Proteins
... • Excess protein cannot be stored and is converted into glucose or fat for later use. • Athletes who are highly trained for endurance activities may need to exceed the RDA for protein. ...
... • Excess protein cannot be stored and is converted into glucose or fat for later use. • Athletes who are highly trained for endurance activities may need to exceed the RDA for protein. ...
05 Cell Respiration Fermentation Anaerobic and
... • Glycolysis accepts a wide range of carbohydrates • Proteins must be digested to amino acids; amino groups can feed glycolysis or the citric acid cycle ...
... • Glycolysis accepts a wide range of carbohydrates • Proteins must be digested to amino acids; amino groups can feed glycolysis or the citric acid cycle ...
Information on Formula
... Formula FS-72 is the flag ship sports food of elite company ATHLETES ADVANTAGE PTY LTD. Exclusive line up of products .FS-72 is a natural food containing vitamins, minerals, proteins and omega 3 and 6. FS-72 can be used by beginners , athletes and body builders. FS-72 can be used for weight lose thr ...
... Formula FS-72 is the flag ship sports food of elite company ATHLETES ADVANTAGE PTY LTD. Exclusive line up of products .FS-72 is a natural food containing vitamins, minerals, proteins and omega 3 and 6. FS-72 can be used by beginners , athletes and body builders. FS-72 can be used for weight lose thr ...
Chemistry 1. The Periodic Table displays the
... the energy release per gram of material interacting is very large in nuclear processes compared to that in chemical processes. The corresponding change in mass (calculated by E=mc2) is small but significant in nuclear processes. c. many naturally occurring isotopes of elements are radioactive, as ar ...
... the energy release per gram of material interacting is very large in nuclear processes compared to that in chemical processes. The corresponding change in mass (calculated by E=mc2) is small but significant in nuclear processes. c. many naturally occurring isotopes of elements are radioactive, as ar ...
Energy Systems
... (B) When phosphocreatine is broken down during muscular contraction, a large amount of energy is released. The energy released is coupled with the energy requirement to resynthesize ATP. PC is an abbreviation for phosphocreatine. PC, like ATP, is stored in the muscle cells, and when it is broken dow ...
... (B) When phosphocreatine is broken down during muscular contraction, a large amount of energy is released. The energy released is coupled with the energy requirement to resynthesize ATP. PC is an abbreviation for phosphocreatine. PC, like ATP, is stored in the muscle cells, and when it is broken dow ...
Cell Energy (Photosynthesis and Respiration) Notes
... Examples: plants + some microorganisms (bacteria and protists) ...
... Examples: plants + some microorganisms (bacteria and protists) ...
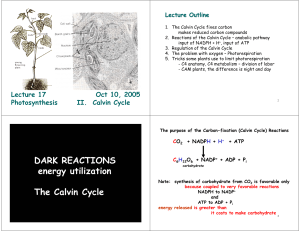
DARK REACTIONS energy utilization The Calvin Cycle
... 3. Rubisco enzyme regulated tightly by allosteric modulators pH, and reducing status of stroma 4. O2 interferes with carbon fixation by Rubisco enzyme ...
... 3. Rubisco enzyme regulated tightly by allosteric modulators pH, and reducing status of stroma 4. O2 interferes with carbon fixation by Rubisco enzyme ...
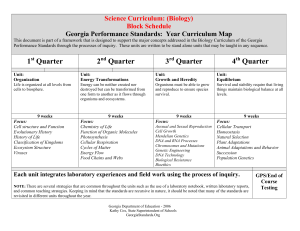
Curriculum Map - Biology
... Georgia Performance Standards: Year Curriculum Map This document is part of a framework that is designed to support the major concepts addressed in the Biology Curriculum of the Georgia Performance Standards through the processes of inquiry. These units are written to be stand alone units that may b ...
... Georgia Performance Standards: Year Curriculum Map This document is part of a framework that is designed to support the major concepts addressed in the Biology Curriculum of the Georgia Performance Standards through the processes of inquiry. These units are written to be stand alone units that may b ...
Healthy pigs with less use of antibiotics
... this ideal amino acid profile as close as possible. The amino acids in the diet are supplied via protein feedstuffs and feed grade amino acids. Today we have the first five limiting amino acids (lysine, threonine, methionine, tryptophan and valine) available in free feed grade form. These feed grade ...
... this ideal amino acid profile as close as possible. The amino acids in the diet are supplied via protein feedstuffs and feed grade amino acids. Today we have the first five limiting amino acids (lysine, threonine, methionine, tryptophan and valine) available in free feed grade form. These feed grade ...
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
... Proteins are responsible for controlling many different processes in our bodies. As enzymes they break things down, put things together, catalyze chemical reactions, they make pigments, they form antigens and antibodies, give structure to cells and membranes, transport substances in cells and across ...
... Proteins are responsible for controlling many different processes in our bodies. As enzymes they break things down, put things together, catalyze chemical reactions, they make pigments, they form antigens and antibodies, give structure to cells and membranes, transport substances in cells and across ...
Modes of Macromolecular Classification
... But how are we to understand tertiary structure? We might abstract away from the peptide bonds (the links between individual amino acids) and think of a protein’s three-dimensional structure as simply the relative location of individual amino acids (in the manner we think of a crystalline structure ...
... But how are we to understand tertiary structure? We might abstract away from the peptide bonds (the links between individual amino acids) and think of a protein’s three-dimensional structure as simply the relative location of individual amino acids (in the manner we think of a crystalline structure ...
Section 6.1 Summary – pages 141-151
... • Everything – whether it is a rock, frog, or flower – is made of substances called elements. ...
... • Everything – whether it is a rock, frog, or flower – is made of substances called elements. ...
Cellular Respiration notes
... • 2nd law- Some usable energy is lost during transformations. During changes from one form of energy to another, some usable energy is lost, usually as heat. The amount of usable energy therefore decreases. ...
... • 2nd law- Some usable energy is lost during transformations. During changes from one form of energy to another, some usable energy is lost, usually as heat. The amount of usable energy therefore decreases. ...
Ribosomes and The Golgi Apparatus
... on the E.R. break off in transport vesicles (made of E.R. membrane) and travel to the golgi apparatus. A vesicle is a membrane bound storage unit like a vacuole, but it is meant for transporting molecules around the cell ...
... on the E.R. break off in transport vesicles (made of E.R. membrane) and travel to the golgi apparatus. A vesicle is a membrane bound storage unit like a vacuole, but it is meant for transporting molecules around the cell ...
©2011 The Simple Homeschool – Simple Days Unit Studies
... take about a day to replenish the storage of energy you just used. Both starch and glycogen are polysaccharides used for storage, but cellulose is used for structure. Cellulose is a major cell wall component of plants. Cellulose is not digestible by humans, but herbivores such as cows, deer, and hor ...
... take about a day to replenish the storage of energy you just used. Both starch and glycogen are polysaccharides used for storage, but cellulose is used for structure. Cellulose is a major cell wall component of plants. Cellulose is not digestible by humans, but herbivores such as cows, deer, and hor ...
Entrance Syllabus for Pre-Ph.D. (Plant Physiology) –HAPPRC 1
... structure and functions. Water and its role in plants, properties and functions of water in the cell, water relations, water potential of plant cells. 2. Energy flow: Principles of thermodynamics, free energy and chemical potential, redox reactions, structure and functions of ATP 3. Fundamentals of ...
... structure and functions. Water and its role in plants, properties and functions of water in the cell, water relations, water potential of plant cells. 2. Energy flow: Principles of thermodynamics, free energy and chemical potential, redox reactions, structure and functions of ATP 3. Fundamentals of ...
September 27 AP Biology - John D. O`Bryant School of Math & Science
... Do Now (Quiz) Five dialysis bags, constructed from a semi-permeable membrane that is impermeable to sucrose, were filled with various concentrations of sucrose and then placed in separate beakers containing an initial concentration of 0.6 M sucrose solution. At 10-minute intervals, the bags were ...
... Do Now (Quiz) Five dialysis bags, constructed from a semi-permeable membrane that is impermeable to sucrose, were filled with various concentrations of sucrose and then placed in separate beakers containing an initial concentration of 0.6 M sucrose solution. At 10-minute intervals, the bags were ...
Pre-post test questions
... 15. Individuals with the diseases -thalassemia and sickle cell anemia both have mutations in the gene for hemoglobin. How could mutations in the same gene cause two different disease phenotypes? The different mutations in the DNA would cause different amino acids to be changed in the protein. The ...
... 15. Individuals with the diseases -thalassemia and sickle cell anemia both have mutations in the gene for hemoglobin. How could mutations in the same gene cause two different disease phenotypes? The different mutations in the DNA would cause different amino acids to be changed in the protein. The ...
pdf-3MB - UW Courses Web Server
... ice. First, almost all ionic impurities are insoluble in the crystal structure of ice, which leads to a network of micron-diameter veins in which microorganisms may utilize ions for metabolism. Second, ice in contact with mineral surfaces develops a nanometrethick film of unfrozen water that provide ...
... ice. First, almost all ionic impurities are insoluble in the crystal structure of ice, which leads to a network of micron-diameter veins in which microorganisms may utilize ions for metabolism. Second, ice in contact with mineral surfaces develops a nanometrethick film of unfrozen water that provide ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.