Extracting DNA from cheek cells
... • After 5 minutes DNA should have precipitated at the interface between the lysis buffer and the alcohol • Swirling so that a vortex forms can aid precipitation • Do not shake or invert the tube ...
... • After 5 minutes DNA should have precipitated at the interface between the lysis buffer and the alcohol • Swirling so that a vortex forms can aid precipitation • Do not shake or invert the tube ...
Organic Chemistry DEFINE the following Vocabulary: Adhesion
... Nucleotides are monomers that consist of pentose (the hexagon shape in the diagram) attached to a phosphate group (in red on diagram) and nitrogen base (in blue on diagram) Class Energy Lipids membranes transport Nucleic acids ...
... Nucleotides are monomers that consist of pentose (the hexagon shape in the diagram) attached to a phosphate group (in red on diagram) and nitrogen base (in blue on diagram) Class Energy Lipids membranes transport Nucleic acids ...
Pfu DNA Polymerase - G
... has superior thermostability and proofreading properties compared to the other thermostable polymerase. Its molecular weight is 90 kD. It can amplify DNA target up to 2kb. The elongation velocity is 0.2~0.4kb/min (70~75°C). Pfu DNA polymerase possesses 3' to 5' exonuclease proofreading activity that ...
... has superior thermostability and proofreading properties compared to the other thermostable polymerase. Its molecular weight is 90 kD. It can amplify DNA target up to 2kb. The elongation velocity is 0.2~0.4kb/min (70~75°C). Pfu DNA polymerase possesses 3' to 5' exonuclease proofreading activity that ...
Questions 33-38
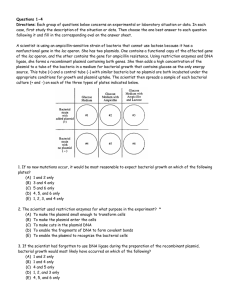
... Directions: Each group of questions below concerns an experimental or laboratory situation or data. In each case, first study the description of the situation or data. Then choose the one best answer to each question following it and fill in the corresponding oval on the answer sheet. A scientist is ...
... Directions: Each group of questions below concerns an experimental or laboratory situation or data. In each case, first study the description of the situation or data. Then choose the one best answer to each question following it and fill in the corresponding oval on the answer sheet. A scientist is ...
TRANSCRIPTOMICS
... The National Human Genome Research Institute (NHGRI) launched a public research consortium named ENCODE the Encyclopedia Of DNA Elements in September 2003 to carry consortium named ENCODE, the Encyclopedia Of DNA Elements, in September 2003, to carry out a project to identify all functional eleme ...
... The National Human Genome Research Institute (NHGRI) launched a public research consortium named ENCODE the Encyclopedia Of DNA Elements in September 2003 to carry consortium named ENCODE, the Encyclopedia Of DNA Elements, in September 2003, to carry out a project to identify all functional eleme ...
DNA sequences at the beginning of genes—at least in
... how they flag a small set of genes for transcription midblastula transition," says Kai Chen, PhD, a former graduate student in Zeitlinger's lab and the before that, holds important information about normal development and disease in animals and in study's first author. "We expected to see widespread ...
... how they flag a small set of genes for transcription midblastula transition," says Kai Chen, PhD, a former graduate student in Zeitlinger's lab and the before that, holds important information about normal development and disease in animals and in study's first author. "We expected to see widespread ...
10 CODON ANTI- CODON CYTOPLASM RIBOSOME tRNA AMINO
... Coded amino acids in correct order: MET (start) PHE ASP LEU 8. Define the term “mutation” in relation to DNA. A mutation is a change in the DNA sequence. This may result in a change to the mRNA sequence, which could cause a change in the protein and trait. 9. Describe a point mutation. Does it alway ...
... Coded amino acids in correct order: MET (start) PHE ASP LEU 8. Define the term “mutation” in relation to DNA. A mutation is a change in the DNA sequence. This may result in a change to the mRNA sequence, which could cause a change in the protein and trait. 9. Describe a point mutation. Does it alway ...
Summary - EUR RePub
... Summary RNA polymerase II mainly transcribes protein-encoding genes, and the transcriptional activity of many of those genes is tightly regulated. Two cooperating components are key in regulating RNAP II transcription. One component acts in cis and requires an element that is located on the same DNA ...
... Summary RNA polymerase II mainly transcribes protein-encoding genes, and the transcriptional activity of many of those genes is tightly regulated. Two cooperating components are key in regulating RNAP II transcription. One component acts in cis and requires an element that is located on the same DNA ...
single cells
... FISH is a cytogenetic technique that uses fluorescent probes that bind to only those parts of the chromosome with a high degree of sequence complementarity. It was developed by biomedical researchers in the early 1980s and is used for detecting RNA (mRNA, long non-coding RNA and miRNA) or DNA sequen ...
... FISH is a cytogenetic technique that uses fluorescent probes that bind to only those parts of the chromosome with a high degree of sequence complementarity. It was developed by biomedical researchers in the early 1980s and is used for detecting RNA (mRNA, long non-coding RNA and miRNA) or DNA sequen ...
ods of time, until activated b), a activated, the I`irtrl DNA hiiacks the
... polynucleotides is enormous. Looking more closely at our polynucleotide, we see in the center of Figure 10.2A that each nucleotide consists of threq co.mpenents: a nitrogenous base (in DNA, A, C, T, or G), a sugar (blue), and a phosphate group (yellow). The nucleotides are joined to one another by c ...
... polynucleotides is enormous. Looking more closely at our polynucleotide, we see in the center of Figure 10.2A that each nucleotide consists of threq co.mpenents: a nitrogenous base (in DNA, A, C, T, or G), a sugar (blue), and a phosphate group (yellow). The nucleotides are joined to one another by c ...
Biol120 Mock Final Examination
... a) DNA uses cytosine, guanine, uracil, and adenine; whereas RNA uses cytosine, thymine, guanine, and adenine b) DNA has no free hydroxyl group on the 2’ carbon and RNA has a free hydroxyl group on the 2’ carbon c) DNA is usually single-stranded and RNA is usually double-stranded d) None of the above ...
... a) DNA uses cytosine, guanine, uracil, and adenine; whereas RNA uses cytosine, thymine, guanine, and adenine b) DNA has no free hydroxyl group on the 2’ carbon and RNA has a free hydroxyl group on the 2’ carbon c) DNA is usually single-stranded and RNA is usually double-stranded d) None of the above ...
Nerve activates contraction
... •When is the gene active (on or off)? That is what protein is made? How can you control this? • Gene expression control = which genes are “on” • Levels of control – • 1) chromatin (DNA) packing and chromatin modification change access sites on DNA for RNA Polymerase so that its binding decreases/inc ...
... •When is the gene active (on or off)? That is what protein is made? How can you control this? • Gene expression control = which genes are “on” • Levels of control – • 1) chromatin (DNA) packing and chromatin modification change access sites on DNA for RNA Polymerase so that its binding decreases/inc ...
The human genome - The Galton Institute
... • Alternative splicing (average 6.3 splice isoforms per gene) • Using alternative promoters (70,292 promoter-like sequences in the genome) ...
... • Alternative splicing (average 6.3 splice isoforms per gene) • Using alternative promoters (70,292 promoter-like sequences in the genome) ...
Lecture#22 - Cloning DNA and the construction of clone libraries
... Various vectors have different size foreign DNA inserts Vectors 1) Plasmids - small circular DNA vectors - can clone 0-10 Kb fragments - easily transformed into cell 2) Lambda phage - linear DNA vector - can clone 15-20 Kb fragments - uses lambda in vitro packaging system to put recombinant DNA into ...
... Various vectors have different size foreign DNA inserts Vectors 1) Plasmids - small circular DNA vectors - can clone 0-10 Kb fragments - easily transformed into cell 2) Lambda phage - linear DNA vector - can clone 15-20 Kb fragments - uses lambda in vitro packaging system to put recombinant DNA into ...
Test 2
... The DnaB then serves as the start of the DNA polymerase complex that will include DNA gyrase and primase a well as DNA polymerase, but that is considered part of the elongation step This process only occurs once in the cell’s life cycle. Overall polymerase reaction includes 3'-5' proofreading so the ...
... The DnaB then serves as the start of the DNA polymerase complex that will include DNA gyrase and primase a well as DNA polymerase, but that is considered part of the elongation step This process only occurs once in the cell’s life cycle. Overall polymerase reaction includes 3'-5' proofreading so the ...
Genomic research concepts and application
... proposed in 1977 by Frederick Sanger, who is the only chemist to have received two Nobel Prizes in Chemistry, the first as the sole recipient in 1958 for his work as the first to sequence a protein, the sequencing of insulin; and the second in 1980, shared with Paul Berg and Walter Gilbert, for ...
... proposed in 1977 by Frederick Sanger, who is the only chemist to have received two Nobel Prizes in Chemistry, the first as the sole recipient in 1958 for his work as the first to sequence a protein, the sequencing of insulin; and the second in 1980, shared with Paul Berg and Walter Gilbert, for ...
Lab 4 Isolation of Total RNA from C. elegans
... only one of many mRNAs in the cells of a worm. 2. The absolute amount of Xbp1 mRNA in a worm is extremely small. Therefore, in order to achieve our goal we must be able to “select” Xbp-1 mRNA from the general population of mRNAs and employ an extremely sensitive means for detecting it. The approach ...
... only one of many mRNAs in the cells of a worm. 2. The absolute amount of Xbp1 mRNA in a worm is extremely small. Therefore, in order to achieve our goal we must be able to “select” Xbp-1 mRNA from the general population of mRNAs and employ an extremely sensitive means for detecting it. The approach ...
Examples - Cloudfront.net
... • When water evaporates, large amounts of heat ___________ are used to break the bonds which results in a large ___________ effect. cooling – Ex. Sweating (water acts as a coolant) ...
... • When water evaporates, large amounts of heat ___________ are used to break the bonds which results in a large ___________ effect. cooling – Ex. Sweating (water acts as a coolant) ...
USMLE Step 1 Web Prep — Transcription and RNA Processing: Part
... transcript prior to transport out of the nucleus. At the 5’ end of the intron is an equally important GT (GU in RNA) sequence that is also necessary for splicing (splice donor site). Capping (choice A) occurs almost immediately after synthesis of the first 30 nucleotides or so. The triphosphate of ...
... transcript prior to transport out of the nucleus. At the 5’ end of the intron is an equally important GT (GU in RNA) sequence that is also necessary for splicing (splice donor site). Capping (choice A) occurs almost immediately after synthesis of the first 30 nucleotides or so. The triphosphate of ...
Big, strong, fast, and aggressive
... with hormones to increase milk production • Pigs – produce more lean meat or high levels of healthy omega-3 acids • Salmon – faster growth to produce more fish • Scientists in Canada combined spider genes ...
... with hormones to increase milk production • Pigs – produce more lean meat or high levels of healthy omega-3 acids • Salmon – faster growth to produce more fish • Scientists in Canada combined spider genes ...
Map of the Human β-Globin Gene – In Brief
... 2. What does the black sequence represent? [complementary strand of DNA] a. How does the black sequence compare with the red sequence? 3. What do the three blue strands represent? [3 forward reading frames] 4. Why are there three blue strands? [Genetic code is a triplet code – so you can begin readi ...
... 2. What does the black sequence represent? [complementary strand of DNA] a. How does the black sequence compare with the red sequence? 3. What do the three blue strands represent? [3 forward reading frames] 4. Why are there three blue strands? [Genetic code is a triplet code – so you can begin readi ...
mutations
... archaebacterial, and eukaryotic sequences. indicate the four clusters where RifR mutations have been identified in E. coli. Mutations that confer RifR in E. coli and M. tuberculosis are indicated directly above (for E. coli) or below (for M. tuberculosis) as follows: D for deletions, V for insertion ...
... archaebacterial, and eukaryotic sequences. indicate the four clusters where RifR mutations have been identified in E. coli. Mutations that confer RifR in E. coli and M. tuberculosis are indicated directly above (for E. coli) or below (for M. tuberculosis) as follows: D for deletions, V for insertion ...
Nucleic acid analogue
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research.Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pucker-shaped pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases.An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix).Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic acid (LNA), as well as glycol nucleic acid (GNA) and threose nucleic acid (TNA). Each of these is distinguished from naturally occurring DNA or RNA by changes to the backbone of the molecule.In May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA, and by including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, were able to passage the bacteria 24 times; they did not create mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides. The artificial nucleotides featured 2 fused aromatic rings.