Population Growth
... • POPULATION: A group of organisms that belong to the same species living in the habitat at the same time. • GROWTH RATE = Births – Deaths ...
... • POPULATION: A group of organisms that belong to the same species living in the habitat at the same time. • GROWTH RATE = Births – Deaths ...
Population ecology
... Change in population size: N=(birth+immigration)-(death+emigration) • Growth occurs if inputs are greater than outputs. • Under ideal conditions, the intrinsic growth rate is observed. • This is the maximum potential for growth of a population. • It is essentially the maximum amount of offspring tha ...
... Change in population size: N=(birth+immigration)-(death+emigration) • Growth occurs if inputs are greater than outputs. • Under ideal conditions, the intrinsic growth rate is observed. • This is the maximum potential for growth of a population. • It is essentially the maximum amount of offspring tha ...
Conservation and Land Management Practices and Their Impact on
... of non-native cool-season grasses (CSG). WSG fields had higher species richness and diversity than CSG fields. In addition, timing of field management influenced bird communities, with fields managed in summer or fall months exhibiting lower avian abundance than those managed in the winter or not a ...
... of non-native cool-season grasses (CSG). WSG fields had higher species richness and diversity than CSG fields. In addition, timing of field management influenced bird communities, with fields managed in summer or fall months exhibiting lower avian abundance than those managed in the winter or not a ...
Review for Ecology Test
... 16. What would happen to the populations of a specific roducers in a certain area if the primary consumer that feeds on that producer suddenly became extinct? ...
... 16. What would happen to the populations of a specific roducers in a certain area if the primary consumer that feeds on that producer suddenly became extinct? ...
Populations - Helena High School
... ecologist determines the population of spotted knapweed to be 10,000. The area under study is 14 square kilometers. What is the population density? A small town in Texas covers 14 square kilometers. There are 420 individuals who live within town limits. What is the population density of this town? ...
... ecologist determines the population of spotted knapweed to be 10,000. The area under study is 14 square kilometers. What is the population density? A small town in Texas covers 14 square kilometers. There are 420 individuals who live within town limits. What is the population density of this town? ...
The Cache River Wetland: Are there differences in swamp rabbit
... rabbit occupancy in southern Illinois, there has not been a comparison of habitat in the LCR vs. the UCR. Our objective is to determine if there is a difference in ...
... rabbit occupancy in southern Illinois, there has not been a comparison of habitat in the LCR vs. the UCR. Our objective is to determine if there is a difference in ...
I can classify organisms as producers, consumers, or decomposers
... 5. I can use food chains, food webs, and energy pyramids to show relationships among populations in an ecosystem. (including labeling producer,1st consumer, 2nd consumer, ...
... 5. I can use food chains, food webs, and energy pyramids to show relationships among populations in an ecosystem. (including labeling producer,1st consumer, 2nd consumer, ...
Chapter 14
... •Competition occurs when two organisms fight for the same limited resource. –Intraspecific competition –Interspecific competition –Predation occurs when one organism captures and eats another. (predator – kills and eats; prey – food source) Any relationship in which 2 species live closely together i ...
... •Competition occurs when two organisms fight for the same limited resource. –Intraspecific competition –Interspecific competition –Predation occurs when one organism captures and eats another. (predator – kills and eats; prey – food source) Any relationship in which 2 species live closely together i ...
Population Dynamics, Part II
... 4A.6e.1: Competition for resources and other factors limits growth and can be described by the logistic model. 4A.6e.2: Competition for resources, territoriality, health, predation, accumulation of wastes and other factors contribute to density-dependent population regulation. 4A.6f: Human activitie ...
... 4A.6e.1: Competition for resources and other factors limits growth and can be described by the logistic model. 4A.6e.2: Competition for resources, territoriality, health, predation, accumulation of wastes and other factors contribute to density-dependent population regulation. 4A.6f: Human activitie ...
Possums reclassified as “endangered”. Western Ringtail Possum
... QBAJ&pg=PA272&lpg=PA272&dq=western+ringtail+ possum+burbidge&source=bl&ots, p 271-75). Over the last ten years, the WRP population is estimated to have decreased by 80%. Over the next decade, as rainfall continues to decline, temperatures rise and leaf quality diminishes, urban development and loggi ...
... QBAJ&pg=PA272&lpg=PA272&dq=western+ringtail+ possum+burbidge&source=bl&ots, p 271-75). Over the last ten years, the WRP population is estimated to have decreased by 80%. Over the next decade, as rainfall continues to decline, temperatures rise and leaf quality diminishes, urban development and loggi ...
Lecture_18.1,18.2_Ecology_and_lecture_19_Populations
... Population: a group of organisms of the same species (capable of interbreeding) that live in the same area at the same time Community: a group of populations living and interacting with each other Species: a group of organisms of similar appearance and which can interbreed to produce viable offsprin ...
... Population: a group of organisms of the same species (capable of interbreeding) that live in the same area at the same time Community: a group of populations living and interacting with each other Species: a group of organisms of similar appearance and which can interbreed to produce viable offsprin ...
Landscape Issues for Wildlife
... – Harsh, sterile, unihabitable habitats may be best! – Good habitat may act as a “wick” rather than a buffer ...
... – Harsh, sterile, unihabitable habitats may be best! – Good habitat may act as a “wick” rather than a buffer ...
Bio 11A
... 1. What is the biodiversity crisis? Name 4 species in our local area that are threatened or endangered. 2. What is the estimated rate of extinction today? Why is this significant? 3. Why is biodiversity important to the human population? 4. What is the geographic distribution pattern of species with ...
... 1. What is the biodiversity crisis? Name 4 species in our local area that are threatened or endangered. 2. What is the estimated rate of extinction today? Why is this significant? 3. Why is biodiversity important to the human population? 4. What is the geographic distribution pattern of species with ...
Chapter 4: ECOSYSTEMS AND COMMUNITIES
... The biosphere is the global sum of all ecosystems; integrating all living beings and their relationships, including their interactions with the elements of the lithosphere, hydrosphere, and atmosphere. ...
... The biosphere is the global sum of all ecosystems; integrating all living beings and their relationships, including their interactions with the elements of the lithosphere, hydrosphere, and atmosphere. ...
Answers to Questions 1-14 From Chapter 8 A sea otter is an
... for young together and hunt together too. -Random distribution is usually seen in plants although it is considered rare, it happens when the wind or water randomly carries seeds or spawn to random places and the organisms sort of grow where they land. 4. Examples would be: Uniform-Joshua Trees in th ...
... for young together and hunt together too. -Random distribution is usually seen in plants although it is considered rare, it happens when the wind or water randomly carries seeds or spawn to random places and the organisms sort of grow where they land. 4. Examples would be: Uniform-Joshua Trees in th ...
Mid Ecology Unit Test Review
... i. All the zebras living in the same area ii. Zebras and giraffes in the same area iii. Zebras, giraffes, and grass in the same area 3. Energy Flow a. The sun is the primary source of energy in most ecosystems. b. Organisms that can convert sunlight into food (glucose) are called producers or autotr ...
... i. All the zebras living in the same area ii. Zebras and giraffes in the same area iii. Zebras, giraffes, and grass in the same area 3. Energy Flow a. The sun is the primary source of energy in most ecosystems. b. Organisms that can convert sunlight into food (glucose) are called producers or autotr ...
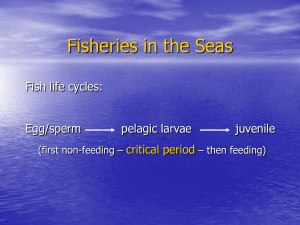
Fisheries in the Seas
... 1. Must be based on a good understanding of the population biology of the fish • Sampling problem – independent sample – use harvest data (landings) ...
... 1. Must be based on a good understanding of the population biology of the fish • Sampling problem – independent sample – use harvest data (landings) ...
Population Distribution
... • Explain how disturbances can throw a community out of a balanced state and into a period of adjustment. • List examples of primary & secondary succession and describe the stages; identify the factors that determine the type of succession that will occur. • Identify a pioneer species & list several ...
... • Explain how disturbances can throw a community out of a balanced state and into a period of adjustment. • List examples of primary & secondary succession and describe the stages; identify the factors that determine the type of succession that will occur. • Identify a pioneer species & list several ...
Animals need food, cover, water, and living space to survive. The
... overflows. Much the same thing happens with wildlife populations and habitat. (But unlike a bucket, carrying capacity changes with time, weather, people’s influence, causing carrying capacity to increase or decrease.) If reproduction or immigration causes the population to exceed the number of anima ...
... overflows. Much the same thing happens with wildlife populations and habitat. (But unlike a bucket, carrying capacity changes with time, weather, people’s influence, causing carrying capacity to increase or decrease.) If reproduction or immigration causes the population to exceed the number of anima ...
Ecology - Images
... (communities) of a particular place together with their nonliving or physical environment. Biome – a group of ecosystems that have the same climate, and similar dominant communities. ...
... (communities) of a particular place together with their nonliving or physical environment. Biome – a group of ecosystems that have the same climate, and similar dominant communities. ...
The Newly Discovered Endangered Species
... This species is a four-legged beast with seven tails covered with dirty blonde hair. The seven tailed swamp beast has gills and a lantern on its head so it can survive underwater as long as it wants to. It has a protective shell to protect it from alligators and crocodiles. When fireflies get caught ...
... This species is a four-legged beast with seven tails covered with dirty blonde hair. The seven tailed swamp beast has gills and a lantern on its head so it can survive underwater as long as it wants to. It has a protective shell to protect it from alligators and crocodiles. When fireflies get caught ...