File - CYPA Psychology
... 17. Loss of feeling in the limbs, partial blindness, and difficulty in coordinated movement may indicate a ________ disease such as ________. A) metabolic; epilepsy B) demyelinating; Alzheimer's disease C) athleroscleritic; Parkinson's disease D) demyelinating; multiple sclerosis ...
... 17. Loss of feeling in the limbs, partial blindness, and difficulty in coordinated movement may indicate a ________ disease such as ________. A) metabolic; epilepsy B) demyelinating; Alzheimer's disease C) athleroscleritic; Parkinson's disease D) demyelinating; multiple sclerosis ...
What is Your Reaction Time?
... Neuron: Nerve cell. The basic units of the central nervous system, neurons are responsible for the transmission of nerve impulses. Unlike any other cell in the body, neurons consist of a central cell body as well as several threadlike "arms" called axons and dendrites, which transmit nerve impulses. ...
... Neuron: Nerve cell. The basic units of the central nervous system, neurons are responsible for the transmission of nerve impulses. Unlike any other cell in the body, neurons consist of a central cell body as well as several threadlike "arms" called axons and dendrites, which transmit nerve impulses. ...
SinirBilimin Kısa Tarihi
... computer science, engineering, mathematics, medicine, philosophy, physics, and psychology. The term neurobiology is usually used interchangeably with the term neuroscience, although the former refers specifically to the biology of the nervous system, whereas the latter refers to the entire science o ...
... computer science, engineering, mathematics, medicine, philosophy, physics, and psychology. The term neurobiology is usually used interchangeably with the term neuroscience, although the former refers specifically to the biology of the nervous system, whereas the latter refers to the entire science o ...
Nerve activates contraction
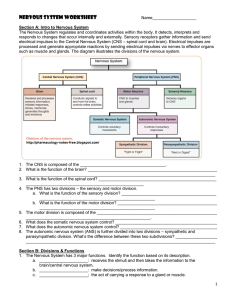
... 1-Somatic nervous system = voluntary, it controls skeletal muscles N. B. skeletal muscle reflexes are involuntary 2-Autonomic nervous system = involuntary, it controls smooth &cardiac muscles &glands This also is divided into sympathetic & parasympathetiuc ...
... 1-Somatic nervous system = voluntary, it controls skeletal muscles N. B. skeletal muscle reflexes are involuntary 2-Autonomic nervous system = involuntary, it controls smooth &cardiac muscles &glands This also is divided into sympathetic & parasympathetiuc ...
Nervous System
... and make synapses all over the body with other neurons, muscles and glands • communicate through action potentials • allows for short response times to changes in homeostasis – Neuroglia • guide developing neurons to make synapses • provide a supportive scaffolding for developed neurons ...
... and make synapses all over the body with other neurons, muscles and glands • communicate through action potentials • allows for short response times to changes in homeostasis – Neuroglia • guide developing neurons to make synapses • provide a supportive scaffolding for developed neurons ...
Unit 3D Worksheet 1) In the Autonomic Nervous System (ANS
... 3)Effectors of the Somatic Nervous System (SNS) innervate skeletal ___________via ______ heavily ________________axon. This would be an afferent/efferent sensory/motor neuron. 4) Effectors of the ANS innervate ___________muscle, __________muscle and ________via a ______neuron __________made up of __ ...
... 3)Effectors of the Somatic Nervous System (SNS) innervate skeletal ___________via ______ heavily ________________axon. This would be an afferent/efferent sensory/motor neuron. 4) Effectors of the ANS innervate ___________muscle, __________muscle and ________via a ______neuron __________made up of __ ...
Nervous System
... and make synapses all over the body with other neurons, muscles and glands • communicate through action potentials • allows for short response times to changes in homeostasis – Neuroglia • guide developing neurons to make synapses • provide a supportive scaffolding for developed neurons ...
... and make synapses all over the body with other neurons, muscles and glands • communicate through action potentials • allows for short response times to changes in homeostasis – Neuroglia • guide developing neurons to make synapses • provide a supportive scaffolding for developed neurons ...
Unit 1: Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium (II) The Nervous System
... Neurotransmitter attaches to receptors on dendrites and excites or inhibits the neuron. NOTE : An excitatory response opens the sodium gates and triggers a wave of depolarization. Inhibitory response makes the postsynaptic neuron more negative on the inside which raises the threshold of the stimulus ...
... Neurotransmitter attaches to receptors on dendrites and excites or inhibits the neuron. NOTE : An excitatory response opens the sodium gates and triggers a wave of depolarization. Inhibitory response makes the postsynaptic neuron more negative on the inside which raises the threshold of the stimulus ...
Nervous System Worksheet - Jackson County Faculty Sites!
... Neurotransmitters are chemicals which carrier the impulse from one neuron to the next neuron. These chemicals allow the transmission of signals across the synapse. Some neurotransmitters are excitatory or inhibitory. Here are a few examples of common neurotransmitters. Acetylcholine – stimulates m ...
... Neurotransmitters are chemicals which carrier the impulse from one neuron to the next neuron. These chemicals allow the transmission of signals across the synapse. Some neurotransmitters are excitatory or inhibitory. Here are a few examples of common neurotransmitters. Acetylcholine – stimulates m ...
Nervous System
... sensory nerves, which carry sensory input to the brain or spinal cord from the environment. • motor nerves, which carry motor impulses from the brain or spinal cord to muscles or glands. • mixed nerves, which have a combination of sensory and motor neurons in one nerve. The peripheral nervous system ...
... sensory nerves, which carry sensory input to the brain or spinal cord from the environment. • motor nerves, which carry motor impulses from the brain or spinal cord to muscles or glands. • mixed nerves, which have a combination of sensory and motor neurons in one nerve. The peripheral nervous system ...
The Nervous System - ESC-2
... nervous system analyzes the data and causes a response. – Putting your hand in front of your face if a ball is coming at you. – Increasing your heart rate when exercising. ...
... nervous system analyzes the data and causes a response. – Putting your hand in front of your face if a ball is coming at you. – Increasing your heart rate when exercising. ...
PSE4U1 - 10.Unit 4
... • Do not transmit impulses • Special type of connective tissue • Maintain functioning of neurons by holding them together and protecting them • 3 types – Astrocytes: large, star shaped, threadlike branches attached to neurons and blood vessels – Microglia: smaller than astrocytes, stationary, when b ...
... • Do not transmit impulses • Special type of connective tissue • Maintain functioning of neurons by holding them together and protecting them • 3 types – Astrocytes: large, star shaped, threadlike branches attached to neurons and blood vessels – Microglia: smaller than astrocytes, stationary, when b ...
answers - Easy Peasy All-in
... thread-like substances that carry messages to the cell body. The axon and axon terminals carry information in and out of the cell. The myelin keeps the electrical charge from traveling out of the axon . (Taken directly from the GA Virtual website) Name the three kinds of neurons and describe what jo ...
... thread-like substances that carry messages to the cell body. The axon and axon terminals carry information in and out of the cell. The myelin keeps the electrical charge from traveling out of the axon . (Taken directly from the GA Virtual website) Name the three kinds of neurons and describe what jo ...
Neurological Systemppt
... Analyze the function of the nervous system. Discuss characteristics and treatment of common nervous system disorders. ...
... Analyze the function of the nervous system. Discuss characteristics and treatment of common nervous system disorders. ...
Introduction to Psychology
... recognizes this is an axon that is responsible for a. carrying signals away from the cell body b. receiving signals from other cells and carrying them toward the cell body c. determining the speed at which an action potential will travel d. directing the growth and repair of neurons ...
... recognizes this is an axon that is responsible for a. carrying signals away from the cell body b. receiving signals from other cells and carrying them toward the cell body c. determining the speed at which an action potential will travel d. directing the growth and repair of neurons ...
Nervous System Notes
... – If received by another neuron, it will open Na+ gates on the next neuron, beginning a new action potential on the new neuron – If received by some body part, it will stimulate some sort of change (muscles, glands, etc.) • After neurotransmitter does its job, the receptor releases it back into syna ...
... – If received by another neuron, it will open Na+ gates on the next neuron, beginning a new action potential on the new neuron – If received by some body part, it will stimulate some sort of change (muscles, glands, etc.) • After neurotransmitter does its job, the receptor releases it back into syna ...
The Nervous System
... ▫ Cerebral cortex: outer layer of gray matter; short and long term memory Convolutions: elevated ridges/folds that increases gray area of brain ...
... ▫ Cerebral cortex: outer layer of gray matter; short and long term memory Convolutions: elevated ridges/folds that increases gray area of brain ...
Blockade of NMDA receptors in the developing cortex and
... autophagy (3-MA, rapamycin) did not interfere with the anti-excitotoxic effect of MK801 observed in deep layers V and VI. In vivo, 3-MA blocked the rapid increase in caspase-3 cleavage induced by NMDA antagonists and prevented death of Gad67-GFP neurons in layers II-IV. Together, these data suggest ...
... autophagy (3-MA, rapamycin) did not interfere with the anti-excitotoxic effect of MK801 observed in deep layers V and VI. In vivo, 3-MA blocked the rapid increase in caspase-3 cleavage induced by NMDA antagonists and prevented death of Gad67-GFP neurons in layers II-IV. Together, these data suggest ...
Autonomic Nervous System
... • Preganglionic fibers arise from the nuclei of cranial nerves and spinal cord segments S2 through S4 • For this reason this division is called the Craniosacral Division (or Craniosacral outflow) ...
... • Preganglionic fibers arise from the nuclei of cranial nerves and spinal cord segments S2 through S4 • For this reason this division is called the Craniosacral Division (or Craniosacral outflow) ...
14-Nervous System - Savita Pall and Chemistry
... neuron carries information from one location to another. Nerve tissue is made up of special cells called neurons. Nerve tissue is found in the brain, spinal cord and the nerves. The term neuron and nerve cell are synonymous. The function of a neuron / nerve cell is to send electrical signals, i.e. n ...
... neuron carries information from one location to another. Nerve tissue is made up of special cells called neurons. Nerve tissue is found in the brain, spinal cord and the nerves. The term neuron and nerve cell are synonymous. The function of a neuron / nerve cell is to send electrical signals, i.e. n ...
31.1 The Neuron The Neuron
... writing a strategy to help you remember the meaning of each term. One has bbeen een done for you. Term ...
... writing a strategy to help you remember the meaning of each term. One has bbeen een done for you. Term ...
File
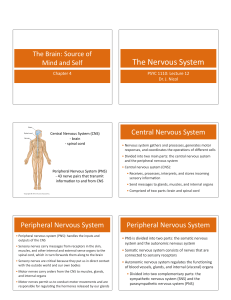
... The nervous system has two parts. The central nervous system consists of the brain and spinal cord. The peripheral nervous system is made up of nerve cells that send messages between the central nervous system and other parts of the body. Nerve cells are called neurons. ...
... The nervous system has two parts. The central nervous system consists of the brain and spinal cord. The peripheral nervous system is made up of nerve cells that send messages between the central nervous system and other parts of the body. Nerve cells are called neurons. ...
CNS II
... inhibit the postsynaptic neuron • Excites with excitatory receptors at the membrane or inhibits with inhibitory receptors – Action potentials cause transmitter release from the presynaptic terminals: role of calcium ions • Presynaptic membrane contains voltage-gated calcium channels • When an action ...
... inhibit the postsynaptic neuron • Excites with excitatory receptors at the membrane or inhibits with inhibitory receptors – Action potentials cause transmitter release from the presynaptic terminals: role of calcium ions • Presynaptic membrane contains voltage-gated calcium channels • When an action ...
The Nervous System
... • Peripheral nervous system (PNS): handles the inputs and outputs of the CNS • Sensory nerves carry messages from receptors in the skin, muscles, and other internal and external sense organs to the spina ...
... • Peripheral nervous system (PNS): handles the inputs and outputs of the CNS • Sensory nerves carry messages from receptors in the skin, muscles, and other internal and external sense organs to the spina ...
Activity Overview - Teacher Enrichment Initiatives
... Neurons are specifically designed for information processing and signaling. They transmit and receive nervous impulses (messages) between the brain and body and within the brain and spinal cord. There are three main types of neurons: motor, sensory, and interneurons (also called association neurons) ...
... Neurons are specifically designed for information processing and signaling. They transmit and receive nervous impulses (messages) between the brain and body and within the brain and spinal cord. There are three main types of neurons: motor, sensory, and interneurons (also called association neurons) ...
Neurotoxin
Neurotoxins are substances that are poisonous or destructive to nerve tissue. Neurotoxins are an extensive class of exogenous chemical neurological insults that can adversely affect function in both developing and mature nervous tissue. The term can also be used to classify endogenous compounds, which, when abnormally contact, can prove neurologically toxic. Though neurotoxins are often neurologically destructive, their ability to specifically target neural components is important in the study of nervous systems. Common examples of neurotoxins include lead, ethanol (drinking alcohol), Manganese glutamate, nitric oxide (NO), botulinum toxin (e.g. Botox), tetanus toxin, and tetrodotoxin. Some substances such as nitric oxide and glutamate are in fact essential for proper function of the body and only exert neurotoxic effects at excessive concentrations.Neurotoxins inhibit neuron control over ion concentrations across the cell membrane, or communication between neurons across a synapse. Local pathology of neurotoxin exposure often includes neuron excitotoxicity or apoptosis but can also include glial cell damage. Macroscopic manifestations of neurotoxin exposure can include widespread central nervous system damage such as intellectual disability, persistent memory impairments, epilepsy, and dementia. Additionally, neurotoxin-mediated peripheral nervous system damage such as neuropathy or myopathy is common. Support has been shown for a number of treatments aimed at attenuating neurotoxin-mediated injury, such as antioxidant, and antitoxin administration.