Lisa Byers UNIT 6: Genetic Transformations Unit Plan
... Unifying concepts: Make biotechnology relevant to the students and tie in how it relates to the science they have already learned. Discover how scientific processes can be used for many different purposes. Visually seeing how DNA goes to RNA, which then is turned into a protein that is expressed a t ...
... Unifying concepts: Make biotechnology relevant to the students and tie in how it relates to the science they have already learned. Discover how scientific processes can be used for many different purposes. Visually seeing how DNA goes to RNA, which then is turned into a protein that is expressed a t ...
Proteins
... If a protein has more than 1 chain, they have a specific arrangement in relation to one another. ...
... If a protein has more than 1 chain, they have a specific arrangement in relation to one another. ...
Registration Forms Preview PDF
... Lentiviral Vectors: http://osp.od.nih.gov/sites/default/files/resources/Lenti_Containment_Guidance_0_0.pdf.), D-4 Experiments that involve the transfer of recombinant or synthetic nuc ...
... Lentiviral Vectors: http://osp.od.nih.gov/sites/default/files/resources/Lenti_Containment_Guidance_0_0.pdf.), D-4 Experiments that involve the transfer of recombinant or synthetic nuc ...
Biochemistry II, Test One
... E. Orotidylate is the common precursor in the biosynthesis of pyrimidines, and inosinate is the common precursor in the biosynthesis of the purines ATP and GTP. 10. In the laboratory, some E. coli cells have been grown with transcription inhibitors so that only replication could occur. You break ope ...
... E. Orotidylate is the common precursor in the biosynthesis of pyrimidines, and inosinate is the common precursor in the biosynthesis of the purines ATP and GTP. 10. In the laboratory, some E. coli cells have been grown with transcription inhibitors so that only replication could occur. You break ope ...
April 8
... suitable vector = DNA molecule with: • Origin of replication that functions in chosen host • “Selectable marker” = gene encoding protein allowing selection of hosts that have taken up the recombinant molecule • Cloning site = dispensable region where foreign DNA can be inserted ...
... suitable vector = DNA molecule with: • Origin of replication that functions in chosen host • “Selectable marker” = gene encoding protein allowing selection of hosts that have taken up the recombinant molecule • Cloning site = dispensable region where foreign DNA can be inserted ...
C8 Challenge
... Mutations in which one or a few nucleotide pairs are deleted or inserted in the DNA are ...
... Mutations in which one or a few nucleotide pairs are deleted or inserted in the DNA are ...
Methylation and demethylation of DNA and histones in
... the global chromatin architecture with regard to gene expression during the cell cycle and development. Methylation is the most complicated epigenetic modification. Unlike other changes, methylation alone affects both DNA and histones: methylation occurs primarily at the C5-cytosine and N6-adenosine ...
... the global chromatin architecture with regard to gene expression during the cell cycle and development. Methylation is the most complicated epigenetic modification. Unlike other changes, methylation alone affects both DNA and histones: methylation occurs primarily at the C5-cytosine and N6-adenosine ...
Amylase structural variants, Ashkenazi trio, SV calls
... assemblies of individuals for detecting and interpreting the many types of structural variation that are refractory to highthroughput or short-read technologies. Using a single-molecule genome analysis system, the Irys® System, we produced high resolution genome maps that were assembled de novo. The ...
... assemblies of individuals for detecting and interpreting the many types of structural variation that are refractory to highthroughput or short-read technologies. Using a single-molecule genome analysis system, the Irys® System, we produced high resolution genome maps that were assembled de novo. The ...
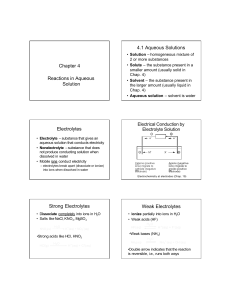
Chapter 4 Reactions in Aqueous Solution 4.1 Aqueous Solutions
... – There are no ionic charges shown, but it is a redox reaction ...
... – There are no ionic charges shown, but it is a redox reaction ...
Searching for Important Amino Acids in DNA
... The process of protein-DNA interaction has been an important subject of recent bioinformatics research, however, it has not been completely understood yet. DNA-binding proteins have a vital role in the biological processing of genetic information like DNA transcription, replication, maintenance and ...
... The process of protein-DNA interaction has been an important subject of recent bioinformatics research, however, it has not been completely understood yet. DNA-binding proteins have a vital role in the biological processing of genetic information like DNA transcription, replication, maintenance and ...
Untitled
... Society in London when a cuddly looking cat with unusually big feet caught my eye. ‘This is a Hemingway cat,’ said the lecturer, pointing at the animal on the large screen behind him. ‘They have six toes – they’re polydactyl. Ernest Hemingway was said to be fond of them, and they still live on his e ...
... Society in London when a cuddly looking cat with unusually big feet caught my eye. ‘This is a Hemingway cat,’ said the lecturer, pointing at the animal on the large screen behind him. ‘They have six toes – they’re polydactyl. Ernest Hemingway was said to be fond of them, and they still live on his e ...
Chapter 22, Proteins
... ¾The C=O and N-H groups of peptide bonds from adjacent chains point toward each other and are in the same plane so that hydrogen bonding is possible between them. ¾All R-groups on any one chain alternate, first above, then below the plane of the sheet, etc. ¾The distinction between secondary structu ...
... ¾The C=O and N-H groups of peptide bonds from adjacent chains point toward each other and are in the same plane so that hydrogen bonding is possible between them. ¾All R-groups on any one chain alternate, first above, then below the plane of the sheet, etc. ¾The distinction between secondary structu ...
Biology Ch. 12
... Answer: A mutagen in a body cell becomes part of the of the genetic sequence in that cell and in future daughter cells. The cell may die or simply not perform its normal function. These mutations are not passed on to the next generation. When mutations occur in sex cells, they will be present in eve ...
... Answer: A mutagen in a body cell becomes part of the of the genetic sequence in that cell and in future daughter cells. The cell may die or simply not perform its normal function. These mutations are not passed on to the next generation. When mutations occur in sex cells, they will be present in eve ...
Genetics ppt 1
... • Three properties of RNA enable it to function as an enzyme – It can form a three-dimensional structure because of its ability to base pair with itself – Some bases in RNA contain functional groups – RNA may hydrogen-bond with other nucleic acid molecules ...
... • Three properties of RNA enable it to function as an enzyme – It can form a three-dimensional structure because of its ability to base pair with itself – Some bases in RNA contain functional groups – RNA may hydrogen-bond with other nucleic acid molecules ...
17. Amino acids are precursors of many specialized biomolecules
... 20. De novo purine nucleotide synthesis begins with the transferring of an amino group from Gln to PRPP • PRPP is synthesized from ribose 5-P. • In the first (committing) step of purine nucleotide synthesis, the PPi part on PRPP (at C-1) is replaced by the side chain amino group of Gln, forming 5-p ...
... 20. De novo purine nucleotide synthesis begins with the transferring of an amino group from Gln to PRPP • PRPP is synthesized from ribose 5-P. • In the first (committing) step of purine nucleotide synthesis, the PPi part on PRPP (at C-1) is replaced by the side chain amino group of Gln, forming 5-p ...
PDF
... analysis that occurs prior to the running of sequence analysis programs; namely on the preparation and assembly of sequence data files. A typical example of the type of problem which we face in the laboratory is presented by the genes for the u and 4 heavy chains of immunoglobu1ins. The biological f ...
... analysis that occurs prior to the running of sequence analysis programs; namely on the preparation and assembly of sequence data files. A typical example of the type of problem which we face in the laboratory is presented by the genes for the u and 4 heavy chains of immunoglobu1ins. The biological f ...
Things to know for the Final - Mercer Island School District
... Be able to compare and contrast DNA and RNA (include 3 differences). Be able to explain the complementary base pairs in a DNA molecule, and how the complementary pairs relate to the ability of DNA to be accurately replicated. Be able to explain the process of DNA replication including when/where it ...
... Be able to compare and contrast DNA and RNA (include 3 differences). Be able to explain the complementary base pairs in a DNA molecule, and how the complementary pairs relate to the ability of DNA to be accurately replicated. Be able to explain the process of DNA replication including when/where it ...
Genetics Workbook
... 5. State the enzymes in the correct order and their function in prokaryotic DNA replication. 6. Indicate the results you would expect in terms of the banding pattern in the ultracentrifugation experiment for the Meselson Stahl experiment if DNA replication was conservative after 2 rounds of DNA syn ...
... 5. State the enzymes in the correct order and their function in prokaryotic DNA replication. 6. Indicate the results you would expect in terms of the banding pattern in the ultracentrifugation experiment for the Meselson Stahl experiment if DNA replication was conservative after 2 rounds of DNA syn ...
Punnett Square Practice
... 10. In four o’clock plants, the dominant allele for flower color is red (F), and the recessive allele is white flowers (f). Flower color in four o’clock plants is also a incomplete dominance, which means when the organism is heterozygous (Ff), the dominant and recessive allele blend to make pink. If ...
... 10. In four o’clock plants, the dominant allele for flower color is red (F), and the recessive allele is white flowers (f). Flower color in four o’clock plants is also a incomplete dominance, which means when the organism is heterozygous (Ff), the dominant and recessive allele blend to make pink. If ...
2011
... If fumarate is not formed, then oxaloacetate cannot be produced, and new molecules cannot enter the Krebs cycle (so CO2 production stops) (+4 points for recognizing that the reason that CO2 production stops is because new molecules cannot enter the cycle). ...
... If fumarate is not formed, then oxaloacetate cannot be produced, and new molecules cannot enter the Krebs cycle (so CO2 production stops) (+4 points for recognizing that the reason that CO2 production stops is because new molecules cannot enter the cycle). ...
UG Curriculum
... The chemistry portion should strive towards providing information on the functional groups, hydrophobic and hydrophilic moieties and weak valence forces that organize macromolecules. Details on structure need not be emphasized. Discussion on metabolic processes should put emphasis on the overall cha ...
... The chemistry portion should strive towards providing information on the functional groups, hydrophobic and hydrophilic moieties and weak valence forces that organize macromolecules. Details on structure need not be emphasized. Discussion on metabolic processes should put emphasis on the overall cha ...
VILLIN MODEL CONSTRUCTION
... complexity that could only be addressed by an engineer with metal construction experience. The hinges would have to be constructed by an engineer. Free rotation around the peptide bond would be more realistic, but would cause two problems. First, the model would collide with other parts of the villi ...
... complexity that could only be addressed by an engineer with metal construction experience. The hinges would have to be constructed by an engineer. Free rotation around the peptide bond would be more realistic, but would cause two problems. First, the model would collide with other parts of the villi ...
NEET MODEL PAPERS - Botany paper 1.
... 100. Radial, Collateral, and Bicollateral vascular bundles are present respectively in anatomy of 1) Dicot and Monocot roots, dicot and monocot stem, and cucurbita stems 2) Dicot and Monocot stem, dicot and monocot root and cucurbita stem 3) Dicot and Monocot Root, cucurbita stem , dicot and Monocot ...
... 100. Radial, Collateral, and Bicollateral vascular bundles are present respectively in anatomy of 1) Dicot and Monocot roots, dicot and monocot stem, and cucurbita stems 2) Dicot and Monocot stem, dicot and monocot root and cucurbita stem 3) Dicot and Monocot Root, cucurbita stem , dicot and Monocot ...
Lecture 8: Life`s Information Molecule III
... MOLECULE III: TRANSLATION AND PROTEIN LOCALIZATION ...
... MOLECULE III: TRANSLATION AND PROTEIN LOCALIZATION ...
Nucleic acid analogue
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research.Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pucker-shaped pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases.An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix).Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic acid (LNA), as well as glycol nucleic acid (GNA) and threose nucleic acid (TNA). Each of these is distinguished from naturally occurring DNA or RNA by changes to the backbone of the molecule.In May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA, and by including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, were able to passage the bacteria 24 times; they did not create mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides. The artificial nucleotides featured 2 fused aromatic rings.