RECOMBINATION IN BACTERIA Transfer of Genetic Material in
... module on bacterial gene regulation. In transformation, a cell surface receptor binds to DNA in the environment. After binding, the DNA is transported across the membrane by the transformation machinery. As this occurs, one strand of the DNA is digested away by an exonuclease, so that the DNA that e ...
... module on bacterial gene regulation. In transformation, a cell surface receptor binds to DNA in the environment. After binding, the DNA is transported across the membrane by the transformation machinery. As this occurs, one strand of the DNA is digested away by an exonuclease, so that the DNA that e ...
Imprinted green beards: a little less than kin and more than kind The
... one-quarter for genes of maternal grandmaternal origin but are unrelated for all ...
... one-quarter for genes of maternal grandmaternal origin but are unrelated for all ...
Knox. The Gene Genie.
... “The project really took off from there.” Scientists in both labs realized that Cas9 might be useful for genome editing, a type of genetic engineering that uses enzymes as molecular pruning shears. The enzymes, called nucleases, create breaks at specific sites in the double-stranded DNA helix; a cel ...
... “The project really took off from there.” Scientists in both labs realized that Cas9 might be useful for genome editing, a type of genetic engineering that uses enzymes as molecular pruning shears. The enzymes, called nucleases, create breaks at specific sites in the double-stranded DNA helix; a cel ...
Screening of SSR marker for sugar and sugar related traits
... sequences for the species of interest are unavailable, making them difficult to apply to unstudied groups. Although microsatellites are in principle codominant markers, mutations in the primer annealing sites may result in the occurrence of null alleles (no amplification of the intended PCR product) ...
... sequences for the species of interest are unavailable, making them difficult to apply to unstudied groups. Although microsatellites are in principle codominant markers, mutations in the primer annealing sites may result in the occurrence of null alleles (no amplification of the intended PCR product) ...
Perkins, D.D. and V.C. Pollard ... tablished and mapped since the 1982 comoendium
... was often observed and regeneration frequencies were low (frequency <1%). Increasing the molarity of buffering KCl from 0.6 M to 0.9 M in protoplasting and regeneration media did not, however, markedly improve protoplast regeneration. Protoplasts released by enzymatic digestion of hyphal "mats" vary ...
... was often observed and regeneration frequencies were low (frequency <1%). Increasing the molarity of buffering KCl from 0.6 M to 0.9 M in protoplasting and regeneration media did not, however, markedly improve protoplast regeneration. Protoplasts released by enzymatic digestion of hyphal "mats" vary ...
SOL Review Packet - Ms. Ottolini`s Biology Wiki!
... Vocabulary: break, join, amino acids, lowering, peptide, dipeptide, polypeptide, substrates, lock and key, speed up, activation energy, active site 1. Proteins are made of amino acids joined by peptide bonds. 2. Two amino acids joined is called a dipeptide. 3. Three or more amino acids joined is cal ...
... Vocabulary: break, join, amino acids, lowering, peptide, dipeptide, polypeptide, substrates, lock and key, speed up, activation energy, active site 1. Proteins are made of amino acids joined by peptide bonds. 2. Two amino acids joined is called a dipeptide. 3. Three or more amino acids joined is cal ...
Yellow Line Walk-through
... displaying a tree and another displaying sequence alignments. How many matches did the search yield? What is the relationship between the match and the query? b. Close all viewers and return to DNA Subway. Create a new project, this time querying rice with the Ping transposase Gene [ORF] as query. a ...
... displaying a tree and another displaying sequence alignments. How many matches did the search yield? What is the relationship between the match and the query? b. Close all viewers and return to DNA Subway. Create a new project, this time querying rice with the Ping transposase Gene [ORF] as query. a ...
BioTeke Corporation Technical Manual
... centrifuged. DNA binds to the silicified membrane while contaminants such as proteins and polysaccharides are efficiently removed by two-step wash. Purified DNA is eluted in a small volume of low ionic strength buffer or water. ...
... centrifuged. DNA binds to the silicified membrane while contaminants such as proteins and polysaccharides are efficiently removed by two-step wash. Purified DNA is eluted in a small volume of low ionic strength buffer or water. ...
RNA sequencing - Bioinformatics.ca
... • If you do remove them, assess duplicates at the level of paired-end reads (fragments) not single end reads • Strategies for flagging duplicates: • 1.) Sequence identity. Sequencing errors make reads appear different even if they were amplified from the same fragment. • 2.) Mapping coordinates. Fra ...
... • If you do remove them, assess duplicates at the level of paired-end reads (fragments) not single end reads • Strategies for flagging duplicates: • 1.) Sequence identity. Sequencing errors make reads appear different even if they were amplified from the same fragment. • 2.) Mapping coordinates. Fra ...
The sequence of the tms transcript 2 locus of the A. tumefaciens
... residue) that are 20 residues in length, the distance required to span a membrane ( 4 0 ) . Thus we conclude that the predicted transcript 2 protein is probably not an integral or transmembrane protein, but rather is a soluble protein. We also hoped to gain insight into the biochemistry and function ...
... residue) that are 20 residues in length, the distance required to span a membrane ( 4 0 ) . Thus we conclude that the predicted transcript 2 protein is probably not an integral or transmembrane protein, but rather is a soluble protein. We also hoped to gain insight into the biochemistry and function ...
AMINO ACID DEGRADATION
... • The C5 family glutamine, proline, arginine and hystidine are converted to alphaketaglutarate via glutamate. Alpha-ketoglutarate is the entry point for glutsamine, proline, arginine and hystidine that are first converted to glutam,ate. • Succinate CoA is an entry point for single apolar amino acids ...
... • The C5 family glutamine, proline, arginine and hystidine are converted to alphaketaglutarate via glutamate. Alpha-ketoglutarate is the entry point for glutsamine, proline, arginine and hystidine that are first converted to glutam,ate. • Succinate CoA is an entry point for single apolar amino acids ...
Cloning and characterization in Escherichia coli of the gene
... forms an operon with a methylase gene. The amino acid sequence of the putative methylase had motifs for adenine-speci¢c methylases, suggesting the possibility that the methylase could play a role in the control of promoter function of a gene(s) or regulation of translation by methylation of rRNA. In ...
... forms an operon with a methylase gene. The amino acid sequence of the putative methylase had motifs for adenine-speci¢c methylases, suggesting the possibility that the methylase could play a role in the control of promoter function of a gene(s) or regulation of translation by methylation of rRNA. In ...
Unit II Chemistry
... substance. Composed of two or more atoms held together by bonds. 12. Monomer-A molecule of any compound that can react with other molecules of the same or different compounds to form a polymer (group of three or more molecules bonded together). 13. Nucleic Acid-Macromolecule (DNA or RNA) composed of ...
... substance. Composed of two or more atoms held together by bonds. 12. Monomer-A molecule of any compound that can react with other molecules of the same or different compounds to form a polymer (group of three or more molecules bonded together). 13. Nucleic Acid-Macromolecule (DNA or RNA) composed of ...
Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry
... catalyze transfer of amino groups of amino acids to a-ketoglutarate ...
... catalyze transfer of amino groups of amino acids to a-ketoglutarate ...
chl - Govt College Aron
... • Chemical components:Chl. A, chl. B, Beta carotine, vialoxanthin, neoxanthin, plastoquinone a,b,c, vitamin k, phaspholipids, nitrogen, Mn, Fe, Cu etc. ...
... • Chemical components:Chl. A, chl. B, Beta carotine, vialoxanthin, neoxanthin, plastoquinone a,b,c, vitamin k, phaspholipids, nitrogen, Mn, Fe, Cu etc. ...
Chapter 1 Answer Key
... 21. The primary structure of a protein refers to the sequence of amino acids. Genes in DNA determine this sequence. 22.(a) The two types of secondary protein structure are α-helices and β-pleated sheets. (b) Hydrogen bonding stabilizes secondary protein structures. 23. The amino acid proline causes ...
... 21. The primary structure of a protein refers to the sequence of amino acids. Genes in DNA determine this sequence. 22.(a) The two types of secondary protein structure are α-helices and β-pleated sheets. (b) Hydrogen bonding stabilizes secondary protein structures. 23. The amino acid proline causes ...
Influenza virus
... characteristic for a particular virus. The capsomeres are made up of monomers called protomers. There may be similar or several types of protomers in the capsid.The protomers are connected to one another with the help of bonds. Protomers as well as capsomeres once exposed to ...
... characteristic for a particular virus. The capsomeres are made up of monomers called protomers. There may be similar or several types of protomers in the capsid.The protomers are connected to one another with the help of bonds. Protomers as well as capsomeres once exposed to ...
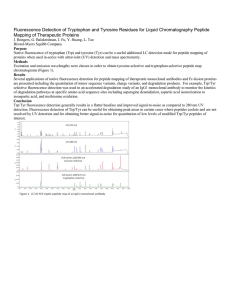
Fluorescence Detection of Tryptophan and Tyrosine Residues for
... Several applications of native fluorescence detection for peptide mapping of therapeutic monoclonal antibodies and Fc-fusion proteins are presented including the quantitation of minor sequence variants, charge variants, and degradation products. For example, Trp/Tyr selective fluorescence detection ...
... Several applications of native fluorescence detection for peptide mapping of therapeutic monoclonal antibodies and Fc-fusion proteins are presented including the quantitation of minor sequence variants, charge variants, and degradation products. For example, Trp/Tyr selective fluorescence detection ...
A Search for Genes Encoding Histidine
... We propose the following regulation mechanism. For brevity, we assume that the rate of leader peptide translation depends on histidine concentration. If it is deficient, the ribosome translating the leader peptide does not reach the stop codon and an RNA hairpin is formed to prevent initiation of st ...
... We propose the following regulation mechanism. For brevity, we assume that the rate of leader peptide translation depends on histidine concentration. If it is deficient, the ribosome translating the leader peptide does not reach the stop codon and an RNA hairpin is formed to prevent initiation of st ...
Chapter 14 Ionic and Covalent Compounds/ Organic compounds
... Nucleic acids are sometimes called the __________ of life, because they contain all the information needed for a cell to make all its proteins. -DNA and RNA There are two kinds of nucleic acids: ____ and _____. - DNA (____________ ________) is the genetic material of the cell. DNA molecules can stor ...
... Nucleic acids are sometimes called the __________ of life, because they contain all the information needed for a cell to make all its proteins. -DNA and RNA There are two kinds of nucleic acids: ____ and _____. - DNA (____________ ________) is the genetic material of the cell. DNA molecules can stor ...
Biological Modelling Gene Expression Data
... cDNA Microarrays • Lay down a full sequence of the gene – Typically 1000s of base pairs long. ...
... cDNA Microarrays • Lay down a full sequence of the gene – Typically 1000s of base pairs long. ...
Computationally Inspired Biotechnologies
... methods for DNA associative search with known BMC methods for solving the SAT problem. – Example: extended queries executed on: • Natural DNA strands (from blood or other tissues) • Appended with DNA words encoding binary information about each strand (e.g, the social security number of the person w ...
... methods for DNA associative search with known BMC methods for solving the SAT problem. – Example: extended queries executed on: • Natural DNA strands (from blood or other tissues) • Appended with DNA words encoding binary information about each strand (e.g, the social security number of the person w ...
Nucleic acid analogue
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research.Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pucker-shaped pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases.An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix).Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic acid (LNA), as well as glycol nucleic acid (GNA) and threose nucleic acid (TNA). Each of these is distinguished from naturally occurring DNA or RNA by changes to the backbone of the molecule.In May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA, and by including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, were able to passage the bacteria 24 times; they did not create mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides. The artificial nucleotides featured 2 fused aromatic rings.