Random-priming in vitro recombination: an effective tool for directed evolution ,
... into full length sequences. Gene reassembly is generally easier with the RPR technique, which employs random priming synthesis to obtain the short DNA fragments. Furthermore, since DNase I hydrolyzes double-stranded DNA preferentially at sites adjacent to pyrimidine nucleotides (6), its use in templ ...
... into full length sequences. Gene reassembly is generally easier with the RPR technique, which employs random priming synthesis to obtain the short DNA fragments. Furthermore, since DNase I hydrolyzes double-stranded DNA preferentially at sites adjacent to pyrimidine nucleotides (6), its use in templ ...
ppt - Department of Plant Sciences
... may not be the TRUE number of EcoRI cut sites in this genome, it can still accurately be assumed that there are A LOT of cut sites. • If restriction digested with EcoRI, the arabidopsis genome would be cut into tens of thousands of pieces, all of unique size. • This is why when you run a sample of d ...
... may not be the TRUE number of EcoRI cut sites in this genome, it can still accurately be assumed that there are A LOT of cut sites. • If restriction digested with EcoRI, the arabidopsis genome would be cut into tens of thousands of pieces, all of unique size. • This is why when you run a sample of d ...
Organic Chemistry
... allow them to perform a variety of functions. • In living organisms, they are used for transport, structure, metabolism, communication, and even to detect stimuli such as light. • The protein hemoglobin carries oxygen in your blood, and the protein keratin helps support your skin, hair and nails. ...
... allow them to perform a variety of functions. • In living organisms, they are used for transport, structure, metabolism, communication, and even to detect stimuli such as light. • The protein hemoglobin carries oxygen in your blood, and the protein keratin helps support your skin, hair and nails. ...
000 EXAM 2 study guide
... 8. In general – how do each of these mutagens modify DNA (base change or insertion or deletion?). A. Alkylating agents, base analogs, deaminating agents, hydroxylating agents, intercalating agents. CHAPTER 8 1. Understand polarity as it relates to the DNA template, mRNA molecule and a polypeptide. 2 ...
... 8. In general – how do each of these mutagens modify DNA (base change or insertion or deletion?). A. Alkylating agents, base analogs, deaminating agents, hydroxylating agents, intercalating agents. CHAPTER 8 1. Understand polarity as it relates to the DNA template, mRNA molecule and a polypeptide. 2 ...
The Production of a
... 8.1 An Overview of Genetic Engineering Goal of genetic engineering is to produce organisms with new, improved characteristics. ...
... 8.1 An Overview of Genetic Engineering Goal of genetic engineering is to produce organisms with new, improved characteristics. ...
PSY236 -‐ Biopsychology and Learning
... Meiosis is a two-‐stage process of cell division that results in four haploid cells, each with half the number of chromosomes as the original parent cell. These mature into reproductive cells (gametes), ...
... Meiosis is a two-‐stage process of cell division that results in four haploid cells, each with half the number of chromosomes as the original parent cell. These mature into reproductive cells (gametes), ...
4 Types Biological Molecules in plants and animals
... Liquid water is essential to life. Most chemical reactions that sustain life only work in solution. 3 important characteristics of water that make it essential: Water is a good solvent: In order to have a chemical reaction, molecules must be able to move around and contact each other. Liquid over a ...
... Liquid water is essential to life. Most chemical reactions that sustain life only work in solution. 3 important characteristics of water that make it essential: Water is a good solvent: In order to have a chemical reaction, molecules must be able to move around and contact each other. Liquid over a ...
Chapter 11
... Liquid water is essential to life. Most chemical reactions that sustain life only work in solution. 3 important characteristics of water that make it essential: Water is a good solvent: In order to have a chemical reaction, molecules must be able to move around and contact each other. Liquid over a ...
... Liquid water is essential to life. Most chemical reactions that sustain life only work in solution. 3 important characteristics of water that make it essential: Water is a good solvent: In order to have a chemical reaction, molecules must be able to move around and contact each other. Liquid over a ...
Transcription
... • The base-pairing during transcription is the same as when DNA replicates, except that RNA has uracil instead of thymine: the base U in RNA pairs with A in DNA. ...
... • The base-pairing during transcription is the same as when DNA replicates, except that RNA has uracil instead of thymine: the base U in RNA pairs with A in DNA. ...
6.2 Recombinant DNA Technology
... DNA extracted from human cells DNA treated with restriction enzyme, cuts the DNA at specific sites, produce “sticky end” Bacterial plasmid cut with same enzyme ...
... DNA extracted from human cells DNA treated with restriction enzyme, cuts the DNA at specific sites, produce “sticky end” Bacterial plasmid cut with same enzyme ...
Chapter 11
... DISCOVERING THE STRUCTURE OF DNA • Francis Crick and James Watson elaborated on the discoveries of Franklin and Chargaff and deduced that the structure of DNA was a double helix. • Two strands of DNA bound together by hydrogen bonds between the bases. • Because a purine of one strand binds to a pyr ...
... DISCOVERING THE STRUCTURE OF DNA • Francis Crick and James Watson elaborated on the discoveries of Franklin and Chargaff and deduced that the structure of DNA was a double helix. • Two strands of DNA bound together by hydrogen bonds between the bases. • Because a purine of one strand binds to a pyr ...
Protocol S1
... whole genomes, and then we set artificially ~89 kb gaps into P1/7 at the position where the corresponding segments reside in 98HAH12 and 05ZYH33. Second, we used 500 bp windows overlapped by 100 bp to compute the G+C% on the ~89 kb segments observed only in 98HAH12 and 05ZYH33. Identification of put ...
... whole genomes, and then we set artificially ~89 kb gaps into P1/7 at the position where the corresponding segments reside in 98HAH12 and 05ZYH33. Second, we used 500 bp windows overlapped by 100 bp to compute the G+C% on the ~89 kb segments observed only in 98HAH12 and 05ZYH33. Identification of put ...
Biology DNA Extraction
... 2. What did the DNA look like? Relate what you know about the chemical structure of DNA to what you observed today. ...
... 2. What did the DNA look like? Relate what you know about the chemical structure of DNA to what you observed today. ...
IV. Diagnosing Gene Disorders
... Normal development of sexual traits and are _____________. 3. Turner Syndrome females with only one affects 1/2000 live female births. Only 1 in ___________ affected zygotes develops to term. Individuals are short in stature, generally lack prominent female secondary sexual characteristics, ...
... Normal development of sexual traits and are _____________. 3. Turner Syndrome females with only one affects 1/2000 live female births. Only 1 in ___________ affected zygotes develops to term. Individuals are short in stature, generally lack prominent female secondary sexual characteristics, ...
DNA and replication
... molecule “unzips” and then produces two new molecules 4. Explain how the DNA molecule makes an exact copy of itself during replication 5. Where does DNA replication take place, in eukaryotic cells? 6. Use the complementary rule to create the complementary strand: ...
... molecule “unzips” and then produces two new molecules 4. Explain how the DNA molecule makes an exact copy of itself during replication 5. Where does DNA replication take place, in eukaryotic cells? 6. Use the complementary rule to create the complementary strand: ...
Biology 303 EXAM II 3/14/00 NAME
... Which of the following is needed in order to amplify a DNA fragment by PCR? 1. a set of primers. 2. knowledge of the complete nucleotide sequence of the fragment to be ...
... Which of the following is needed in order to amplify a DNA fragment by PCR? 1. a set of primers. 2. knowledge of the complete nucleotide sequence of the fragment to be ...
Platform Partition in Translational Medicine Data
... Hogg M, Grujic ZM, Baker M, Demirci S, Guillozet AL, Sweet AP, et al. The L266V tau mutation is associated with frontotemporal dementia and Picklike 3R and 4R tauopathy. Acta Neuropathol (Berl). 2003;106(4):323-36 http://myhealth-guide.org/glioblastoma-multiforme-pathology-andpictures/613 ...
... Hogg M, Grujic ZM, Baker M, Demirci S, Guillozet AL, Sweet AP, et al. The L266V tau mutation is associated with frontotemporal dementia and Picklike 3R and 4R tauopathy. Acta Neuropathol (Berl). 2003;106(4):323-36 http://myhealth-guide.org/glioblastoma-multiforme-pathology-andpictures/613 ...
Mutations File
... – Haemoglobin is a globular protein made from four polypeptide chains, each of which has an iron containing haem group. – There are two α and two β polypeptides. ...
... – Haemoglobin is a globular protein made from four polypeptide chains, each of which has an iron containing haem group. – There are two α and two β polypeptides. ...
TRASK Zool 3200: Cell Biology Exam 2
... mutant tRNA with an asparagine amino acid, it is unable to do so. When the ribosome encounters an AAC codon, what happens to the polypeptide that is being synthesized? (1 point) a.) Because an amino acid is not attached to the tRNA, the ribosome ‘skips over’ the AAC codon and simply creates a pep ...
... mutant tRNA with an asparagine amino acid, it is unable to do so. When the ribosome encounters an AAC codon, what happens to the polypeptide that is being synthesized? (1 point) a.) Because an amino acid is not attached to the tRNA, the ribosome ‘skips over’ the AAC codon and simply creates a pep ...
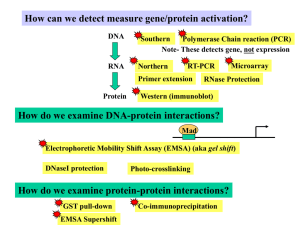
Techniques
... 2. ___________- Detect RNA 3. ___________- Detect RNA of ____ of expressed genes 4. ________ ( Reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction- to detect RNA) 5. ________________________ Detect protein 6. _______________- Detect proteins in situ 7. _________- protein-DNA interactions 8. ________– Pr ...
... 2. ___________- Detect RNA 3. ___________- Detect RNA of ____ of expressed genes 4. ________ ( Reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction- to detect RNA) 5. ________________________ Detect protein 6. _______________- Detect proteins in situ 7. _________- protein-DNA interactions 8. ________– Pr ...
Macromolecules
... Name 3 examples of foods that contain these organic molecules, 1 being high in starch. What % of your food is sugar per package? What is the organic molecule made of the subunits amino acids? Name one organism that contains a high percentage of protein. What % of your food is protein per package? Wh ...
... Name 3 examples of foods that contain these organic molecules, 1 being high in starch. What % of your food is sugar per package? What is the organic molecule made of the subunits amino acids? Name one organism that contains a high percentage of protein. What % of your food is protein per package? Wh ...
Nucleic acid analogue
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research.Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pucker-shaped pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases.An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix).Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic acid (LNA), as well as glycol nucleic acid (GNA) and threose nucleic acid (TNA). Each of these is distinguished from naturally occurring DNA or RNA by changes to the backbone of the molecule.In May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA, and by including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, were able to passage the bacteria 24 times; they did not create mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides. The artificial nucleotides featured 2 fused aromatic rings.