Know your species - The Darwin Initiative
... Lowland Forest Day Gecko Phelsuma guimbeaui. Status This species is rare and declining. Exact status unclear. Distribution The species is restricted to Mauritius. Historically it was probably found over lowland. Limited to a few forested areas and along rivers and streams in the south west and north ...
... Lowland Forest Day Gecko Phelsuma guimbeaui. Status This species is rare and declining. Exact status unclear. Distribution The species is restricted to Mauritius. Historically it was probably found over lowland. Limited to a few forested areas and along rivers and streams in the south west and north ...
Components of an Ecosystem.b
... What would happen to an ecosystem if there were no more bugs? S7L4 ...
... What would happen to an ecosystem if there were no more bugs? S7L4 ...
SNC 1D Ecosystems preserving biodiversity
... When all individuals of a species dies. When death rate exceeds birth rate over a long period of time. There are patterns of extinction that happened naturally: Background extinction: apparent over long periods as ecosystems change, some species become extinct Mass extinction: relatively s ...
... When all individuals of a species dies. When death rate exceeds birth rate over a long period of time. There are patterns of extinction that happened naturally: Background extinction: apparent over long periods as ecosystems change, some species become extinct Mass extinction: relatively s ...
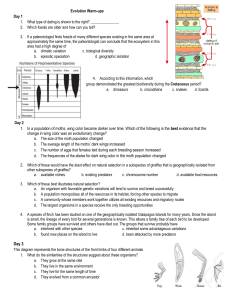
Unit 11 Evolution Warm ups
... 2. The different species of Hawaiian honeycreepers shown all descended from a single species of North American bird. They now have different beaks, eat different foods, sing different songs, and live in different environments on the islands. Which factor probably contributed most to the development ...
... 2. The different species of Hawaiian honeycreepers shown all descended from a single species of North American bird. They now have different beaks, eat different foods, sing different songs, and live in different environments on the islands. Which factor probably contributed most to the development ...
Pre-AP Biology Ecology Exam Study Guide
... What are some density-dependent factors that can cause a population’s growth to slow and level out at carrying capacity? ...
... What are some density-dependent factors that can cause a population’s growth to slow and level out at carrying capacity? ...
Ecosystem Interactions
... Know what a predator – prey relsationship is and why they are important Know what competition is and what the two types of competitive relationships are Understand the concept of equilibrium and how limiting factors contribute to creating it (e.g. carrying capacity) ...
... Know what a predator – prey relsationship is and why they are important Know what competition is and what the two types of competitive relationships are Understand the concept of equilibrium and how limiting factors contribute to creating it (e.g. carrying capacity) ...
Ecology and Conservation
... Outline the factors that affect the distribution of plant species including temperature, water, light, soil pH, salinity, and mineral nutrients *High temperature denatures enzymes and retards growth of plants; the rate of transpiration (loss of :water) is also increased. *Low temperatures decrease ...
... Outline the factors that affect the distribution of plant species including temperature, water, light, soil pH, salinity, and mineral nutrients *High temperature denatures enzymes and retards growth of plants; the rate of transpiration (loss of :water) is also increased. *Low temperatures decrease ...
Human Impact
... in a close, long-term association. They can be beneficial, harmful, or neutral. (we already mentioned parasitism or (+,-) • Mutualism – symbiotic relationship in which both participating species benefit (+,+) • Commensalism – symbiotic relationship in which one species benefits and the other is neit ...
... in a close, long-term association. They can be beneficial, harmful, or neutral. (we already mentioned parasitism or (+,-) • Mutualism – symbiotic relationship in which both participating species benefit (+,+) • Commensalism – symbiotic relationship in which one species benefits and the other is neit ...
Organisms and Their Environment
... Biotic factors-living things Ex: trees, animals, bacteria Abiotic factors-non-living things Ex: sun, soil, air, water Examples of ecosystems made up of biotic and abiotic factors: ...
... Biotic factors-living things Ex: trees, animals, bacteria Abiotic factors-non-living things Ex: sun, soil, air, water Examples of ecosystems made up of biotic and abiotic factors: ...
Interactions Among Living Things (pp. 410–416)
... 16. In a parasitic relationship, the organism that benefits is called a(n) ______________________________, and the organism it lives on or in is called a(n) ______________________________. ...
... 16. In a parasitic relationship, the organism that benefits is called a(n) ______________________________, and the organism it lives on or in is called a(n) ______________________________. ...
Presentation
... 1. Species of highland forests appear not to be as specialized ecologically 2. No animal or plant is absolutely dependent on another 3. Flora and fauna are not characterized by the kinds of life history features that predispose species to extinction 4. Sizes of seed crops of plants and animals do no ...
... 1. Species of highland forests appear not to be as specialized ecologically 2. No animal or plant is absolutely dependent on another 3. Flora and fauna are not characterized by the kinds of life history features that predispose species to extinction 4. Sizes of seed crops of plants and animals do no ...
Quiz12_noAnswers
... B. Relatively stationary individuals C. A blastopore that becomes the anus C. A large population D. Greater number of species than the protostomes D. Both a and b E. Well-developed coelomic body cavities in most E. None of the above of them 6) Which of the following statements about age 2) Which of ...
... B. Relatively stationary individuals C. A blastopore that becomes the anus C. A large population D. Greater number of species than the protostomes D. Both a and b E. Well-developed coelomic body cavities in most E. None of the above of them 6) Which of the following statements about age 2) Which of ...
Population Genetics
... Evolution of species (speciation) Divergent evolution: species become different over a long period of time. Adaptative radiation (species spread out to new territories). Convergent evolution: Different species undergoing similar adaptations and evolving more alike ...
... Evolution of species (speciation) Divergent evolution: species become different over a long period of time. Adaptative radiation (species spread out to new territories). Convergent evolution: Different species undergoing similar adaptations and evolving more alike ...
File
... Vocabulary: You will have a vocabulary quiz on these terms. You may be required to provided examples for some terms. 1. population dynamics 2. territoriality 3. interference competition 4. exploitation competition 5. symbiosis 6. social parasitism 7. biotic potential 8. minimum viable population 9. ...
... Vocabulary: You will have a vocabulary quiz on these terms. You may be required to provided examples for some terms. 1. population dynamics 2. territoriality 3. interference competition 4. exploitation competition 5. symbiosis 6. social parasitism 7. biotic potential 8. minimum viable population 9. ...
Humans change Ecosystems - Marana Unified School District
... • Pollution, hunting, and competition from exotic species also causes extinction. ...
... • Pollution, hunting, and competition from exotic species also causes extinction. ...
Unit A - Lesson 9 - JA Williams High School
... https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FlUes_NPa6M Extiration He disappearance of a species from a certain area ...
... https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FlUes_NPa6M Extiration He disappearance of a species from a certain area ...
Symbiosis Activity
... Two individuals of the same or different species may interact in a variety of different ways. A very specific interaction that may occur between the organisms is defined as symbiosis, a close, coevolutionary association between one species (host) and another species (symbiont). Species may interact ...
... Two individuals of the same or different species may interact in a variety of different ways. A very specific interaction that may occur between the organisms is defined as symbiosis, a close, coevolutionary association between one species (host) and another species (symbiont). Species may interact ...
Brett
... ecosystem restoration design and implementation; land acquisition, land use regulation, sustainable land use and redevelopment; threatened & endangered (TE) species ecology; habitat conservation/restoration and protection; vernal habitat and species ecology; stormwater management and water quality. ...
... ecosystem restoration design and implementation; land acquisition, land use regulation, sustainable land use and redevelopment; threatened & endangered (TE) species ecology; habitat conservation/restoration and protection; vernal habitat and species ecology; stormwater management and water quality. ...
Theoretical ecology

Theoretical ecology is the scientific discipline devoted to the study of ecological systems using theoretical methods such as simple conceptual models, mathematical models, computational simulations, and advanced data analysis. Effective models improve understanding of the natural world by revealing how the dynamics of species populations are often based on fundamental biological conditions and processes. Further, the field aims to unify a diverse range of empirical observations by assuming that common, mechanistic processes generate observable phenomena across species and ecological environments. Based on biologically realistic assumptions, theoretical ecologists are able to uncover novel, non-intuitive insights about natural processes. Theoretical results are often verified by empirical and observational studies, revealing the power of theoretical methods in both predicting and understanding the noisy, diverse biological world.The field is broad and includes foundations in applied mathematics, computer science, biology, statistical physics, genetics, chemistry, evolution, and conservation biology. Theoretical ecology aims to explain a diverse range of phenomena in the life sciences, such as population growth and dynamics, fisheries, competition, evolutionary theory, epidemiology, animal behavior and group dynamics, food webs, ecosystems, spatial ecology, and the effects of climate change.Theoretical ecology has further benefited from the advent of fast computing power, allowing the analysis and visualization of large-scale computational simulations of ecological phenomena. Importantly, these modern tools provide quantitative predictions about the effects of human induced environmental change on a diverse variety of ecological phenomena, such as: species invasions, climate change, the effect of fishing and hunting on food network stability, and the global carbon cycle.