Chapter 8 & 9 Review
... • A) the most developed countries • B) the least developed countries • C) countries in the second stage of demographic transition ...
... • A) the most developed countries • B) the least developed countries • C) countries in the second stage of demographic transition ...
ECOLOGY- (population growth) notes
... 1. Some ecologists study populations and monitor the sizes of populations over time. 2. Populations change in size when new members join the population (through birth or immigration) or when members leave the population (through death or emigration). 3. If birth rate > death rate, population size in ...
... 1. Some ecologists study populations and monitor the sizes of populations over time. 2. Populations change in size when new members join the population (through birth or immigration) or when members leave the population (through death or emigration). 3. If birth rate > death rate, population size in ...
Chapter 35
... growth? Population limiting factors - environmental factors that restrict population growth Human Population We have a major problem here. What is our future? The number one problem on this planet for humans and many, many other species is our own overpopulation. What is the solution? ...
... growth? Population limiting factors - environmental factors that restrict population growth Human Population We have a major problem here. What is our future? The number one problem on this planet for humans and many, many other species is our own overpopulation. What is the solution? ...
EVPP 111 Lecture - Exam #1 Study Guide
... • explain what is meant by the "diversity" of a community and why it is important • what are the two components of community diversity? • explain what is meant by "species richness" of a community • explain what is meant by "relative abundance of different species" in a community • explain what is m ...
... • explain what is meant by the "diversity" of a community and why it is important • what are the two components of community diversity? • explain what is meant by "species richness" of a community • explain what is meant by "relative abundance of different species" in a community • explain what is m ...
Ecological Reference Points for Forage Species
... MSY level for data poor stocks, or when there is a high degree of uncertainty about stock status, is F=M or where F is a fraction of M, e.g., F=0.75M. xxiii It is commonly assumed that when harvesting at MSY, F is roughly equal to M, so this is an FMSY proxy. If the goal is to maintain a higher biom ...
... MSY level for data poor stocks, or when there is a high degree of uncertainty about stock status, is F=M or where F is a fraction of M, e.g., F=0.75M. xxiii It is commonly assumed that when harvesting at MSY, F is roughly equal to M, so this is an FMSY proxy. If the goal is to maintain a higher biom ...
Examining the Stages in Ecological Succession
... The relationship is that of predation. One primary consumer feeding on the producer and a secondary consumer(carnivore) feeding on the primary consumer(herbivore). Q3. Which organisms are producers, and which are consumers? Nitella is the aquatic producer. Snails are primary consumers and minnows ar ...
... The relationship is that of predation. One primary consumer feeding on the producer and a secondary consumer(carnivore) feeding on the primary consumer(herbivore). Q3. Which organisms are producers, and which are consumers? Nitella is the aquatic producer. Snails are primary consumers and minnows ar ...
1 www.protectingusnow.org Speaker notes for Invasive Species and
... Population growth – is the change in the number of individuals that make up a particular population over time. Population growth can be positive or negative. For example, if a population was 60 one year and 70 the next year, then we would say that the population growth is positive 9it has increased) ...
... Population growth – is the change in the number of individuals that make up a particular population over time. Population growth can be positive or negative. For example, if a population was 60 one year and 70 the next year, then we would say that the population growth is positive 9it has increased) ...
Study Questions - Geocycles, communities, populations
... 5. What is exponential growth of populations? What shape does this growth curve often take? Be able to draw, label, and explain a graph of exponential growth. 6. What is logistic growth? What does a graph of this type of growth look like? Be able to draw, label, and explain a graph of this type. 7. ...
... 5. What is exponential growth of populations? What shape does this growth curve often take? Be able to draw, label, and explain a graph of exponential growth. 6. What is logistic growth? What does a graph of this type of growth look like? Be able to draw, label, and explain a graph of this type. 7. ...
5–2 Limits to Growth
... response to such factors, many species show a characteristic crash in population size. After the crash, the population may soon build up again, or it may stay low for some time. For some species, storms or hurricanes can nearly extinguish a population. For example, thrips, aphids, and other insects ...
... response to such factors, many species show a characteristic crash in population size. After the crash, the population may soon build up again, or it may stay low for some time. For some species, storms or hurricanes can nearly extinguish a population. For example, thrips, aphids, and other insects ...
NOTES ON BIO 201 – GENERAL ECOLOGY INTRODUCTION
... their respective trophic (feeding) levels they naturally sort into a PYRAMID OF NUMBERS . One of the several patterns that is repeated amongst the planet’s ecosystems is the emergent pyramidal arrangement or trophic levels with amounts of energy transfer decreasing as species become further removed ...
... their respective trophic (feeding) levels they naturally sort into a PYRAMID OF NUMBERS . One of the several patterns that is repeated amongst the planet’s ecosystems is the emergent pyramidal arrangement or trophic levels with amounts of energy transfer decreasing as species become further removed ...
Row
... predator species would not show population changes caused by density-dependent factors low numbers of caribou would cause wolf starvation if the moose population was also low wolf and prey population would decline as the same diseases spread through the three populations an area would have the same ...
... predator species would not show population changes caused by density-dependent factors low numbers of caribou would cause wolf starvation if the moose population was also low wolf and prey population would decline as the same diseases spread through the three populations an area would have the same ...
Natural Selection
... individuals within a population must face a struggle for survival, and that only a few individuals need to survive to pass on their characteristics to the next generation. The rest fail to develop; die of starvation, predation, or other causes before they reproduce; or do not reproduce for other rea ...
... individuals within a population must face a struggle for survival, and that only a few individuals need to survive to pass on their characteristics to the next generation. The rest fail to develop; die of starvation, predation, or other causes before they reproduce; or do not reproduce for other rea ...
ecologyexam-mentor08..
... 2. What type of growth pattern is exhibited by the fruit fly population? ___________________ 3. What type of growth pattern is exhibited by the rabbit population? _____________________ 4. Does either graph indicate that there is a carrying capacity for the population? If so, which population? ______ ...
... 2. What type of growth pattern is exhibited by the fruit fly population? ___________________ 3. What type of growth pattern is exhibited by the rabbit population? _____________________ 4. Does either graph indicate that there is a carrying capacity for the population? If so, which population? ______ ...
the publication
... more coefficients of the initial matrix and calculating the dominant latent root for the new matrix. There are many examples of the use of matrices to model the demography of tropical trees, see Hartshorn, 1975; Enright and Ogden, 1979; Peters, 1991; Debroux, 1998. With these models, the sustainabil ...
... more coefficients of the initial matrix and calculating the dominant latent root for the new matrix. There are many examples of the use of matrices to model the demography of tropical trees, see Hartshorn, 1975; Enright and Ogden, 1979; Peters, 1991; Debroux, 1998. With these models, the sustainabil ...
ap biology notes on ecology
... Factors that influence the distribution of species: o Behavior and habitat selection – Certain behaviors like mating, reproduction, nest building habits, etc. can eliminate habitats that otherwise would be very suitable. (ex. European corn borer only deposits its eggs on corn although they eat a w ...
... Factors that influence the distribution of species: o Behavior and habitat selection – Certain behaviors like mating, reproduction, nest building habits, etc. can eliminate habitats that otherwise would be very suitable. (ex. European corn borer only deposits its eggs on corn although they eat a w ...
Chapter 52: An Introduction to Ecology and the
... graph, add a third line that approximates a population with an exponential value of 1.25. ...
... graph, add a third line that approximates a population with an exponential value of 1.25. ...
Ecosystems are always changing.
... Patterns of Change All types of ecosystems go through succession. Succession can establish a forest community, a wetland community, a coastal community, or even an ocean community. Succession can happen over tens or hundreds of years. The pattern is the same, however. First a community of producers ...
... Patterns of Change All types of ecosystems go through succession. Succession can establish a forest community, a wetland community, a coastal community, or even an ocean community. Succession can happen over tens or hundreds of years. The pattern is the same, however. First a community of producers ...
View PDF
... Patterns of Change All types of ecosystems go through succession. Succession can establish a forest community, a wetland community, a coastal community, or even an ocean community. Succession can happen over tens or hundreds of years. The pattern is the same, however. First a community of producers ...
... Patterns of Change All types of ecosystems go through succession. Succession can establish a forest community, a wetland community, a coastal community, or even an ocean community. Succession can happen over tens or hundreds of years. The pattern is the same, however. First a community of producers ...
Chapter 4 - OneOcean.org
... economic profit. MSY corresponds to a higher level of effort; but where profits are less and fish catch is sustainable through time. Lastly, the OAE level is the point where cost and revenues are equal, profits are zero and catch rates are not sustainable. At this point, there are too many fishers ( ...
... economic profit. MSY corresponds to a higher level of effort; but where profits are less and fish catch is sustainable through time. Lastly, the OAE level is the point where cost and revenues are equal, profits are zero and catch rates are not sustainable. At this point, there are too many fishers ( ...
Chapter 14 Study Guide A-Answers
... MAIN IDEA: Survivorship curves help to describe the reproductive strategy of a species. Fill in the blank with the term or phrase that best completes the sentence. ...
... MAIN IDEA: Survivorship curves help to describe the reproductive strategy of a species. Fill in the blank with the term or phrase that best completes the sentence. ...
Consumer-Resource Interactions II
... rather, this boost gets transmitted to the predator population. This was confirmed by studies of bacteria and phage (virus that infects bacteria) e. Criticisms of the Model - instantaneous response with no time lags – biologically unrealistic. - no density dependence in prey, even at low predator de ...
... rather, this boost gets transmitted to the predator population. This was confirmed by studies of bacteria and phage (virus that infects bacteria) e. Criticisms of the Model - instantaneous response with no time lags – biologically unrealistic. - no density dependence in prey, even at low predator de ...
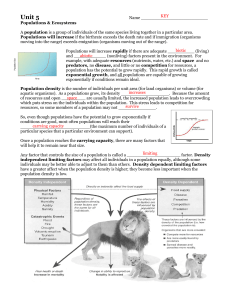
Unit 5 - kehsscience.org
... Population density is the number of individuals per unit area (for land organisms) or volume (for increases aquatic organisms). As a populations grow, its density __________________. Because the amount space of resources and open _________ are usually limited, the increased population leads to overc ...
... Population density is the number of individuals per unit area (for land organisms) or volume (for increases aquatic organisms). As a populations grow, its density __________________. Because the amount space of resources and open _________ are usually limited, the increased population leads to overc ...
Multiple Choice Review – Ecology Which level of biological
... 10,000 J of energy stored in primary producers, what is the production efficiency of the primary producers? 5. Production efficiency varies by organism. Birds have a production efficiency of about 1% while fish are more efficient at 10%. Insects have even higher production efficiencies at 40%. If 20 ...
... 10,000 J of energy stored in primary producers, what is the production efficiency of the primary producers? 5. Production efficiency varies by organism. Birds have a production efficiency of about 1% while fish are more efficient at 10%. Insects have even higher production efficiencies at 40%. If 20 ...
Carrying capacity reconsidered
... the environment, they argued, it was possible to understand how species might persist even though their populations fluctuated. Andrewartha and Birch supported their case with meticulously gathered empirical data, while Nicholson, who was primarily a theorist, presented little data in support of his ...
... the environment, they argued, it was possible to understand how species might persist even though their populations fluctuated. Andrewartha and Birch supported their case with meticulously gathered empirical data, while Nicholson, who was primarily a theorist, presented little data in support of his ...
Study Guide B - Fort Bend ISD
... Choose a word from the box below that best completes each sentence. ...
... Choose a word from the box below that best completes each sentence. ...