A Data Mining Survey of the Allen Brain Atlas
... Neuromodulatory systems are structures located in the sub-cortical region of the brain composed of neurons (on the order of 1,000 in a mouse and 10,000 in a human per system) that control fundamental behaviors by interacting with many areas of the brain, including the amygdala, hippocampus, and fron ...
... Neuromodulatory systems are structures located in the sub-cortical region of the brain composed of neurons (on the order of 1,000 in a mouse and 10,000 in a human per system) that control fundamental behaviors by interacting with many areas of the brain, including the amygdala, hippocampus, and fron ...
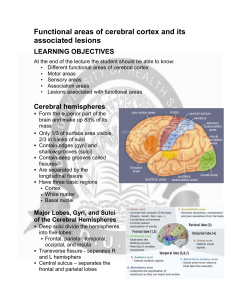
Functional areas of cerebral cortex and its associated lesions
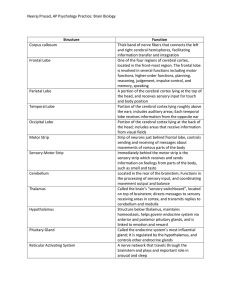
... Receives information related to pitch, rhythm, and loudness Auditory association area (area 22) Located posterior to the primary auditory cortex Stores memories of sounds and permits perception of sounds Involved in recognizing and understanding speech Lies in the center of Wernicke’s area ...
... Receives information related to pitch, rhythm, and loudness Auditory association area (area 22) Located posterior to the primary auditory cortex Stores memories of sounds and permits perception of sounds Involved in recognizing and understanding speech Lies in the center of Wernicke’s area ...
Damage to the frontal lobes can lead to
... Research, clinical observation, and case studies (HM anterograde amnesia) Split-brain patients (Sperry, Gazzaniga) Lesions and stimulation experiments (rats, cats) ...
... Research, clinical observation, and case studies (HM anterograde amnesia) Split-brain patients (Sperry, Gazzaniga) Lesions and stimulation experiments (rats, cats) ...
Biopsychology, Neuroscience, Physiological Psychology
... understanding. Damage to Broca’s area disrupts speaking ...
... understanding. Damage to Broca’s area disrupts speaking ...
The Brain
... responsible for combining sounds into words and arranging words into meaningful sentences? A. B. C. D. E. ...
... responsible for combining sounds into words and arranging words into meaningful sentences? A. B. C. D. E. ...
ap psychology
... AIM: Explain how neurons are at the center of our existence. How does neural communication relate to behavior? ...
... AIM: Explain how neurons are at the center of our existence. How does neural communication relate to behavior? ...
Griggs_Chapter_02_Neuroscience
... With split-brained people, the information cannot transfer between hemispheres because the corpus callosum has been cut Split-brain people can only identify information orally when it is presented briefly in the right visual field (and thus processing in the left hemisphere) If a spoon was flashed ...
... With split-brained people, the information cannot transfer between hemispheres because the corpus callosum has been cut Split-brain people can only identify information orally when it is presented briefly in the right visual field (and thus processing in the left hemisphere) If a spoon was flashed ...
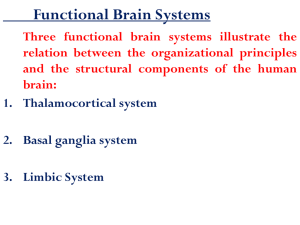
Older Brain Structures
... Note: She is lecturing from a different book, but the material is the same. . . ...
... Note: She is lecturing from a different book, but the material is the same. . . ...
Chapter 8: Sensation and Perception
... Functions: Directs messages to the sensory receiving areas in the cortex Transmits replies to the cerebellum and medulla ...
... Functions: Directs messages to the sensory receiving areas in the cortex Transmits replies to the cerebellum and medulla ...
Set 3
... Human emotions are largely learned and include: affection, pride, guilt, pity, envy, and resentment Emotions are represented in the prefrontal cortex and the limbic system namely the amygdala Lesion of the left prefrontal area produces depression Lesion of right prefrontal produces laughter ...
... Human emotions are largely learned and include: affection, pride, guilt, pity, envy, and resentment Emotions are represented in the prefrontal cortex and the limbic system namely the amygdala Lesion of the left prefrontal area produces depression Lesion of right prefrontal produces laughter ...
Griggs Chapter 2: Neuroscience
... With split-brained people, the information cannot transfer between hemispheres because the corpus callosum has been cut Split-brain people can only identify information orally when it is presented briefly in the right visual field (and thus processing in the left hemisphere) If a spoon was flashed ...
... With split-brained people, the information cannot transfer between hemispheres because the corpus callosum has been cut Split-brain people can only identify information orally when it is presented briefly in the right visual field (and thus processing in the left hemisphere) If a spoon was flashed ...
ANPS 019 Beneyto-Santonja 10-24
... 5. Adult neural canal regions a. Lateral ventricles b. Third ventricle c. Cerebral aqueduct d. Fourth ventricle e. Central canal Ventricles The fluid-filled (CSF, cerebrospinal fluid) spaces within the brain resulting from neural tube closure Delivers nutrients and removes wastes How do we tell ...
... 5. Adult neural canal regions a. Lateral ventricles b. Third ventricle c. Cerebral aqueduct d. Fourth ventricle e. Central canal Ventricles The fluid-filled (CSF, cerebrospinal fluid) spaces within the brain resulting from neural tube closure Delivers nutrients and removes wastes How do we tell ...
Frequently asked questions Psychology 1010.06M A Biologically-Oriented
... The ‘Split Brain’ studies • Special apparatus – picture input to just one side of brain – screen blocks objects on table from view ...
... The ‘Split Brain’ studies • Special apparatus – picture input to just one side of brain – screen blocks objects on table from view ...
Brain and Consciousness - Oakton Community College
... tissue becomes. The thicker the myelin tissue, the faster the electric impulse can travel through the axon, up to 200 miles per hour. ...
... tissue becomes. The thicker the myelin tissue, the faster the electric impulse can travel through the axon, up to 200 miles per hour. ...
ANATOMY NEURO REVALIDA QUESTIONS
... innermost): cerebral cortex, medulla, skull, dura mater, midbrain What are the structures included in the brain stem? What are their functions? You have learned a couple of prefixes/suffixes that will help you understand nursing terms. Give me at least 3 and tell me what they stand for. (Example: ~p ...
... innermost): cerebral cortex, medulla, skull, dura mater, midbrain What are the structures included in the brain stem? What are their functions? You have learned a couple of prefixes/suffixes that will help you understand nursing terms. Give me at least 3 and tell me what they stand for. (Example: ~p ...
Methods in Cognitive Neuroscience I
... suppression of visual perception with TMS over the occipital cortex (letter detection, trigram recognition) ...
... suppression of visual perception with TMS over the occipital cortex (letter detection, trigram recognition) ...
Autonomic Nervous System Peripheral NS and Spinal Cord A
... muscle tone, circulation. Cessation of activity in hind brain required for determination of brain death. It also relays sensory information from the various parts of the body to the brain and sends back motor messages through it. Also Medulla is crossover point of axons to brain. Messages for right ...
... muscle tone, circulation. Cessation of activity in hind brain required for determination of brain death. It also relays sensory information from the various parts of the body to the brain and sends back motor messages through it. Also Medulla is crossover point of axons to brain. Messages for right ...
New Brain Information
... http://www.communication.northwestern.edu/departments/csd/research/devel opmental_cognitive_neuroscience/participate/fmri.php ...
... http://www.communication.northwestern.edu/departments/csd/research/devel opmental_cognitive_neuroscience/participate/fmri.php ...
Essential Questions and Vocabulary
... neurotransmitters, acetylcholine, endorphins, nervous system, central nervous system, peripheral nervous system, nerves, sensory neurons, motor neurons, interneurons, somatic nervous system, autonomic nervous system, sympathetic nervous system, parasympathetic nervous system, reflex, neural networks ...
... neurotransmitters, acetylcholine, endorphins, nervous system, central nervous system, peripheral nervous system, nerves, sensory neurons, motor neurons, interneurons, somatic nervous system, autonomic nervous system, sympathetic nervous system, parasympathetic nervous system, reflex, neural networks ...
Limbic System - WordPress.com
... white matter include: A. Gray matter does not contain synapses; white matter does. B. White matter is largely composed of myelinated axons; gray matter is not. C. White matter functions primarily to transmit impulses to other areas of the CNS. ...
... white matter include: A. Gray matter does not contain synapses; white matter does. B. White matter is largely composed of myelinated axons; gray matter is not. C. White matter functions primarily to transmit impulses to other areas of the CNS. ...
Lateralization of brain function

The longitudinal fissure separates the human brain into two distinct cerebral hemispheres, connected by the corpus callosum. The hemispheres exhibit strong, but not complete, bilateral symmetry in both structure and function. For example, structurally, the lateral sulcus generally is longer in the left hemisphere than in the right hemisphere, and functionally, Broca's area and Wernicke's area are located in the left cerebral hemisphere for about 95% of right-handers, but about 70% of left-handers.Broad generalizations are often made in ""pop"" psychology about one side or the other having characteristic labels, such as ""logical"" for the left side or ""creative"" for the right. These labels are not supported by studies on lateralization, as lateralization does not add specialized usage from either hemisphere. Both hemispheres contribute to both kinds of processes, and experimental evidence provides little support for correlating the structural differences between the sides with such broadly defined functional differences.The extent of any modularity, or specialization of brain function by area, remains under investigation. If a specific region of the brain, or even an entire hemisphere, is injured or destroyed, its functions can sometimes be assumed by a neighboring region in the same hemisphere or the corresponding region in the other hemisphere, depending upon the area damaged and the patient's age. When injury interferes with pathways from one area to another, alternative (indirect) connections may develop to communicate information with detached areas, despite the inefficiencies.Brain function lateralization is evident in the phenomena of right- or left-handedness and of right or left ear preference, but a person's preferred hand is not a clear indication of the location of brain function. Although 95% of right-handed people have left-hemisphere dominance for language, 18.8% of left-handed people have right-hemisphere dominance for language function. Additionally, 19.8% of the left-handed have bilateral language functions. Even within various language functions (e.g., semantics, syntax, prosody), degree (and even hemisphere) of dominance may differ.Additionally, although some functions are lateralized, these are only a tendency. The trend across many individuals may also vary significantly as to how any specific function is implemented. The areas of exploration of this causal or effectual difference of a particular brain function include its gross anatomy, dendritic structure, and neurotransmitter distribution. The structural and chemical variance of a particular brain function, between the two hemispheres of one brain or between the same hemisphere of two different brains, is still being studied. Short of having undergone a hemispherectomy (removal of a cerebral hemisphere), no one is a ""left-brain only"" or ""right-brain only"" person.