Genetics: The Science of Heredity
... 1. An organism’s habitat must provide all of the following except a. food. b. predators. c. water. d. shelter. 2. To produce their own food, algae and plants use the abiotic factors sunlight, carbon dioxide, and a. soil. b. water. c. salt. d. bacteria. 3. Which of the following is an example of a po ...
... 1. An organism’s habitat must provide all of the following except a. food. b. predators. c. water. d. shelter. 2. To produce their own food, algae and plants use the abiotic factors sunlight, carbon dioxide, and a. soil. b. water. c. salt. d. bacteria. 3. Which of the following is an example of a po ...
Ecosystems Day 5 Populations Interactions
... Intraspecific Competition: members of the same species compete for the same resource in an ecosystem (e.g. food, light, nutrients, space). Interspecific Competition: individuals of different species compete for the same resource in an ecosystem (e.g. food or living space). ...
... Intraspecific Competition: members of the same species compete for the same resource in an ecosystem (e.g. food, light, nutrients, space). Interspecific Competition: individuals of different species compete for the same resource in an ecosystem (e.g. food or living space). ...
Populations and Resources
... Urban sprawl is the growth of relatively lowdensity development on the edges of urban areas. Human population in the Golden Horseshoe is expected to increase by 3.7 million between 2005 and 2031. How do we make room for all these people without affecting other ecosystems? ...
... Urban sprawl is the growth of relatively lowdensity development on the edges of urban areas. Human population in the Golden Horseshoe is expected to increase by 3.7 million between 2005 and 2031. How do we make room for all these people without affecting other ecosystems? ...
EDWG Grouse Presentation_10.9.15
... Priority habitat Management Areas: The encompass the SFAs and additional priority habitat. The plans seek to limit or eliminate new habitat disturbance with limited exceptions. The plans put in place a disturbance cap in priority habitat that limits how much fragmentation of habitat can occur. The c ...
... Priority habitat Management Areas: The encompass the SFAs and additional priority habitat. The plans seek to limit or eliminate new habitat disturbance with limited exceptions. The plans put in place a disturbance cap in priority habitat that limits how much fragmentation of habitat can occur. The c ...
Swainson`s Warbler Best Management Practices
... the Missouri Department of Conservation with assistance from state and federal agencies, contractors and others to provide guidance to those people who wish to voluntarily act to protect wildlife and habitat. Compliance with these Best Management Practices is not required by the Missouri wildlife an ...
... the Missouri Department of Conservation with assistance from state and federal agencies, contractors and others to provide guidance to those people who wish to voluntarily act to protect wildlife and habitat. Compliance with these Best Management Practices is not required by the Missouri wildlife an ...
populations - University of Warwick
... change of patch occupancy at low p, then this is called a metapopulation ‘Allee effect’ (Amarasekare 1998. Allee effects in metapopulation dynamics. American Naturalist. 152). Just as the Levin’s model can be thought of as analogous to the logistic model of population growth rate, if the per capita ...
... change of patch occupancy at low p, then this is called a metapopulation ‘Allee effect’ (Amarasekare 1998. Allee effects in metapopulation dynamics. American Naturalist. 152). Just as the Levin’s model can be thought of as analogous to the logistic model of population growth rate, if the per capita ...
1. What is a population? Distinguish between density
... mortality being more constant over the life span • Type III curve show very high death rates for the young followed by lower death rates after individuals have survived to a certain critical age ...
... mortality being more constant over the life span • Type III curve show very high death rates for the young followed by lower death rates after individuals have survived to a certain critical age ...
the exerpt from the 2010 Action Plan
... heath 1–1.5 m high. Near Waychinicup R. and in the Fitzgerald R. National Park, the main habitat is closed heath 0.5–1 m high, sometimes with scattered patches of mallee eucalypts, though more open heaths may be used if there are enough patches of dense shrubs in the area (McNee 1986). Territory siz ...
... heath 1–1.5 m high. Near Waychinicup R. and in the Fitzgerald R. National Park, the main habitat is closed heath 0.5–1 m high, sometimes with scattered patches of mallee eucalypts, though more open heaths may be used if there are enough patches of dense shrubs in the area (McNee 1986). Territory siz ...
chapter 10
... 2. An association of individuals of different species living in the same habitat and having functional interactions is (a)Biotic community (b) Ecologic niche (c)Population (d)Ecosystem 3. Association between sea Anemone and Hermit crab in gastropod shell is that of (a)Parasitism (b) Commensalism (c) ...
... 2. An association of individuals of different species living in the same habitat and having functional interactions is (a)Biotic community (b) Ecologic niche (c)Population (d)Ecosystem 3. Association between sea Anemone and Hermit crab in gastropod shell is that of (a)Parasitism (b) Commensalism (c) ...
proposal_gnlcc_grant_ctcr_2014
... managed for variable production and wild fish returns. Success is based on meeting targets for abundance and composition of natural escapement and hatchery broodstock. The Okanogan Subbasin Habitat and Improvement Program (OSHIP) implements the Okanogan Subbasin Plan to describe in detail the curren ...
... managed for variable production and wild fish returns. Success is based on meeting targets for abundance and composition of natural escapement and hatchery broodstock. The Okanogan Subbasin Habitat and Improvement Program (OSHIP) implements the Okanogan Subbasin Plan to describe in detail the curren ...
Characteristics of Populations
... Carrying capacity refers to the maximum size of population the environment will support. The curve depicting the growth of a population that is limited by a definite carrying capacity is shaped like the letter “S”. A population crash occurs when a population overshoots its carrying capacity and envi ...
... Carrying capacity refers to the maximum size of population the environment will support. The curve depicting the growth of a population that is limited by a definite carrying capacity is shaped like the letter “S”. A population crash occurs when a population overshoots its carrying capacity and envi ...
Envi Sci @ CHS
... b. __________________ The population size of a species with a fairly unchanging population fluctuates slightly above and below its carrying capacity. c. __________________ The population undergoes sharp increases in size, followed by crashes ...
... b. __________________ The population size of a species with a fairly unchanging population fluctuates slightly above and below its carrying capacity. c. __________________ The population undergoes sharp increases in size, followed by crashes ...
7.11
... Science Standards of Learning Curriculum Framework 2010 Life Science – Page 24 LS.11 The student will investigate and understand the relationships between ecosystem dynamics and human activity. Key concepts include a) food production and harvest; b) change in habitat size, quality, or structure; c) ...
... Science Standards of Learning Curriculum Framework 2010 Life Science – Page 24 LS.11 The student will investigate and understand the relationships between ecosystem dynamics and human activity. Key concepts include a) food production and harvest; b) change in habitat size, quality, or structure; c) ...
ECOLOGY VOCAB QUESTIONS
... 8. For Foreign species introduction, habitat, and niche: How would introduction of foreign species affect an organisms habitat and niche? 9. For Primary Succession and Secondary Succession: Explain Re-growth of a forest using appropriate term. 10. For Competition, Herbivores, omnivores, carnivores: ...
... 8. For Foreign species introduction, habitat, and niche: How would introduction of foreign species affect an organisms habitat and niche? 9. For Primary Succession and Secondary Succession: Explain Re-growth of a forest using appropriate term. 10. For Competition, Herbivores, omnivores, carnivores: ...
Chapter 1 Vocabulary Review
... (number of total individuals captured X number of originally marked ) Total number of individuals recaptured with mark ...
... (number of total individuals captured X number of originally marked ) Total number of individuals recaptured with mark ...
Ecosystem Review Game
... If two species occupy the same niche, one of the species will eventually ___________. ...
... If two species occupy the same niche, one of the species will eventually ___________. ...
Breeding Bird Use of Hybrid Poplar Plantations in Minnesota
... landscapes are colonized earlier by forest birds ...
... landscapes are colonized earlier by forest birds ...
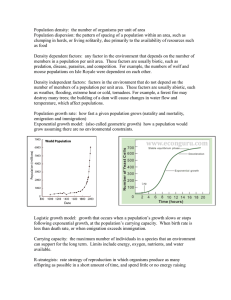
Population density: the number of organisms per unit of area
... Logistic growth model: growth that occurs when a population’s growth slows or stops following exponential growth, at the population’s carrying capacity. When birth rate is less than death rate, or when emigration exceeds immigration. Carrying capacity: the maximum number of individuals in a species ...
... Logistic growth model: growth that occurs when a population’s growth slows or stops following exponential growth, at the population’s carrying capacity. When birth rate is less than death rate, or when emigration exceeds immigration. Carrying capacity: the maximum number of individuals in a species ...
Populations
... A group of individuals of the same species living in the same area Ex: A population of giraffes in eastern Africa OR a population of giraffes in ...
... A group of individuals of the same species living in the same area Ex: A population of giraffes in eastern Africa OR a population of giraffes in ...
Chapter 23 Notes: Population Genetics
... the light variety continued to dominate in unpolluted areas outside of London. 3) Diversifying (a.k.a. Disruptive) Selection: occurs when environment while selecting against common traits 4) Sexual Selection: differential mating of males in a population; -females tend to increase their fitness by ...
... the light variety continued to dominate in unpolluted areas outside of London. 3) Diversifying (a.k.a. Disruptive) Selection: occurs when environment while selecting against common traits 4) Sexual Selection: differential mating of males in a population; -females tend to increase their fitness by ...
Intraspecific Competition
... A: Interspecific Competition B: Intraspecific Competition 1. Two squirrels race up a tree to reach a hidden pile of nuts. 2. A hyena chases off a vulture to feast on an antelope ...
... A: Interspecific Competition B: Intraspecific Competition 1. Two squirrels race up a tree to reach a hidden pile of nuts. 2. A hyena chases off a vulture to feast on an antelope ...
Ecology 2
... • Food is placed into a Petri dish, and bacteria is introduced to the food. • The first 2 hours is the “lag phase”, followed with exponential growth. • During the 2nd hour, bacteria begin to reproduce because there is plenty of food available. • The bacteria will grow exponentially until there is no ...
... • Food is placed into a Petri dish, and bacteria is introduced to the food. • The first 2 hours is the “lag phase”, followed with exponential growth. • During the 2nd hour, bacteria begin to reproduce because there is plenty of food available. • The bacteria will grow exponentially until there is no ...