"Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)". In: Encyclopedia of Life Sciences
... This technique involves using RNA rather than DNA as the template for amplification. The procedure is very similar to conventional PCR but includes an initial step in which a DNA copy of the RNA template is produced using the enzyme reverse transcriptase. This enzyme, which is of viral origin, is a ...
... This technique involves using RNA rather than DNA as the template for amplification. The procedure is very similar to conventional PCR but includes an initial step in which a DNA copy of the RNA template is produced using the enzyme reverse transcriptase. This enzyme, which is of viral origin, is a ...
AB Balance Lecture 1_2015
... • It can act as a proton donor (an acid) • It can act as a proton acceptor (a base) • Plays a considerable role in acid-base balance ...
... • It can act as a proton donor (an acid) • It can act as a proton acceptor (a base) • Plays a considerable role in acid-base balance ...
The origin of the RNA world: Co-evolution of genes and metabolism
... doi:10.1016/j.bioorg.2007.08.001 ...
... doi:10.1016/j.bioorg.2007.08.001 ...
book ppt - Castle High School
... Ancient DNA is usually destroyed—but can still be studied in samples found frozen or from the interior of bones. The PCR reaction is used to amplify tiny amounts of DNA. DNA from Neanderthals has been sequenced and is over 99% identical to our human DNA. ...
... Ancient DNA is usually destroyed—but can still be studied in samples found frozen or from the interior of bones. The PCR reaction is used to amplify tiny amounts of DNA. DNA from Neanderthals has been sequenced and is over 99% identical to our human DNA. ...
o How is covariation used in RNA structure
... b. ____ The process by which information in RNA is used to make proteins is called translation. c. ____ The process in which information in DNA is copied into RNA is called transcription. d. ____ Peptide bonds are both planar and flexible. e. ____ Enzymes that catalyze reactions in the cell are alwa ...
... b. ____ The process by which information in RNA is used to make proteins is called translation. c. ____ The process in which information in DNA is copied into RNA is called transcription. d. ____ Peptide bonds are both planar and flexible. e. ____ Enzymes that catalyze reactions in the cell are alwa ...
PowerPoint 演示文稿
... Viroids are small, circular, single-stranded RNA molecules that are the smallest known pathogens. The extracellular form of the viroid is naked RNA-there is no capsid of any kind. Even more interestingly, the RNA molecule contains no protein-encoding genes, and therefore the viroid is totally depend ...
... Viroids are small, circular, single-stranded RNA molecules that are the smallest known pathogens. The extracellular form of the viroid is naked RNA-there is no capsid of any kind. Even more interestingly, the RNA molecule contains no protein-encoding genes, and therefore the viroid is totally depend ...
Nerve activates contraction
... • Because of different details between prokaryotes and eukaryotes, inducing a cloned eukaryotic gene to function in a prokaryotic host can be difficult. • One way around this is to employ an expression vector, a cloning vector containing the requisite prokaryotic promotor upstream of the restrictio ...
... • Because of different details between prokaryotes and eukaryotes, inducing a cloned eukaryotic gene to function in a prokaryotic host can be difficult. • One way around this is to employ an expression vector, a cloning vector containing the requisite prokaryotic promotor upstream of the restrictio ...
Section A: DNA Cloning CHAPTER 20 DNA TECHNOLOGY AND
... • A more limited kind of gene library can be developed from complementary DNA. • During the process of producing cDNA, all mRNAs are converted to cDNA strands. • This cDNA library represents that part of a cell’s genome that was transcribed in the starting cells. • This is an advantage if a researc ...
... • A more limited kind of gene library can be developed from complementary DNA. • During the process of producing cDNA, all mRNAs are converted to cDNA strands. • This cDNA library represents that part of a cell’s genome that was transcribed in the starting cells. • This is an advantage if a researc ...
A Mad Scientist`s Chemistry Presentation
... • If the sugar is deoxyribose, then the nucleic acid is called deoxyribonucleic acid, or DNA. • If the sugar is ribose, then the nucleic acid is called ribonucleic acid, or RNA. ...
... • If the sugar is deoxyribose, then the nucleic acid is called deoxyribonucleic acid, or DNA. • If the sugar is ribose, then the nucleic acid is called ribonucleic acid, or RNA. ...
Quantification of transcription factor binding in cell extracts using an
... Hz. Initial experiments were performed at frequencies ranging from 10 Hz to 2000 Hz, and optimal signal change upon protein binding was seen at 60 Hz. Non-optimal sensor designs: Several additional conformation-switching variant structures were investigated for their ability to form an electrochemic ...
... Hz. Initial experiments were performed at frequencies ranging from 10 Hz to 2000 Hz, and optimal signal change upon protein binding was seen at 60 Hz. Non-optimal sensor designs: Several additional conformation-switching variant structures were investigated for their ability to form an electrochemic ...
Chapter 15 The Techniques of Molecular Genetics
... PCR because it is heat-stable. Taq polymerase lacks proofreading activity, so errors are introduced into the amplified DNA at low but significant frequencies. – When high fidelity is required, heat-stable polymerases with proofreading activity are used (Pfu or Tli). ...
... PCR because it is heat-stable. Taq polymerase lacks proofreading activity, so errors are introduced into the amplified DNA at low but significant frequencies. – When high fidelity is required, heat-stable polymerases with proofreading activity are used (Pfu or Tli). ...
Interaction of a Nuclear Protein with 5` Flanking Region of
... four classes: alpha zein (sulphur-poor), and beta-, gamma-, and delta-zein (all sulphur-rich). The expression of genes encoding the four zein classes is coordinately regulated during endosperm development (Larkins et af., 1989). The opaque-2 mutation causes a significant reduction in the transcripti ...
... four classes: alpha zein (sulphur-poor), and beta-, gamma-, and delta-zein (all sulphur-rich). The expression of genes encoding the four zein classes is coordinately regulated during endosperm development (Larkins et af., 1989). The opaque-2 mutation causes a significant reduction in the transcripti ...
build-a-bug 1
... Build-A-Bug Protein Synthesis Activity Part I: Your bug’s DNA codes for proteins, which are made of amino acids. The proteins made by your bug’s cells determine your bug’s traits. Use the mRNA codon chart and your knowledge of transcription and translation to complete the chart below. Part 2: Once y ...
... Build-A-Bug Protein Synthesis Activity Part I: Your bug’s DNA codes for proteins, which are made of amino acids. The proteins made by your bug’s cells determine your bug’s traits. Use the mRNA codon chart and your knowledge of transcription and translation to complete the chart below. Part 2: Once y ...
video slide - Manchester Township School District
... • DNA technology has revolutionized biotechnology, the manipulation of organisms or their genetic components to make useful products • An example of DNA technology is the microarray, a measurement of gene expression of thousands of different genes ...
... • DNA technology has revolutionized biotechnology, the manipulation of organisms or their genetic components to make useful products • An example of DNA technology is the microarray, a measurement of gene expression of thousands of different genes ...
U4Word
... 1) Nucleosome core particle: 146 bp of ds DNA is wrapped around a histone octamer, which consists of 2 each of H2A, H2B, H3, H4; the octamer is an eight subunit protein, about 100 Å in diameter. A tetramer, (H3)2(H4)2 forms a central disk with a H2A-H2B dimer above and below. 2) A segment of DNA, 8 ...
... 1) Nucleosome core particle: 146 bp of ds DNA is wrapped around a histone octamer, which consists of 2 each of H2A, H2B, H3, H4; the octamer is an eight subunit protein, about 100 Å in diameter. A tetramer, (H3)2(H4)2 forms a central disk with a H2A-H2B dimer above and below. 2) A segment of DNA, 8 ...
Structure of B-DNA with Cations Tethered in the Major Groove†
... geometry. These distortions are inferred by comparing DDD4+ with native DDD structures. Here, we compare DDD4+ with a series of DDD structures determined from crystals obtained in the presence of various cations, in our laboratory. The members of this ensemble were determined independently and give ...
... geometry. These distortions are inferred by comparing DDD4+ with native DDD structures. Here, we compare DDD4+ with a series of DDD structures determined from crystals obtained in the presence of various cations, in our laboratory. The members of this ensemble were determined independently and give ...
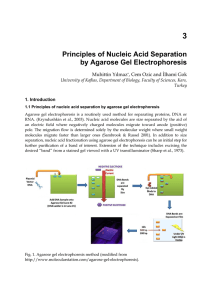
Principles of Nucleic Acid Separation by Agarose Gel Electrophoresis
... Fig. 3. Schematic illustration of a typical horizontal gel electrophoresis setup for the separation of nucleic acids. The two buffers vary according to the advantages and disadvantages. For instance, Borate has disadvantages as it polymerizes and/or interacts with cis diols found in RNA. TAE on the ...
... Fig. 3. Schematic illustration of a typical horizontal gel electrophoresis setup for the separation of nucleic acids. The two buffers vary according to the advantages and disadvantages. For instance, Borate has disadvantages as it polymerizes and/or interacts with cis diols found in RNA. TAE on the ...
R–groups
... A. Primary Structure—the unique sequence of amino acids, type sequence and number; determines the other three structures It is held together by peptide bonds between the carboxyl group of one amino acid with the amino group of another amino acid B. Secondary Structure― regular repeated coiling and f ...
... A. Primary Structure—the unique sequence of amino acids, type sequence and number; determines the other three structures It is held together by peptide bonds between the carboxyl group of one amino acid with the amino group of another amino acid B. Secondary Structure― regular repeated coiling and f ...
Ninety-nine Point Nine Percent of the Time, Nature Uses the... Acids, and We Don’t Know Exactly Why
... existed have built themselves out of the same particular group of 20 amino acids. Why? Attempts to answer this question have often produced creative and daring hypotheses, from the high level mathematical analysis of the symmetry between amino acids and codons (Yang 2003) to a theoretical speculatio ...
... existed have built themselves out of the same particular group of 20 amino acids. Why? Attempts to answer this question have often produced creative and daring hypotheses, from the high level mathematical analysis of the symmetry between amino acids and codons (Yang 2003) to a theoretical speculatio ...
Mdr and xdr tuberculosis
... PCR reagents and host the PCR process. The Xpert MTB/RIF assay uses 3 specific primers and 5 unique molecular probes to ensure a high degree of specificity. Assay targets the rpoB gene, which is critical for identifying mutations associated with rifampicin resistance. ...
... PCR reagents and host the PCR process. The Xpert MTB/RIF assay uses 3 specific primers and 5 unique molecular probes to ensure a high degree of specificity. Assay targets the rpoB gene, which is critical for identifying mutations associated with rifampicin resistance. ...
Document
... Heredity: Transmission of characteristics from parents to offspring. Traits: The characteristics a person has. Example: Phenotype: PHYSICAL looks, or traits that we can see a person has. Example: Genotype: GENETIC makeup, the traits a persons DNA says they will have Example: ...
... Heredity: Transmission of characteristics from parents to offspring. Traits: The characteristics a person has. Example: Phenotype: PHYSICAL looks, or traits that we can see a person has. Example: Genotype: GENETIC makeup, the traits a persons DNA says they will have Example: ...
chapter 20 lo
... You should be able to use structures of amino acids and a pKa table to draw the step-wise ionization of any of the 20 standard amino acids. You should then be able to use the step-wise ionization to determine the charge an amino acid has at a particular pH. What is electrophoresis? You should be abl ...
... You should be able to use structures of amino acids and a pKa table to draw the step-wise ionization of any of the 20 standard amino acids. You should then be able to use the step-wise ionization to determine the charge an amino acid has at a particular pH. What is electrophoresis? You should be abl ...
Nucleic acid analogue
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research.Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pucker-shaped pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases.An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix).Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic acid (LNA), as well as glycol nucleic acid (GNA) and threose nucleic acid (TNA). Each of these is distinguished from naturally occurring DNA or RNA by changes to the backbone of the molecule.In May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA, and by including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, were able to passage the bacteria 24 times; they did not create mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides. The artificial nucleotides featured 2 fused aromatic rings.