increases the amount of reactant molecules that achieve a sufficient level of energy, such that they reach the activation energy and form the product. As with other catalysts, the enzyme is not consumed during the reaction (as a substrate is) but is recycled such that a single enzyme performs many rounds of catalysis.