Neuronal Development
... Further Development of Telencephalon • Page 89, Figure 5-8 • The cerebral hemispheres expand so that they cover the diencephalon • The hemispheres become C-shaped • The insula region does not grow as fast, and it becomes covered by the frontal and temporal lobes • Surface folds to produce gyri and ...
... Further Development of Telencephalon • Page 89, Figure 5-8 • The cerebral hemispheres expand so that they cover the diencephalon • The hemispheres become C-shaped • The insula region does not grow as fast, and it becomes covered by the frontal and temporal lobes • Surface folds to produce gyri and ...
Brain Anatomy - Southwest High School
... • Frontal lobe: The front of the brain. This is what makes you you. This is where you interpret and control emotions, make decisions and carry out plans. In the back of the frontal lobe, you work the voluntary muscles. • Parietal lobe: behind the frontal lobe. ...
... • Frontal lobe: The front of the brain. This is what makes you you. This is where you interpret and control emotions, make decisions and carry out plans. In the back of the frontal lobe, you work the voluntary muscles. • Parietal lobe: behind the frontal lobe. ...
chapter 7 the nervous system
... Parietal Lobe = understanding speech and choosing the words needed to express thoughts and feelings Temporal Lobe = understanding speech and reading printed words, memory of visual scenes and music Occipital Lobe = analyzing visual patterns and recognizing another person or an object ...
... Parietal Lobe = understanding speech and choosing the words needed to express thoughts and feelings Temporal Lobe = understanding speech and reading printed words, memory of visual scenes and music Occipital Lobe = analyzing visual patterns and recognizing another person or an object ...
Nervous System - cloudfront.net
... Part of the Autonomic System that is responsible for “Rest and Digest” Lowers blood pressure, heart rate and works to save ...
... Part of the Autonomic System that is responsible for “Rest and Digest” Lowers blood pressure, heart rate and works to save ...
Sam Wangdescribes some of the physics of our most complex organ
... Brains have long been compared to the most advanced existing technology – including, at one point, telephone switchboards. Today, people often talk about brains as if they were a sort of biological computer, with pink mushy “hardware” and “software” generated by life experiences. However, any compar ...
... Brains have long been compared to the most advanced existing technology – including, at one point, telephone switchboards. Today, people often talk about brains as if they were a sort of biological computer, with pink mushy “hardware” and “software” generated by life experiences. However, any compar ...
Brainfunction - Oakton Community College
... tissue becomes. The thicker the myelin tissue, the faster the electric impulse can travel through the axon, up to 200 miles per hour. ...
... tissue becomes. The thicker the myelin tissue, the faster the electric impulse can travel through the axon, up to 200 miles per hour. ...
ANPS 019 Black 10-28
... This lecture will introduce you to the terms we will discuss throughout the rest of the semester ORGANIZEATION OF THE CNS How neurons and glia arranged? How does the CNS get its adult shape? How do we tell one part from another? What does each part of the brain do? Glial cells are smaller than neuro ...
... This lecture will introduce you to the terms we will discuss throughout the rest of the semester ORGANIZEATION OF THE CNS How neurons and glia arranged? How does the CNS get its adult shape? How do we tell one part from another? What does each part of the brain do? Glial cells are smaller than neuro ...
Behavioral Neuroscience: The NeuroPsychological approach
... deficits in language comprehension. ...
... deficits in language comprehension. ...
Introduction
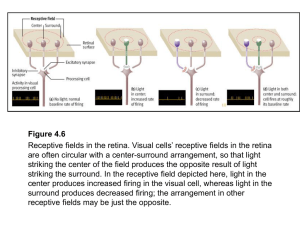
... retina and is transmitted to the left hemisphere (shown in red). Input from the left half of the visual field strikes the right side of each retina and is transmitted to the right hemisphere (shown in green). The nerve fibers from each eye meet at the optic chiasm, where fibers from the inside half ...
... retina and is transmitted to the left hemisphere (shown in red). Input from the left half of the visual field strikes the right side of each retina and is transmitted to the right hemisphere (shown in green). The nerve fibers from each eye meet at the optic chiasm, where fibers from the inside half ...
Keeping the Nervous System Healthy Quiz Answers
... 7. Ways to keep your nervous system safe include a) wearing safety goggles or sunglasses to protect your eyes from injury. b) wearing ear plugs to protect your ears from soft sounds. c) wearing a safety helmet for activities like running and biking. d) all of the above ...
... 7. Ways to keep your nervous system safe include a) wearing safety goggles or sunglasses to protect your eyes from injury. b) wearing ear plugs to protect your ears from soft sounds. c) wearing a safety helmet for activities like running and biking. d) all of the above ...
HW CH 5 PSY 2513 Submit your answers on canvas
... the areas of the brain are strongly committed to specific functions, and there is a high capacity for learning. b. if a part of the cortex is damaged, other parts can take over the tasks it would have handled. c. spatial skills develop more rapidly than language skills and are easier to recover afte ...
... the areas of the brain are strongly committed to specific functions, and there is a high capacity for learning. b. if a part of the cortex is damaged, other parts can take over the tasks it would have handled. c. spatial skills develop more rapidly than language skills and are easier to recover afte ...
The Brain The brain is responsible for everything we think, feel and
... Aphasia: a language disorder apparent in speech, writing or reading produced by an injury to brain regions specialised in these functions. Broca’s aphasia: a language disorder that affects the production of speech, consisting of very short sentences comprising mostly nouns and verbs. Wernicke’s apha ...
... Aphasia: a language disorder apparent in speech, writing or reading produced by an injury to brain regions specialised in these functions. Broca’s aphasia: a language disorder that affects the production of speech, consisting of very short sentences comprising mostly nouns and verbs. Wernicke’s apha ...
Central Nervous System Functional Anatomy of the Brain
... brain stem and is enclosed by the cerebral hemispheres (see Figure 7.12). The major structures of the diencephalon are the thalamus, hypothalamus, and epithalamus (see Figure 7.15). The thalamus, which encloses the shallow third ventricle of the brain, is a relay station for sensory impulses passing ...
... brain stem and is enclosed by the cerebral hemispheres (see Figure 7.12). The major structures of the diencephalon are the thalamus, hypothalamus, and epithalamus (see Figure 7.15). The thalamus, which encloses the shallow third ventricle of the brain, is a relay station for sensory impulses passing ...
How Psychologists Study the Brain
... powerful magnetic forces and radio-frequency (RF) waves to make detailed 3-dimensional pictures of organs, soft tissues, bone and most other internal body structures. Some MRI scans require a contrast medium to provide clearer images. Different tissues react differently to the magnetic current and t ...
... powerful magnetic forces and radio-frequency (RF) waves to make detailed 3-dimensional pictures of organs, soft tissues, bone and most other internal body structures. Some MRI scans require a contrast medium to provide clearer images. Different tissues react differently to the magnetic current and t ...
Chapter 1 - Faculty Server Contact
... Macroelectrode - An electrode designed to record from many neurons at once. Microelectrode - An electrode designed to record the activity of one or a few neurons. Electroencephalogram - EEG; a graphical record of the electrical activity of the cerebral cortex. Evoked potential - A neural response to ...
... Macroelectrode - An electrode designed to record from many neurons at once. Microelectrode - An electrode designed to record the activity of one or a few neurons. Electroencephalogram - EEG; a graphical record of the electrical activity of the cerebral cortex. Evoked potential - A neural response to ...
The Nervous System
... The brain has about 100 billion brain cells. The spinal cord is crucial for everyday function as it transmits commands from the brain to the rest of the body. ...
... The brain has about 100 billion brain cells. The spinal cord is crucial for everyday function as it transmits commands from the brain to the rest of the body. ...
3NervCase
... B. depression of emotions C. loss of motivated drives D. loss of motor coordination 11. Look up the cerebral blood vessels in the Atlas of Human Anatomy. Can you identify a blood vessel that could have been damaged to cause these various symptoms? 12. The patient can feel an object that he is touchi ...
... B. depression of emotions C. loss of motivated drives D. loss of motor coordination 11. Look up the cerebral blood vessels in the Atlas of Human Anatomy. Can you identify a blood vessel that could have been damaged to cause these various symptoms? 12. The patient can feel an object that he is touchi ...
Using POCS Method of Problem
... The term exocytosis (Pinel pages 94-95) refers to the process of releasing a neurotransmitter. Neurotransmitter chemicals work a bit like keys in locks. In this case, the “locks” are special receptor sites in the dendrites of the receiving neuron. These sites accept only one kind of chemical. For th ...
... The term exocytosis (Pinel pages 94-95) refers to the process of releasing a neurotransmitter. Neurotransmitter chemicals work a bit like keys in locks. In this case, the “locks” are special receptor sites in the dendrites of the receiving neuron. These sites accept only one kind of chemical. For th ...
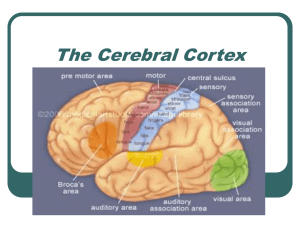
The Cerebral Cortex
... ¾ of the cerebral cortex is uncommitted to sensory or muscular activity Neurons in these association areas integrate information & therefore cannot be neatly mapped Found in all four lobes & increase in more intelligent animals. ...
... ¾ of the cerebral cortex is uncommitted to sensory or muscular activity Neurons in these association areas integrate information & therefore cannot be neatly mapped Found in all four lobes & increase in more intelligent animals. ...
Nervous system
... The temporal lobes contain a large number of substructures, whose functions include perception, face ...
... The temporal lobes contain a large number of substructures, whose functions include perception, face ...
Lateralization of brain function

The longitudinal fissure separates the human brain into two distinct cerebral hemispheres, connected by the corpus callosum. The hemispheres exhibit strong, but not complete, bilateral symmetry in both structure and function. For example, structurally, the lateral sulcus generally is longer in the left hemisphere than in the right hemisphere, and functionally, Broca's area and Wernicke's area are located in the left cerebral hemisphere for about 95% of right-handers, but about 70% of left-handers.Broad generalizations are often made in ""pop"" psychology about one side or the other having characteristic labels, such as ""logical"" for the left side or ""creative"" for the right. These labels are not supported by studies on lateralization, as lateralization does not add specialized usage from either hemisphere. Both hemispheres contribute to both kinds of processes, and experimental evidence provides little support for correlating the structural differences between the sides with such broadly defined functional differences.The extent of any modularity, or specialization of brain function by area, remains under investigation. If a specific region of the brain, or even an entire hemisphere, is injured or destroyed, its functions can sometimes be assumed by a neighboring region in the same hemisphere or the corresponding region in the other hemisphere, depending upon the area damaged and the patient's age. When injury interferes with pathways from one area to another, alternative (indirect) connections may develop to communicate information with detached areas, despite the inefficiencies.Brain function lateralization is evident in the phenomena of right- or left-handedness and of right or left ear preference, but a person's preferred hand is not a clear indication of the location of brain function. Although 95% of right-handed people have left-hemisphere dominance for language, 18.8% of left-handed people have right-hemisphere dominance for language function. Additionally, 19.8% of the left-handed have bilateral language functions. Even within various language functions (e.g., semantics, syntax, prosody), degree (and even hemisphere) of dominance may differ.Additionally, although some functions are lateralized, these are only a tendency. The trend across many individuals may also vary significantly as to how any specific function is implemented. The areas of exploration of this causal or effectual difference of a particular brain function include its gross anatomy, dendritic structure, and neurotransmitter distribution. The structural and chemical variance of a particular brain function, between the two hemispheres of one brain or between the same hemisphere of two different brains, is still being studied. Short of having undergone a hemispherectomy (removal of a cerebral hemisphere), no one is a ""left-brain only"" or ""right-brain only"" person.