Applicability and sensitivity of PCR SSCP method for milk species
... techniques. Food Control, 18, 1246-1249. AMILLS, M., FRANCINO, O., JANSA, M. & SÁNCHEZ, A. (1997): Isolation of genomic DNA from milk samples by using Chelex resin. Journal of Dairy Research, 64, 231-238. COMMISSION REGULATION (2006): The protection of geographical indications and designations of or ...
... techniques. Food Control, 18, 1246-1249. AMILLS, M., FRANCINO, O., JANSA, M. & SÁNCHEZ, A. (1997): Isolation of genomic DNA from milk samples by using Chelex resin. Journal of Dairy Research, 64, 231-238. COMMISSION REGULATION (2006): The protection of geographical indications and designations of or ...
Translation Activity Guide
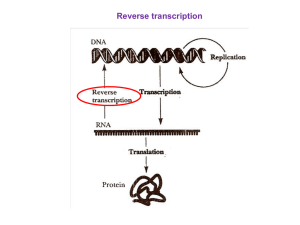
... translation. Transcription is the process in which DNA is used as a template to produce a single-stranded RNA molecule. Translation is the process in which the DNA code, now contained in the single-stranded RNA, is deciphered into a sequence of linked amino acids that become a protein. In eukaryotic ...
... translation. Transcription is the process in which DNA is used as a template to produce a single-stranded RNA molecule. Translation is the process in which the DNA code, now contained in the single-stranded RNA, is deciphered into a sequence of linked amino acids that become a protein. In eukaryotic ...
Vitamin B3 or Niacin Niacin is the name given to vitamin B3 (B
... from Alzheimer´s to cancer. Regular daily intake of vitamin B3-rich foods is essential, but even a diet high in B3 foods is no guarantee the benefits will be released without the presence of a healthy gut flora. Niacin actually refers to several chemically similar forms of vitamin B3, nicotinic acid ...
... from Alzheimer´s to cancer. Regular daily intake of vitamin B3-rich foods is essential, but even a diet high in B3 foods is no guarantee the benefits will be released without the presence of a healthy gut flora. Niacin actually refers to several chemically similar forms of vitamin B3, nicotinic acid ...
Bacteria and Viruses Jeopardy
... $100 Answer from H1 They are unable to perform many of the characteristics of life on their own and must do so INSIDE a HOST cell. ...
... $100 Answer from H1 They are unable to perform many of the characteristics of life on their own and must do so INSIDE a HOST cell. ...
Chapter 20: Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles
... The tertiary structure of a globular protein is the result of many intramolecular attractions that can be disrupted by a change of the environment, causing the protein to become denatured Solubility is drastically decreased as in heating egg white, where the albumins unfold and coagulate ...
... The tertiary structure of a globular protein is the result of many intramolecular attractions that can be disrupted by a change of the environment, causing the protein to become denatured Solubility is drastically decreased as in heating egg white, where the albumins unfold and coagulate ...
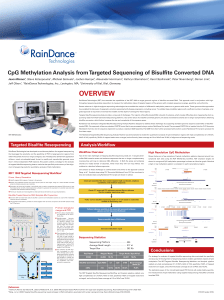
CpG methylation analysis from targeted
... RainDance Technologies (RDT) has extended the capabilities of the RDT 1000 to target genomic regions of bisulfite converted DNA. This approach used in conjunction with highthroughput sequencing enables researchers to measure the methylation status of targeted regions of the genome with complete sequ ...
... RainDance Technologies (RDT) has extended the capabilities of the RDT 1000 to target genomic regions of bisulfite converted DNA. This approach used in conjunction with highthroughput sequencing enables researchers to measure the methylation status of targeted regions of the genome with complete sequ ...
2014 Gateway Bio Packet
... Brown eyes are dominant to blue. The father’s genotype is Bb. The mother has blue eyes. 6) Create a Punnett square to see the chances of them having a blue-eyed child. 7) How many of the possible children will be heterozygous? ...
... Brown eyes are dominant to blue. The father’s genotype is Bb. The mother has blue eyes. 6) Create a Punnett square to see the chances of them having a blue-eyed child. 7) How many of the possible children will be heterozygous? ...
Python Practice
... b. A program that reads and executes source code one line at a time. Does not create an executable file that can run independently. c. A program that reads, interprets, and executes a program, eliminating the need for compiling source code. Running a program through an interpreter can reduce the edi ...
... b. A program that reads and executes source code one line at a time. Does not create an executable file that can run independently. c. A program that reads, interprets, and executes a program, eliminating the need for compiling source code. Running a program through an interpreter can reduce the edi ...
Protein Unit Study Guide/Review Sheets
... If you have questions, make sure to ask them. Stop in before or after school. Review questions: 1. What elements comprise proteins? C, H, O, N 2. Are proteins organic? YES – CONTAIN CARBON AND HYDROGEN, THE REQUIREMENT FOR BEING AN ORGANIC MOLECULE 3. What is the name of the monomer of proteins? AMI ...
... If you have questions, make sure to ask them. Stop in before or after school. Review questions: 1. What elements comprise proteins? C, H, O, N 2. Are proteins organic? YES – CONTAIN CARBON AND HYDROGEN, THE REQUIREMENT FOR BEING AN ORGANIC MOLECULE 3. What is the name of the monomer of proteins? AMI ...
Camp 1 - University of California, Santa Cruz
... CoA) produces NADH +H Oxidation of acetyl CoA by the common metabolic ...
... CoA) produces NADH +H Oxidation of acetyl CoA by the common metabolic ...
Application of PCR-technique in biological labs
... When these genes are expressed in prokaryotic cells for protein production or purification, the RNA produced from transcription need not undergo splicing as it contains only exons. ...
... When these genes are expressed in prokaryotic cells for protein production or purification, the RNA produced from transcription need not undergo splicing as it contains only exons. ...
Learning Objectives
... 12. Explain the evolutionary significance of a nearly universal genetic code. The Synthesis and Processing of RNA 13. Explain how RNA polymerase recognizes where transcription should begin. Describe the role of the promoter, the terminator, and the transcription unit. 14. Explain the general process ...
... 12. Explain the evolutionary significance of a nearly universal genetic code. The Synthesis and Processing of RNA 13. Explain how RNA polymerase recognizes where transcription should begin. Describe the role of the promoter, the terminator, and the transcription unit. 14. Explain the general process ...
Biostat Jhsph Edu Hji Courses Genomics Sequencing Ppt
... beads that are also included in the reaction. A low template concentration results in most bead-containing compartments having either zero or one template molecule present. In productive emulsion compartments (where both a bead and template molecule is present), PCR amplicons are captured to the sur ...
... beads that are also included in the reaction. A low template concentration results in most bead-containing compartments having either zero or one template molecule present. In productive emulsion compartments (where both a bead and template molecule is present), PCR amplicons are captured to the sur ...
Serum `uracil + uridine` - Journal of Clinical Pathology
... of RNA and the precursor of two of the basesthymine and cytosine-which enter into the composition of DNA. Its main interest, however, is that under certain circumstances it has mutagenic properties (Freese, 1959; Vielmetter and Schuster, 1960; Freese, 1963). The molecular basis of the latter is illu ...
... of RNA and the precursor of two of the basesthymine and cytosine-which enter into the composition of DNA. Its main interest, however, is that under certain circumstances it has mutagenic properties (Freese, 1959; Vielmetter and Schuster, 1960; Freese, 1963). The molecular basis of the latter is illu ...
TPJ_4378_sm_FigS1-7
... Figure S7. Amino acid sequence of MPL1 and homology to key regions of lipases. (a) Amino acid sequence of MPL1. Residues S190, D360 and H393 (all marked in black bold) are likely active site residues based on sequence of other TAG lipases. Underlined sequence GHSLG corresponds to the GXSXG motif, co ...
... Figure S7. Amino acid sequence of MPL1 and homology to key regions of lipases. (a) Amino acid sequence of MPL1. Residues S190, D360 and H393 (all marked in black bold) are likely active site residues based on sequence of other TAG lipases. Underlined sequence GHSLG corresponds to the GXSXG motif, co ...
Mutations Handout
... ______18. Why are insertion and deletion mutations usually more serious than substitutions? A. they can be passed on to offspring B. they change every codon after the mutation C. they always cause some form of cancer D. they cause recessive traits to become dominant traits ______19. Why do some gen ...
... ______18. Why are insertion and deletion mutations usually more serious than substitutions? A. they can be passed on to offspring B. they change every codon after the mutation C. they always cause some form of cancer D. they cause recessive traits to become dominant traits ______19. Why do some gen ...
IDENTIFYING A KNOCKOUT PLANT
... The fluorescence enhancement provided by using the H33258 dye has been shown to be highly specific for DNA, binding preferentially to A-T rich regions (Brunk et al., 1979; Labarca and Paigen, 1980). The dye binds twice as well to double-stranded DNA as to single-stranded DNA, but does not appear to ...
... The fluorescence enhancement provided by using the H33258 dye has been shown to be highly specific for DNA, binding preferentially to A-T rich regions (Brunk et al., 1979; Labarca and Paigen, 1980). The dye binds twice as well to double-stranded DNA as to single-stranded DNA, but does not appear to ...
Nucleic acid analogue
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research.Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pucker-shaped pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases.An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix).Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic acid (LNA), as well as glycol nucleic acid (GNA) and threose nucleic acid (TNA). Each of these is distinguished from naturally occurring DNA or RNA by changes to the backbone of the molecule.In May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA, and by including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, were able to passage the bacteria 24 times; they did not create mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides. The artificial nucleotides featured 2 fused aromatic rings.