PoL2e Ch03 Lecture-Nucleic Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes
... Proteins interact with other molecules. R groups on the surface may form weak interactions (e.g., hydrogen bonds) with groups on the surface of another molecule. This can change the tertiary structure and thus the shape of the protein. Protein structure can also be modified by covalent bonding of a ...
... Proteins interact with other molecules. R groups on the surface may form weak interactions (e.g., hydrogen bonds) with groups on the surface of another molecule. This can change the tertiary structure and thus the shape of the protein. Protein structure can also be modified by covalent bonding of a ...
Biotoxins
... Deliberate formation of recombinant DNA containing genes for the biosynthesis of toxin molecules lethal for vertebrates at an LD50 of less than 100 nanograms per kilogram body weight (e.g., microbial toxins such as the botulinum toxins, tetanus toxin, diphtheria toxin, and Shigella dysenteriae neuro ...
... Deliberate formation of recombinant DNA containing genes for the biosynthesis of toxin molecules lethal for vertebrates at an LD50 of less than 100 nanograms per kilogram body weight (e.g., microbial toxins such as the botulinum toxins, tetanus toxin, diphtheria toxin, and Shigella dysenteriae neuro ...
Sample Exam 2
... ATP for the complete catabolism of a single molecule of glucose. a. 2 of 34 b. 4 of 34 c. 19 of 38 d. 34 of 38 e. 30 of 34 38. The first enzyme complex of the electron transport chain converts hydrogen atoms into ______ and ______. a. a proton, an electron b. a proton, a neutron c. an electron, wate ...
... ATP for the complete catabolism of a single molecule of glucose. a. 2 of 34 b. 4 of 34 c. 19 of 38 d. 34 of 38 e. 30 of 34 38. The first enzyme complex of the electron transport chain converts hydrogen atoms into ______ and ______. a. a proton, an electron b. a proton, a neutron c. an electron, wate ...
(mRNA). - canesbio
... • The discovery of ribozymes rendered obsolete the belief that all biological catalysts were proteins. ...
... • The discovery of ribozymes rendered obsolete the belief that all biological catalysts were proteins. ...
Amino Acids of the Sulfolobus solfataricus Mini-chromosome
... 194 and at histidine 146 to alanine by PCR-based mutagenesis of the corresponding gene (30). The synthetic oligonucleotides used to create the site-directed mutant proteins are available on request. The amplification products were subcloned back into the SsoMCM-pET19b vector and sequenced to check i ...
... 194 and at histidine 146 to alanine by PCR-based mutagenesis of the corresponding gene (30). The synthetic oligonucleotides used to create the site-directed mutant proteins are available on request. The amplification products were subcloned back into the SsoMCM-pET19b vector and sequenced to check i ...
Access Slides
... Structure of RNAPII and interaction of the enzyme with promoter DNA. This schematic representation of the polymerase (shown in orange) emphasizes the way in which the clamp and wall domains restrict access to the active site. Subunits Rpb4 and Rpb7 form a complex (shown in blue) that can dissociate ...
... Structure of RNAPII and interaction of the enzyme with promoter DNA. This schematic representation of the polymerase (shown in orange) emphasizes the way in which the clamp and wall domains restrict access to the active site. Subunits Rpb4 and Rpb7 form a complex (shown in blue) that can dissociate ...
Sequence Alignment Introduction
... In modern taxonomic practice, scientists routinely analyze the DNA from specimens they collect to obtain a “DNA barcode,” a short DNA sequence unique to a particular species, which is used to identify the species it belongs to. For animals and many other eukaryotes, different genes have been used ...
... In modern taxonomic practice, scientists routinely analyze the DNA from specimens they collect to obtain a “DNA barcode,” a short DNA sequence unique to a particular species, which is used to identify the species it belongs to. For animals and many other eukaryotes, different genes have been used ...
Demo notes update - UK Association for Science and Discovery
... Samples 1 and 2 should be the same as A and B whereas both 3 and 4 have an additional band. Explain that new M types can potentially emerge at any time and that they can be linked with new characteristics such as antibiotic resistance (although these may not be directly linked to a change in the em ...
... Samples 1 and 2 should be the same as A and B whereas both 3 and 4 have an additional band. Explain that new M types can potentially emerge at any time and that they can be linked with new characteristics such as antibiotic resistance (although these may not be directly linked to a change in the em ...
DNA Sequencing
... • Most methods for cloning pieces of DNA in the laboratory share general features, such as the use of bacteria and their plasmids. • Plasmids are small circular DNA molecules that replicate separately from the bacterial chromosome. • Cloned genes are useful for making copies of a particular gene and ...
... • Most methods for cloning pieces of DNA in the laboratory share general features, such as the use of bacteria and their plasmids. • Plasmids are small circular DNA molecules that replicate separately from the bacterial chromosome. • Cloned genes are useful for making copies of a particular gene and ...
Introduction
... one polypeptide chain(a-helical and b-sheet structure) Tertiary structure: Ionic interaction, hydrophobic interaction, hydrogen bonding and Van der Waals attraction formed among moieties within one polypeptide chain Quaternary structure: Weak chemical interactions among different polypeptide chains ...
... one polypeptide chain(a-helical and b-sheet structure) Tertiary structure: Ionic interaction, hydrophobic interaction, hydrogen bonding and Van der Waals attraction formed among moieties within one polypeptide chain Quaternary structure: Weak chemical interactions among different polypeptide chains ...
Chapter 14 Proteins
... ◦ Peptide: A short polymer of amino acids joined by peptide bonds; they are classified by the number of amino acids in the chain. ◦ Dipeptide: A molecule containing two amino acids joined by a peptide bond. ◦ Tripeptide: A molecule containing three amino acids joined by peptide bonds. ◦ Polypeptide: ...
... ◦ Peptide: A short polymer of amino acids joined by peptide bonds; they are classified by the number of amino acids in the chain. ◦ Dipeptide: A molecule containing two amino acids joined by a peptide bond. ◦ Tripeptide: A molecule containing three amino acids joined by peptide bonds. ◦ Polypeptide: ...
Chapter 1
... Lipids, the third type of biopolymer, are not very soluble in water, and can form membrane-like structures if mixed with water. Usually the lipids will form film layers, but fatty acids (hydrocarbons with a carboxyl-group, COOH, on one end) will spontaneously form vesicles in water: multiple molecul ...
... Lipids, the third type of biopolymer, are not very soluble in water, and can form membrane-like structures if mixed with water. Usually the lipids will form film layers, but fatty acids (hydrocarbons with a carboxyl-group, COOH, on one end) will spontaneously form vesicles in water: multiple molecul ...
Summer Internship project
... Development of RNA as a proxy for microbial abundance in the Columbia River Ecosystem ...
... Development of RNA as a proxy for microbial abundance in the Columbia River Ecosystem ...
Lab Stn #1 Unit 5 DNA to Protein
... In transcription, DNA bases are paired with complementary RNA bases according to the base-pairing rules: C-G and A-U. The enzyme RNA polymerase catalyzes this reaction using ATP. The number of DNA base-pairs is determined by the number of amino acids in the resulting polypeptide. The length of DNA c ...
... In transcription, DNA bases are paired with complementary RNA bases according to the base-pairing rules: C-G and A-U. The enzyme RNA polymerase catalyzes this reaction using ATP. The number of DNA base-pairs is determined by the number of amino acids in the resulting polypeptide. The length of DNA c ...
fingerprint - West Essex Regional School District
... murders. A trail of DNA leaving the crime scene was consistent with O.J’s profile, as was the DNA found entering Simpson’s home. Simpson’s DNA profile was found in the Bronco along with that of both victims. The glove contained the DNA profiles of Nicole and Ron, and the sock had Nicole’s DNA profil ...
... murders. A trail of DNA leaving the crime scene was consistent with O.J’s profile, as was the DNA found entering Simpson’s home. Simpson’s DNA profile was found in the Bronco along with that of both victims. The glove contained the DNA profiles of Nicole and Ron, and the sock had Nicole’s DNA profil ...
Mutations - Fulton County Schools
... structure of genetic material of an organism Mutations can be in DNA or can be chromosomal Mutations can happen more than once in a sequence [and typically do] Causes: mutagens – radiation or chemical substances that increase the rate of mutations ...
... structure of genetic material of an organism Mutations can be in DNA or can be chromosomal Mutations can happen more than once in a sequence [and typically do] Causes: mutagens – radiation or chemical substances that increase the rate of mutations ...
cha2
... Basic Gene Grammars and DNA-ChartParser for language processing of Escherichia coli promoter DNA sequences ...
... Basic Gene Grammars and DNA-ChartParser for language processing of Escherichia coli promoter DNA sequences ...
Array comparative genomic hybridization (array
... In principle, both karyotyping and arrays are genome-wide technologies which can be used to assess the presence of genomic imbalance such as CNVs. Although they may look like very different technologies, the primary difference between them is in the resolution, which is a measure of the level of mag ...
... In principle, both karyotyping and arrays are genome-wide technologies which can be used to assess the presence of genomic imbalance such as CNVs. Although they may look like very different technologies, the primary difference between them is in the resolution, which is a measure of the level of mag ...
Exam 3
... 5. Add a radioactive secondary antibody that binds to the primary antibody in step 4. 6. Detect the radioactive spot using autoradiography (exposing a piece of X-ray film). 7. Pick the colony that corresponds to the radioactive spot. 8. Inoculate fresh media with the colony. The bacteria will grow, ...
... 5. Add a radioactive secondary antibody that binds to the primary antibody in step 4. 6. Detect the radioactive spot using autoradiography (exposing a piece of X-ray film). 7. Pick the colony that corresponds to the radioactive spot. 8. Inoculate fresh media with the colony. The bacteria will grow, ...
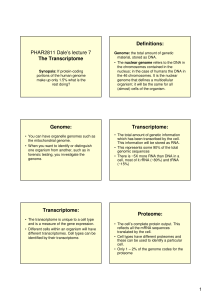
PHAR2811 Dale`s lecture 7 The Transcriptome Definitions: Genome
... • It was this enzyme that led scientists to the discovery of ribozymes; the RNA species capable of catalytic activity. ...
... • It was this enzyme that led scientists to the discovery of ribozymes; the RNA species capable of catalytic activity. ...
humanbiolecture2
... •Smooth endoplasmic reticulum functions in different ways - as storage containers for ions, sites of detoxification, sites of lipid synthesis or break-down, depending on the cell’s needs •Metabolism – the chemical reactions in the organism, either anabolism where ...
... •Smooth endoplasmic reticulum functions in different ways - as storage containers for ions, sites of detoxification, sites of lipid synthesis or break-down, depending on the cell’s needs •Metabolism – the chemical reactions in the organism, either anabolism where ...
Nucleic acid analogue
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research.Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pucker-shaped pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases.An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix).Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic acid (LNA), as well as glycol nucleic acid (GNA) and threose nucleic acid (TNA). Each of these is distinguished from naturally occurring DNA or RNA by changes to the backbone of the molecule.In May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA, and by including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, were able to passage the bacteria 24 times; they did not create mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides. The artificial nucleotides featured 2 fused aromatic rings.