Practice Questions
... A really bad doctor took X-Rays of a patient’s leg. The doctor didn’t give the patient a protective lead apron to wear over the genital region and the patient’s gametes (sperm or egg cells) were severely mutated as a result of the high powered rays. Will this mutation be passed down the offspring? T ...
... A really bad doctor took X-Rays of a patient’s leg. The doctor didn’t give the patient a protective lead apron to wear over the genital region and the patient’s gametes (sperm or egg cells) were severely mutated as a result of the high powered rays. Will this mutation be passed down the offspring? T ...
Electron-Transport Chain and ATP production
... Occurs in the inner mitochondrial membrane where NADH and FADH2 are oxidized back to NAD+ and FAD. They transfer their e- in a series of steps and ultimately to O2: O2 + 4e- + 4H+ → 2H2O The energy released in these e- transfers is used to pump H+ (protons) out of the matrix into the intermembrane s ...
... Occurs in the inner mitochondrial membrane where NADH and FADH2 are oxidized back to NAD+ and FAD. They transfer their e- in a series of steps and ultimately to O2: O2 + 4e- + 4H+ → 2H2O The energy released in these e- transfers is used to pump H+ (protons) out of the matrix into the intermembrane s ...
CAPE CHEMISTRY UNIT TWO REVISION PAPER MODULE 1 (a
... [2 marks] In partition chromatography the solutes are partitioned between the mobile phase and a thin film of liquid (commonly water) firmly absorbed on the surface of the stationary phase. Stationary phase: paper - cellulose fibre composed of glucose molecules, which have a large number of hydroxyl ...
... [2 marks] In partition chromatography the solutes are partitioned between the mobile phase and a thin film of liquid (commonly water) firmly absorbed on the surface of the stationary phase. Stationary phase: paper - cellulose fibre composed of glucose molecules, which have a large number of hydroxyl ...
Pharos university Faculty of Allied Medical SCIENCE Biochemistry 1
... bonded to an amino group (-NH2), a carboxyl group (-COOH), a hydrogen atom, and a fourth group that differs from one amino acid to another and often is referred to as the-R group or the side chain. ...
... bonded to an amino group (-NH2), a carboxyl group (-COOH), a hydrogen atom, and a fourth group that differs from one amino acid to another and often is referred to as the-R group or the side chain. ...
EXCRETION
... ammonia to less toxic urea and the nontoxic uric acid. 3. excretion maintains homeostasis by regulating the chemistry of body fluids and maintaining body temperature. ...
... ammonia to less toxic urea and the nontoxic uric acid. 3. excretion maintains homeostasis by regulating the chemistry of body fluids and maintaining body temperature. ...
answer key
... iv. oxaloacetate (C4) cannot be made into pyruvate (C3) v. a molecule of oxaloacetate (C4) is consumed when acetyl CoA enters the Krebs cycle so that the oxaloacetate produced only replaces the one that was consumed -- CORRECT R. Membrane-spanning regions of proteins generally i. are about five amin ...
... iv. oxaloacetate (C4) cannot be made into pyruvate (C3) v. a molecule of oxaloacetate (C4) is consumed when acetyl CoA enters the Krebs cycle so that the oxaloacetate produced only replaces the one that was consumed -- CORRECT R. Membrane-spanning regions of proteins generally i. are about five amin ...
Fermentation Pre-test/Post-test
... SC.912.L.18.8 Identify the reactants, products, and basic functions of aerobic and anaerobic cellular respiration. SC.912.L.18.9 Explain the interrelated nature of photosynthesis and cellular respiration. SC.912.N.1.1 Define a problem based on specific body of knowledge and perform scientific method ...
... SC.912.L.18.8 Identify the reactants, products, and basic functions of aerobic and anaerobic cellular respiration. SC.912.L.18.9 Explain the interrelated nature of photosynthesis and cellular respiration. SC.912.N.1.1 Define a problem based on specific body of knowledge and perform scientific method ...
Citric Acid Cycle (CAC) - LSU School of Medicine
... • Pyruvate (actually the acetyl group) from glycolysis is degraded to CO2 – The acetyl group is formed in stage II of metabolism from carbohydrate and amino acid metabolism ...
... • Pyruvate (actually the acetyl group) from glycolysis is degraded to CO2 – The acetyl group is formed in stage II of metabolism from carbohydrate and amino acid metabolism ...
Bio 201, Fall 2010 Test 3 Study Guide Questions to be able to
... 12. What is the purpose of chemical communication between cells? 13. What are the steps in signal transduction? 14. What things make receptors bind to specific ligands? 15. What kinds of conditions result in high and low ligand/receptor affinity? 16. What is the dissociation constant? As the dissoci ...
... 12. What is the purpose of chemical communication between cells? 13. What are the steps in signal transduction? 14. What things make receptors bind to specific ligands? 15. What kinds of conditions result in high and low ligand/receptor affinity? 16. What is the dissociation constant? As the dissoci ...
Metabolic System and Exercise
... from glucose to be stored in the liver Glycogenolysis—Process by which glycogen is broken into glucose-1-phosphate to be used by muscles ...
... from glucose to be stored in the liver Glycogenolysis—Process by which glycogen is broken into glucose-1-phosphate to be used by muscles ...
PEPCK: a model of eukaryotic gene expression
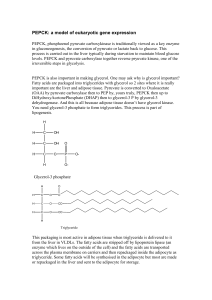
... Glycerol-3 P demand would be highest in the adipocyte in a fed state when there are lots of fatty acids to be repackaged. Glycerol-3 P is made in the liver by glycerol kinase, perhaps because that produced by glycolysis is being rapidly converted to pyruvate for fatty acid synthesis and the glycero ...
... Glycerol-3 P demand would be highest in the adipocyte in a fed state when there are lots of fatty acids to be repackaged. Glycerol-3 P is made in the liver by glycerol kinase, perhaps because that produced by glycolysis is being rapidly converted to pyruvate for fatty acid synthesis and the glycero ...
Chapter 2
... The pH of the fluids within most cells in the human body must generally be kept between ______________ in order to maintain _________. If the pH is lower or higher, it will affect the chemical reactions that take place within the cells. One of the ways that organisms control pH is through dissolved ...
... The pH of the fluids within most cells in the human body must generally be kept between ______________ in order to maintain _________. If the pH is lower or higher, it will affect the chemical reactions that take place within the cells. One of the ways that organisms control pH is through dissolved ...
GLYCOLYSIS
... • Provide the cell with usable energy as ATP • Cells with high energy demands make more mitochondria • Muscle cells have very high number of mitochondria • We breath to get oxygen to our mitochondria and to to rid ourselves of the carbon dioxide the mitochondria produce • The blood carries these gas ...
... • Provide the cell with usable energy as ATP • Cells with high energy demands make more mitochondria • Muscle cells have very high number of mitochondria • We breath to get oxygen to our mitochondria and to to rid ourselves of the carbon dioxide the mitochondria produce • The blood carries these gas ...
Cell Respiration SAT II Review
... To ATP in order to perform work (ATP is form of chemical energy that is usable by the cell). ...
... To ATP in order to perform work (ATP is form of chemical energy that is usable by the cell). ...
Central Dogma of Genetics
... • Building blocks are Amino acids • AA’s are joined between the carboxyl end of one AA to the amino group of the other – One water molecule is lost – Enzyme called peptidyl transferase is ...
... • Building blocks are Amino acids • AA’s are joined between the carboxyl end of one AA to the amino group of the other – One water molecule is lost – Enzyme called peptidyl transferase is ...
Ch_2-3 review2012
... Know how polymers are constructed and broken down-specific reaction, different types of polymers ...
... Know how polymers are constructed and broken down-specific reaction, different types of polymers ...
Presentation
... glycogenolysis. These processes are regulated by the pancreas, intestine, liver, kidneys and muscle. Hyperglycaemia can result from disruption of the hormones involved in glucose regulation such as insulin or glucagon or from dysfunction of the organs involved in glucose homeostasis. ...
... glycogenolysis. These processes are regulated by the pancreas, intestine, liver, kidneys and muscle. Hyperglycaemia can result from disruption of the hormones involved in glucose regulation such as insulin or glucagon or from dysfunction of the organs involved in glucose homeostasis. ...
Protein Structure
... each part of the polypeptide chain can participate in (see Figure 4 and Table II). Only charged polar groups can form ionic bonds (the strongest type of noncovalent bond). Within the physiological range of pH (pH 5 – 8), the charged polar groups in proteins include the N terminus and C terminus as w ...
... each part of the polypeptide chain can participate in (see Figure 4 and Table II). Only charged polar groups can form ionic bonds (the strongest type of noncovalent bond). Within the physiological range of pH (pH 5 – 8), the charged polar groups in proteins include the N terminus and C terminus as w ...
BIOL 313: Introduction to Biochemistry
... AN UNDERLYING SIMPLICITY AND ELEGANCE: - Most biological compounds are made of only SIX elements: C, H, O, N, P, S - Only 31 chemical elements occur naturally in plants and animals - All organisms have similar biochemical pathways. - All organisms use the - Limited number of molecular building block ...
... AN UNDERLYING SIMPLICITY AND ELEGANCE: - Most biological compounds are made of only SIX elements: C, H, O, N, P, S - Only 31 chemical elements occur naturally in plants and animals - All organisms have similar biochemical pathways. - All organisms use the - Limited number of molecular building block ...
Exam Name___________________________________
... A) The triacylglycerols are less soluble in water than the carbohydrates. B) The carbohydrates contain fewer carbon-carbon bonds. C) The carbohydrates are already in a more oxidized state than the triacylglycerols. D) The triacylglycerols have an extremely high group transfer potential. ...
... A) The triacylglycerols are less soluble in water than the carbohydrates. B) The carbohydrates contain fewer carbon-carbon bonds. C) The carbohydrates are already in a more oxidized state than the triacylglycerols. D) The triacylglycerols have an extremely high group transfer potential. ...
In Vitro Protein Synthesis of Perdeuterated Proteins for NMR Studies
... It is well documented that high levels of deuteration are indispensable for solution NMR studies of polypeptides in structures of sizes above 40 kDa (Fiaux et al., 2002; LeMaster 1989; Pachter et al. 1992). In addition to studies on protein structure and dynamics, obtaining a perdeuterated backgroun ...
... It is well documented that high levels of deuteration are indispensable for solution NMR studies of polypeptides in structures of sizes above 40 kDa (Fiaux et al., 2002; LeMaster 1989; Pachter et al. 1992). In addition to studies on protein structure and dynamics, obtaining a perdeuterated backgroun ...
summary slides
... A population of cells with similar characteristics Clone: A population of cells derived from a single cell Strain: A subgroup within a species with one or more characteristics that distinguish it from other subgroups in the species ...
... A population of cells with similar characteristics Clone: A population of cells derived from a single cell Strain: A subgroup within a species with one or more characteristics that distinguish it from other subgroups in the species ...
Exam I Cell and Molecular Biology September 26, 2007 This exam
... complex cellular extract by absorption to an antibody that binds that protein specifically. Antibodies bind proteins based on molecular complementarity through a variety of noncovalent interactions. Name three noncovalent bonds that might mediate antibody-protein binding. Suggest three mechanisms to ...
... complex cellular extract by absorption to an antibody that binds that protein specifically. Antibodies bind proteins based on molecular complementarity through a variety of noncovalent interactions. Name three noncovalent bonds that might mediate antibody-protein binding. Suggest three mechanisms to ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.