Regulation of Populations - Deans Community High School
... sparsely distributed in the ecosystem. e.g. forest fire, lava flow, flood, drought, unusually extreme temperatures. In contrast, some factors affect a population only once it has reached a particular density. Up to that point, a small population will increase - until its growth rate is affected by a ...
... sparsely distributed in the ecosystem. e.g. forest fire, lava flow, flood, drought, unusually extreme temperatures. In contrast, some factors affect a population only once it has reached a particular density. Up to that point, a small population will increase - until its growth rate is affected by a ...
List the ecological levels of organization from the largest to smallest
... Without wolves: Elk pushed the carrying capacity of the park. With wolves: Elk decreased from 16,791 in winter 1995 to 8,335 in winter 2004. ...
... Without wolves: Elk pushed the carrying capacity of the park. With wolves: Elk decreased from 16,791 in winter 1995 to 8,335 in winter 2004. ...
5.3 Populations
... – Natality – number of new species due to reproduction – Mortality – number of deaths – Immigration – members arriving from other places – Emigration – members leaving the population ...
... – Natality – number of new species due to reproduction – Mortality – number of deaths – Immigration – members arriving from other places – Emigration – members leaving the population ...
PowerPoint
... Population Mortality • Organisms differ on strategies of reproduction and differ on types of predation • Those organisms that put much care into their few young tend to have good survivorship of young • Those organisms that spread their young all over tend to have poor survivorship of their young • ...
... Population Mortality • Organisms differ on strategies of reproduction and differ on types of predation • Those organisms that put much care into their few young tend to have good survivorship of young • Those organisms that spread their young all over tend to have poor survivorship of their young • ...
Populations
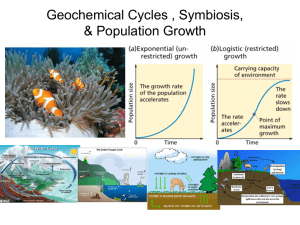
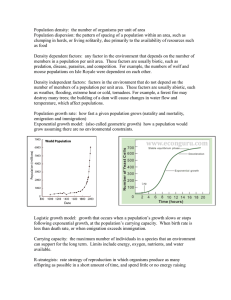
... Exponential Growth • Occurs when the individuals in a population reproduce at a constant rate • Under ideal conditions with unlimited resources, a population will grow exponentially ...
... Exponential Growth • Occurs when the individuals in a population reproduce at a constant rate • Under ideal conditions with unlimited resources, a population will grow exponentially ...
PopulationsPP
... • The continuous flow of phosphorus from land to water to organisms and back to land, • P is important in the production of DNA and RNA. • phosphorus is NOT found in the atmosphere. Found in rocks and minerals. ...
... • The continuous flow of phosphorus from land to water to organisms and back to land, • P is important in the production of DNA and RNA. • phosphorus is NOT found in the atmosphere. Found in rocks and minerals. ...
Chapter 4 Outline – Population Dynamics
... movement, birth rates, and death rates B. Humans can alter their environment – eradicate diseases, created new food sources C. Calculating growth rate ( GR = BR + IR – DR + ER) 1. Birthrate – number of live births per 1 000 in a given year 2. Death rate – number of deaths per 1 000 in a given year 3 ...
... movement, birth rates, and death rates B. Humans can alter their environment – eradicate diseases, created new food sources C. Calculating growth rate ( GR = BR + IR – DR + ER) 1. Birthrate – number of live births per 1 000 in a given year 2. Death rate – number of deaths per 1 000 in a given year 3 ...
Ecology Unit Review Questions
... How is the density of a population calculated? You will be asked to be able to calculate the population density of a specific population. What factors affect population growth or decline? Don’t forget to define words like immigration vs. emigration. Understand exponential and logistic growth curves. ...
... How is the density of a population calculated? You will be asked to be able to calculate the population density of a specific population. What factors affect population growth or decline? Don’t forget to define words like immigration vs. emigration. Understand exponential and logistic growth curves. ...
Population Growth
... the growth of a the MAXIMUM population number of individuals an environment and – Available resources its resources can (food, space, mates) support – Competition, predation, parasitism, disease – Natural disasters, unusual weather Limiting factors determine the carrying capacity for a species. ...
... the growth of a the MAXIMUM population number of individuals an environment and – Available resources its resources can (food, space, mates) support – Competition, predation, parasitism, disease – Natural disasters, unusual weather Limiting factors determine the carrying capacity for a species. ...
Growth Cycles and Stresses PPT
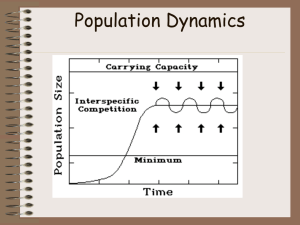
... Environmental resistance – combination of all factors that act to limit the growth of a population Carrying capacity (K) – maximum population of a given species that a habitat can sustain indefinitely without being degraded ...
... Environmental resistance – combination of all factors that act to limit the growth of a population Carrying capacity (K) – maximum population of a given species that a habitat can sustain indefinitely without being degraded ...
ch5,6review
... Important Facts • 40% of population growth is US is due to immigration (legal and illegal) • China and India have 36% of world’s population--US is 3rd with 4.5 • US infant mortality level is higher than 39 other countries. WHY? ...
... Important Facts • 40% of population growth is US is due to immigration (legal and illegal) • China and India have 36% of world’s population--US is 3rd with 4.5 • US infant mortality level is higher than 39 other countries. WHY? ...
population - wsscience
... GROWTH RATE – change in size of a population over time change in population size = births - deaths POPULATION GROWTH REPRODUCTIVE POTENTIAL WHAT IT IS – the maximum number of offspring that each member in a population can produce HOW TO CHANGE IT: >produce more offspring at a time >reproduce more of ...
... GROWTH RATE – change in size of a population over time change in population size = births - deaths POPULATION GROWTH REPRODUCTIVE POTENTIAL WHAT IT IS – the maximum number of offspring that each member in a population can produce HOW TO CHANGE IT: >produce more offspring at a time >reproduce more of ...
Carrying Capacity
... A giraffe must eat 10 kg of leaves each day The trees in an area can provide 100 kg per day while remaining healthy Could 15 giraffes live in this area? What is the carrying capacity? ...
... A giraffe must eat 10 kg of leaves each day The trees in an area can provide 100 kg per day while remaining healthy Could 15 giraffes live in this area? What is the carrying capacity? ...
Population Dynamics
... Logistic Growth Occurs when resources become less available (Slows population growth rate) Slow population growth rate due to 1. Decrease in birthrate 2. Increase in deathrate 3. Immigration decreases 4. Emigration increases ...
... Logistic Growth Occurs when resources become less available (Slows population growth rate) Slow population growth rate due to 1. Decrease in birthrate 2. Increase in deathrate 3. Immigration decreases 4. Emigration increases ...
Chapter 5 Reading Questions
... Name ________________________________ Period _____ Score _______ Page 103 1. What is a Population? 2. Why is understanding population growth important? ...
... Name ________________________________ Period _____ Score _______ Page 103 1. What is a Population? 2. Why is understanding population growth important? ...
Three Key Features of Populations Size
... • R Strategists Short life span Small body size Reproduce quickly Have many young Little parental care Ex: cockroaches, ...
... • R Strategists Short life span Small body size Reproduce quickly Have many young Little parental care Ex: cockroaches, ...
Earth`s Population Growth
... people the amount of fresh water available to each person decreases decreases. Only 0.3% of the water on the planet is available for human use. Due to mismanagement, over 40% of the groundwater in the U.S. is contaminated by industrial, agricultural, and household pollution, making it extremely diff ...
... people the amount of fresh water available to each person decreases decreases. Only 0.3% of the water on the planet is available for human use. Due to mismanagement, over 40% of the groundwater in the U.S. is contaminated by industrial, agricultural, and household pollution, making it extremely diff ...
Population density: the number of organisms per unit of area
... following exponential growth, at the population’s carrying capacity. When birth rate is less than death rate, or when emigration exceeds immigration. Carrying capacity: the maximum number of individuals in a species that an environment can support for the long term. Limits include energy, oxygen, nu ...
... following exponential growth, at the population’s carrying capacity. When birth rate is less than death rate, or when emigration exceeds immigration. Carrying capacity: the maximum number of individuals in a species that an environment can support for the long term. Limits include energy, oxygen, nu ...
4 Bio
... Growth Rate – is the difference between the birthrate and the death rate What is the trend of the U.S.? Age Structure – can help predict if a population is growing rapidly, growing slowly or not growing at all. Immigration – movement into a population Emigration – movement from a population ...
... Growth Rate – is the difference between the birthrate and the death rate What is the trend of the U.S.? Age Structure – can help predict if a population is growing rapidly, growing slowly or not growing at all. Immigration – movement into a population Emigration – movement from a population ...
World population
In demographics and general statistics, the term world population refers to the total number of living humans on Earth. The United States Census Bureau estimates that the world population exceeded 7 billion on March 12, 2012. According to a separate estimate by the United Nations Population Fund, it reached this milestone on October 31, 2011. In July 2015, the Population Division of the United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs estimated the world population at approximately 7.3 billion.The world population has experienced continuous growth since the end of the Great Famine and the Black Death in 1350, when it was near 370 million. The highest growth rates – global population increases above 1.8% per year – occurred briefly during the 1950s, and for longer during the 1960s and 1970s. The global growth rate peaked at 2.2% in 1963, and has declined to 1.1% as of 2012. Total annual births were highest in the late 1980s at about 139 million, and are now expected to remain essentially constant at their 2011 level of 135 million, while deaths number 56 million per year, and are expected to increase to 80 million per year by 2040.The 2012 UN projections show a continued increase in population in the near future with a steady decline in population growth rate; the global population is expected to reach between 8.3 and 10.9 billion by 2050. 2003 UN Population Division population projections for the year 2150 range between 3.2 and 24.8 billion. One of many independent mathematical models supports the lower estimate, while a 2014 estimate forecasts between 9.3 and 12.6 billion in 2100, and continued growth thereafter. Some analysts have questioned the sustainability of further world population growth, highlighting the growing pressures on the environment, global food supplies, and energy resources.Various scholarly estimates have been made of the total number of humans who have ever lived, giving figures ranging from approximately 100 billion to 115 billion.