Chapter 4 Population and Environment
... The special branch of ecology which deals with the study of individuals of the same species and the related processes such as aggregation interactions between individuals and the factors leading to those processes is known as population ecology Population is a group of individuals of a particular sp ...
... The special branch of ecology which deals with the study of individuals of the same species and the related processes such as aggregation interactions between individuals and the factors leading to those processes is known as population ecology Population is a group of individuals of a particular sp ...
File - layfieldsci.com
... example of each. Biotic – Living – Predators thin herd of deer, Abiotic – Non-Living – Natural Disaster (tornado) wipes out herd of deer. 4. Give an example of a predator-prey relationship. LION eats WILDEBEEST! 5. What level of the energy pyramid for an ecosystem will have the largest population? W ...
... example of each. Biotic – Living – Predators thin herd of deer, Abiotic – Non-Living – Natural Disaster (tornado) wipes out herd of deer. 4. Give an example of a predator-prey relationship. LION eats WILDEBEEST! 5. What level of the energy pyramid for an ecosystem will have the largest population? W ...
a Table of Contents - Marcia`s Science Teaching Ideas
... Limiting Factors PPT Printed Slides Factors Limiting Growth of a Population Worksheet Limiting Factors of the Physical Environment Worksheet Limiting Factors of the Biological Environment Worksheet Limiting Factors Worksheet #1 Limiting Factors Worksheet #2 ...
... Limiting Factors PPT Printed Slides Factors Limiting Growth of a Population Worksheet Limiting Factors of the Physical Environment Worksheet Limiting Factors of the Biological Environment Worksheet Limiting Factors Worksheet #1 Limiting Factors Worksheet #2 ...
Relating Foraging Behavior to Wildlife Management
... – EPS = size of “ideal” population that looses genetic variation at same rate as does real population – Variation is lost at 1/2N% per generation, and replaced at mutation rate per generation--this loss and creation usually balance out – Loss is at > 1/2N% when sex ratios are not balanced, mating is ...
... – EPS = size of “ideal” population that looses genetic variation at same rate as does real population – Variation is lost at 1/2N% per generation, and replaced at mutation rate per generation--this loss and creation usually balance out – Loss is at > 1/2N% when sex ratios are not balanced, mating is ...
Local environment
... Examine trends in population sizes for some plat and animal species with an ecosystem. Trends in population sizes, their rise and falls can be directly observed when studying ecosystems over a period of time. Generally, trends in population may be because of, number of predators, number of produces, ...
... Examine trends in population sizes for some plat and animal species with an ecosystem. Trends in population sizes, their rise and falls can be directly observed when studying ecosystems over a period of time. Generally, trends in population may be because of, number of predators, number of produces, ...
Tax and Evol 6 Speciation
... extreme trait is selected for again and again. Driving the trait in one direction. Eg u Black bears in Europe u Shrank in size during interglacial (warm) periods u Grew in size during ice ages ...
... extreme trait is selected for again and again. Driving the trait in one direction. Eg u Black bears in Europe u Shrank in size during interglacial (warm) periods u Grew in size during ice ages ...
Abiotic Biotic
... Introduction In ecology and biology, abiotic components are non-living chemical and physical factors in the environment which affect ecosystems. Examples Water, light, wind, soil, humidity, minerals, gases. ...
... Introduction In ecology and biology, abiotic components are non-living chemical and physical factors in the environment which affect ecosystems. Examples Water, light, wind, soil, humidity, minerals, gases. ...
Invasive Species Presentation Invasive_species Honors
... species you discovered while doing your homework from last night. Brainstorm a list of characteristics that invasive species must generally have in order to “do better” than native species ...
... species you discovered while doing your homework from last night. Brainstorm a list of characteristics that invasive species must generally have in order to “do better” than native species ...
The Norwegian Nature Index - Science for the Environment 2015
... Trends in abundance of selected species ...
... Trends in abundance of selected species ...
Ecology - Images
... and in addition, adding a "false" eye spot near its tail, the raccoon butterflyfish may fool a predator into striking at the wrong end of its body - allowing it to escape. (Chaetodon lunula) ...
... and in addition, adding a "false" eye spot near its tail, the raccoon butterflyfish may fool a predator into striking at the wrong end of its body - allowing it to escape. (Chaetodon lunula) ...
“Ecology and the Environment” Handbook in Philosophy of Biology
... experimental manipulations, either in the laboratory or field. Most models of hypothesis testing in ecology take experimental manipulation and control to be central (Hairston, 1989). However, experiment should not be emphasized to the exclusion of all other methods of investigation. Some of the most ...
... experimental manipulations, either in the laboratory or field. Most models of hypothesis testing in ecology take experimental manipulation and control to be central (Hairston, 1989). However, experiment should not be emphasized to the exclusion of all other methods of investigation. Some of the most ...
Behavioral Ecology
... they apply to an example organism – focus on the adaptive benefit of the life history. Are there any disadvantages? This is a core concept. - semelparity/ big-bang reproduction: a life history in which adults have but a single reproductive opportunity to produce large #s of offspring (+) agave plant ...
... they apply to an example organism – focus on the adaptive benefit of the life history. Are there any disadvantages? This is a core concept. - semelparity/ big-bang reproduction: a life history in which adults have but a single reproductive opportunity to produce large #s of offspring (+) agave plant ...
Eight part test in accordance with Section 94 of the Threatened
... Littoral Rainforest occurs in numerous, small stands and in total comprises less than 1% of the total area of rainforest in NSW. Many, but not all, stands of Littoral Rainforest have been included in mapping for State Environmental Planning Policy 26 Littoral Rainforest, but degradation of the ecolo ...
... Littoral Rainforest occurs in numerous, small stands and in total comprises less than 1% of the total area of rainforest in NSW. Many, but not all, stands of Littoral Rainforest have been included in mapping for State Environmental Planning Policy 26 Littoral Rainforest, but degradation of the ecolo ...
Ecology Review I
... Levels of Organization Levels of ecological organization include; species, which are organisms that are so similar they can interbreed and produce more of the same organisms. A group of the same species in an area is a population. All the different species in an area is called a community The living ...
... Levels of Organization Levels of ecological organization include; species, which are organisms that are so similar they can interbreed and produce more of the same organisms. A group of the same species in an area is a population. All the different species in an area is called a community The living ...
Areas of high Natural Character that are also Ecological Sites
... With regard to the area defined as ‘Coastal Environment’ in the notified PDP, an additional 62 Ecological Sites are located either fully or partially within this area but outside of the SEV’s defined ‘Coastal Environment’. © 2015 Environmental Management Services ...
... With regard to the area defined as ‘Coastal Environment’ in the notified PDP, an additional 62 Ecological Sites are located either fully or partially within this area but outside of the SEV’s defined ‘Coastal Environment’. © 2015 Environmental Management Services ...
Chapter 9
... Ecosystems 1. Map and inventory the world’s terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems 2. Locate and protect the most endangered ecosystems, with a focus on biodiversity 3. Seek to restore as many degraded ecosystems as possible ...
... Ecosystems 1. Map and inventory the world’s terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems 2. Locate and protect the most endangered ecosystems, with a focus on biodiversity 3. Seek to restore as many degraded ecosystems as possible ...
Chapter 19 Communities & Ecosystems (General Biology)
... • Herbivores, which eat plants, algae, or autotrophic bacteria, are the primary consumers of an ecosystem • Above the primary consumers, the trophic levels are made up of carnivores, which eat the consumers from the levels below ...
... • Herbivores, which eat plants, algae, or autotrophic bacteria, are the primary consumers of an ecosystem • Above the primary consumers, the trophic levels are made up of carnivores, which eat the consumers from the levels below ...
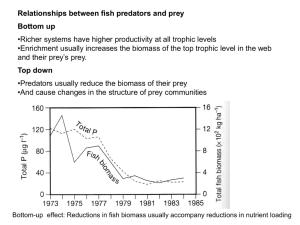
Food webs & top-down effects
... toward smaller species and species with more effective defenses •Similar effects have been noted in benthic invertebrate communities. ...
... toward smaller species and species with more effective defenses •Similar effects have been noted in benthic invertebrate communities. ...
No Slide Title
... S = EG + ER - EM : when surplus energy is available there is a positive (S) - E can be partitioned between somatic growth and gametes ...
... S = EG + ER - EM : when surplus energy is available there is a positive (S) - E can be partitioned between somatic growth and gametes ...
Biodiversity and Restoration
... this diversity from a scientific perspective, much less from the perspective of management. One way to simplify this diversity is to focus on an individual’s functions, rather than its taxonomy (i.e., its evolutionary relationship to other organisms). If you can “bin” species depending on function t ...
... this diversity from a scientific perspective, much less from the perspective of management. One way to simplify this diversity is to focus on an individual’s functions, rather than its taxonomy (i.e., its evolutionary relationship to other organisms). If you can “bin” species depending on function t ...
Unit 6 Vocabulary Flashcards
... Diagram that shows the path of energy transfer from producers to consumers; show the path that one piece of energy takes; usually a circle where a decomposer returns the nutrients to the soil for the producer to use again ...
... Diagram that shows the path of energy transfer from producers to consumers; show the path that one piece of energy takes; usually a circle where a decomposer returns the nutrients to the soil for the producer to use again ...
Envir Science - Ecosystem OEQs
... Explain how we that do not live in countries with rainforests can help to protect them and why it is important that we do so. Use specific details to support your answer! There are 5 levels of ecological study that describe the theme of interconnectedness through various forms of symbiosis. Iden ...
... Explain how we that do not live in countries with rainforests can help to protect them and why it is important that we do so. Use specific details to support your answer! There are 5 levels of ecological study that describe the theme of interconnectedness through various forms of symbiosis. Iden ...
Biology Study Guide - Barnstable Academy
... 9. A scientist discovers an important breakthrough in cancer treatment. The scientist thinks the information could save thousands of lives and immediately announces the results on national television, skipping peer review. How might other scientists react to this news? a. They will be skeptical beca ...
... 9. A scientist discovers an important breakthrough in cancer treatment. The scientist thinks the information could save thousands of lives and immediately announces the results on national television, skipping peer review. How might other scientists react to this news? a. They will be skeptical beca ...
Theoretical ecology

Theoretical ecology is the scientific discipline devoted to the study of ecological systems using theoretical methods such as simple conceptual models, mathematical models, computational simulations, and advanced data analysis. Effective models improve understanding of the natural world by revealing how the dynamics of species populations are often based on fundamental biological conditions and processes. Further, the field aims to unify a diverse range of empirical observations by assuming that common, mechanistic processes generate observable phenomena across species and ecological environments. Based on biologically realistic assumptions, theoretical ecologists are able to uncover novel, non-intuitive insights about natural processes. Theoretical results are often verified by empirical and observational studies, revealing the power of theoretical methods in both predicting and understanding the noisy, diverse biological world.The field is broad and includes foundations in applied mathematics, computer science, biology, statistical physics, genetics, chemistry, evolution, and conservation biology. Theoretical ecology aims to explain a diverse range of phenomena in the life sciences, such as population growth and dynamics, fisheries, competition, evolutionary theory, epidemiology, animal behavior and group dynamics, food webs, ecosystems, spatial ecology, and the effects of climate change.Theoretical ecology has further benefited from the advent of fast computing power, allowing the analysis and visualization of large-scale computational simulations of ecological phenomena. Importantly, these modern tools provide quantitative predictions about the effects of human induced environmental change on a diverse variety of ecological phenomena, such as: species invasions, climate change, the effect of fishing and hunting on food network stability, and the global carbon cycle.