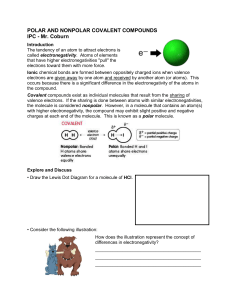
Polar and Nonpolar Covalent Compounds
... electrons toward them with more force. Ionic chemical bonds are formed between oppositely charged ions when valence electrons are given away by one atom and received by another atom (or atoms). This occurs because there is a significant difference in the electronegativity of the atoms in the compoun ...
... electrons toward them with more force. Ionic chemical bonds are formed between oppositely charged ions when valence electrons are given away by one atom and received by another atom (or atoms). This occurs because there is a significant difference in the electronegativity of the atoms in the compoun ...
Carbohydrate Metabolism-1
... In glycogenolysis, glycogen stored in the liver and muscles, is converted first to glucose-1- phosphate and then into glucose-6-phosphate. Two hormones which control glycogenolysis are a peptide, glucagon from the pancreas and epinephrine from the adrenal glands. Glucagon is released from the pancre ...
... In glycogenolysis, glycogen stored in the liver and muscles, is converted first to glucose-1- phosphate and then into glucose-6-phosphate. Two hormones which control glycogenolysis are a peptide, glucagon from the pancreas and epinephrine from the adrenal glands. Glucagon is released from the pancre ...
26.9 Purines ond pyrimidines ,,,,,f sr`-c
... Organisms need to synthesizepurine and pyrimidine basesfor incorporation into the nucleic acids RNA and DNA. Moreover, nucleosides such as adenosine are found as part of ATB cyclic AMf; CoA (coenzymeA), NAD+ (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide), and FAD (flavin adenine dinucleotide). The atoms that c ...
... Organisms need to synthesizepurine and pyrimidine basesfor incorporation into the nucleic acids RNA and DNA. Moreover, nucleosides such as adenosine are found as part of ATB cyclic AMf; CoA (coenzymeA), NAD+ (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide), and FAD (flavin adenine dinucleotide). The atoms that c ...
Searching for Genes
... sequences. So, when the Roberts lab began studying the evolution of cellulose synthesis, one place they looked was at the available DNA sequence information. Even now, as they expand their studies to include additional species of plants and algae, this is where they start. Cellulose is an important ...
... sequences. So, when the Roberts lab began studying the evolution of cellulose synthesis, one place they looked was at the available DNA sequence information. Even now, as they expand their studies to include additional species of plants and algae, this is where they start. Cellulose is an important ...
Microbial nutrition
... Microbial cell require a basic nutrient elements for growth and replication as fallow : 1- Microbial cell composition is made up of few major elements like carbon , oxygen , hydrogen, nitrogen , sulfur , phosphorus , potassium , calcium, magnesium and iron are called macro elements because they are ...
... Microbial cell require a basic nutrient elements for growth and replication as fallow : 1- Microbial cell composition is made up of few major elements like carbon , oxygen , hydrogen, nitrogen , sulfur , phosphorus , potassium , calcium, magnesium and iron are called macro elements because they are ...
Chapter 5 : MAJOR METABOLIC PATHWAYS
... of photosynthesis happens, and on the other hand this photosynthesis makes it possible with the passage of time on earth to accumulate free oxygen in the earth's atmosphere making possible the evolution of respiration. Respiration is important for bioenergetics as it stores the energy to form a mole ...
... of photosynthesis happens, and on the other hand this photosynthesis makes it possible with the passage of time on earth to accumulate free oxygen in the earth's atmosphere making possible the evolution of respiration. Respiration is important for bioenergetics as it stores the energy to form a mole ...
Session 11 nr. 1 - Nordic Congress in Clinical Biochemistry 2016
... The gut hormone, cholecystokinin (CCK), was discovered in 1928 as a gallbladder contractor. In 1968 the structure was identified as a 33 amino acid peptide with a C-terminal “active site” sequence that revealed close homology with that of gastrin. Later the CCK gene has been shown to be expressed at ...
... The gut hormone, cholecystokinin (CCK), was discovered in 1928 as a gallbladder contractor. In 1968 the structure was identified as a 33 amino acid peptide with a C-terminal “active site” sequence that revealed close homology with that of gastrin. Later the CCK gene has been shown to be expressed at ...
Nitrogen Metabolism - Oregon State University
... Nitrosamines in Tobacco Form From Nicotine NNK is Nicotine Derived and Important in Carcinogenesis NNK in Tobacco and E-cigarettes NNK Activation by P-450 Activated Signaling Cascades & Uncontrolled Growth ...
... Nitrosamines in Tobacco Form From Nicotine NNK is Nicotine Derived and Important in Carcinogenesis NNK in Tobacco and E-cigarettes NNK Activation by P-450 Activated Signaling Cascades & Uncontrolled Growth ...
How do living things take in nutrients, breathe, and
... Proteins are a major component of most tissues including muscles, bodily organs, and cells. ...
... Proteins are a major component of most tissues including muscles, bodily organs, and cells. ...
Matabolic Stoichiometry and Energetics in
... In order to grow and reproduce, cells must ingest the raw materials necessary to manufacture membrane, protein, walls, chromosomes and other components Four major requirements are evident: – carbon, nitrogen, sulfur and phosphorus ...
... In order to grow and reproduce, cells must ingest the raw materials necessary to manufacture membrane, protein, walls, chromosomes and other components Four major requirements are evident: – carbon, nitrogen, sulfur and phosphorus ...
LESSON 2.5 WORKBOOK Blood glucose in sleep, a 5 mile
... Using the things we have explored throughout Unit 2, in this lesson we will expand upon our knowledge of how the metabolic pathways affect specific body systems. We will focus on which organs are primarily involved in each metabolic pathway, and relate this to how the body maintains blood glucose ho ...
... Using the things we have explored throughout Unit 2, in this lesson we will expand upon our knowledge of how the metabolic pathways affect specific body systems. We will focus on which organs are primarily involved in each metabolic pathway, and relate this to how the body maintains blood glucose ho ...
energy - Old Saybrook Public Schools
... which enter glycolysis. Lipids break down to fatty acids and glycerol. Fatty acids can be converted to acetyl CoA. Proteins are hydrolyzed to amino acids that can feed into glycolysis or the citric acid cycle. ...
... which enter glycolysis. Lipids break down to fatty acids and glycerol. Fatty acids can be converted to acetyl CoA. Proteins are hydrolyzed to amino acids that can feed into glycolysis or the citric acid cycle. ...
The Science of Classification
... the chemistry of blood, enzymes and other specific substances produced by animals and plants. Example The hemoglobins in the blood cells of gorillas and humans are the same except for one ...
... the chemistry of blood, enzymes and other specific substances produced by animals and plants. Example The hemoglobins in the blood cells of gorillas and humans are the same except for one ...
Study Guide for Exam 1 Dr. Osborne
... Amino acids have carbon with an amino group, a carboxyl group, hydrogen and a side chain ii. - There are about-20 different side chains therefore about 20 differentaminoacids - - - - - --- b.Synthesis of proteins involves condensation reactions between the component amino acids c. Amino acids of pr ...
... Amino acids have carbon with an amino group, a carboxyl group, hydrogen and a side chain ii. - There are about-20 different side chains therefore about 20 differentaminoacids - - - - - --- b.Synthesis of proteins involves condensation reactions between the component amino acids c. Amino acids of pr ...
Test 1
... isomerase, Pyruvate kinase, Triose phosphate isomerase. On this key I am not going to take the time to make the structures, but I will check that you have the correct structure Glucose + ATP ...
... isomerase, Pyruvate kinase, Triose phosphate isomerase. On this key I am not going to take the time to make the structures, but I will check that you have the correct structure Glucose + ATP ...
Document
... • How did we get from glucose to lactic acid? • In the liver, the process is “reversed” using ATP from aerobic respiration ...
... • How did we get from glucose to lactic acid? • In the liver, the process is “reversed” using ATP from aerobic respiration ...
Protein Synthesis and Processing
... found within the nucleus (or nucleoplasm). 11. What is the base found in pre-mRNA that is not present in DNA? Uracil 12. What is the base pair rule for making pre-mRNA from DNA?) A-U; U-A; C-G; G-C 13. Which strand of the DNA is “read” to produce pre-mRNA? The template strand or coding strand 14. Wh ...
... found within the nucleus (or nucleoplasm). 11. What is the base found in pre-mRNA that is not present in DNA? Uracil 12. What is the base pair rule for making pre-mRNA from DNA?) A-U; U-A; C-G; G-C 13. Which strand of the DNA is “read” to produce pre-mRNA? The template strand or coding strand 14. Wh ...
18 Q1 (1 point). Name three amino acids that are typically found at
... Q1 (1 point). Name three amino acids that are typically found at the surface of integrated membrane proteins. ...
... Q1 (1 point). Name three amino acids that are typically found at the surface of integrated membrane proteins. ...
Chem 331 Section 002
... a. stronger acid: CH3CO2H or FCH2CO2H b. stronger base: NH2- or CH3c. stronger acid: H2Te or H2Se ...
... a. stronger acid: CH3CO2H or FCH2CO2H b. stronger base: NH2- or CH3c. stronger acid: H2Te or H2Se ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 1. Draw the ring structures for and name it. 2. What is D-xylitol? Give two important uses of it. 3. Write the structures of aspartic acid and lysine. Comment on their acidity/basicity. 4. Write a note on the properties of histidine. 5. What are conjugated proteins? Give two examples. 6. What are en ...
... 1. Draw the ring structures for and name it. 2. What is D-xylitol? Give two important uses of it. 3. Write the structures of aspartic acid and lysine. Comment on their acidity/basicity. 4. Write a note on the properties of histidine. 5. What are conjugated proteins? Give two examples. 6. What are en ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.























