* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 4 Bio
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
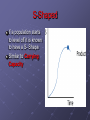
Chapter 4 Population Biology Linear Growth Rainfall Rainfall in millimeters Growth occurs in a straight line when graphed. Steady equal increase. 12 10 8 Day 6 Rainfall 4 2 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Day Exponential Growth As a population gets larger, it also grows faster. Natures population growth. J-CURVE Questions To Think About Can a population of organisms grow indefinitely? NOOOOOOOOOOOOOOO Why? What will limit the population from growing? Natural Disaster Disease Food Supply War Stop Reproducing S-Shaped If a population starts to level off it is known to have a S- Shape Similar to Carrying Capacity Effects of Competition Competition density-dependent factor Depends on population size Effects of Crowding And Stress Aggression Decrease parental care Decreased resistance to disease Demography Study of human population growth characteristics Demographer studies population characteristics as growth rate, age structure, and geographic distribution Effects of Birth and Death Rates Growth Rate – is the difference between the birthrate and the death rate What is the trend of the U.S.? Age Structure – can help predict if a population is growing rapidly, growing slowly or not growing at all. Immigration – movement into a population Emigration – movement from a population Carrying Capacity The number of organisms of one species that an environment can support. When populations are under the carrying capacity births > deaths until the carrying capacity is reached Populations exceeds carrying capacity deaths > births Environmental Limits to Population Growth Limiting Factors Density Dependent Factors – disease, competition, parasites, and food have an increasing effect as the population increases Density Independent Factors – affect all populations regardless of their density Ex. – hurricanes, abiotic factors, storms, floods Organisms Interactions Limit Population Size Predation Affects Population Size 1. when predator consumes prey, it can affect the population size of the prey population 2. Predator Prey Relationships Very Healthy For Populations