SAM Teachers Guide - RI
... Identify the primary structure of a protein as a linear sequence of amino acids. Identify the unique side chains of amino acids that give them their properties. Explore how amino acids interact with water and how that affects the way proteins fold. Differentiate among the common secondary st ...
... Identify the primary structure of a protein as a linear sequence of amino acids. Identify the unique side chains of amino acids that give them their properties. Explore how amino acids interact with water and how that affects the way proteins fold. Differentiate among the common secondary st ...
Lec 15: Nitrogen in biochemistry
... and is vital for crop production. However, biological N2 fixation is limited in rate as N=N is extremely stable. • In 1909 – Fritz Haber invented the direct chemical synthesis of NH3 from N2 + H2 in lab. immediately German chemical company BASF bought the process and tried to scale it up. BASF engin ...
... and is vital for crop production. However, biological N2 fixation is limited in rate as N=N is extremely stable. • In 1909 – Fritz Haber invented the direct chemical synthesis of NH3 from N2 + H2 in lab. immediately German chemical company BASF bought the process and tried to scale it up. BASF engin ...
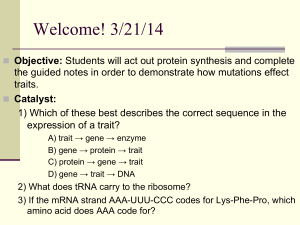
Welcome! 3/21/14
... does not always result in a visible change. n Mutations may change the DNA but not the amino acid n That mutations MAY result in a change in the PHENOTYPE of an organism, but not always. n Think-Pair-Share n WHY ...
... does not always result in a visible change. n Mutations may change the DNA but not the amino acid n That mutations MAY result in a change in the PHENOTYPE of an organism, but not always. n Think-Pair-Share n WHY ...
Biophysics - Fayetteville State University
... Discussion question: Try to define life (living organisms). b. Life and energy. What is energy and why do organisms need it? Where do they get it? Discussion question: How much energy do you expend in climbing up a mountain? How much energy is needed to pull RNA into a viral capsid? 2. Forces and en ...
... Discussion question: Try to define life (living organisms). b. Life and energy. What is energy and why do organisms need it? Where do they get it? Discussion question: How much energy do you expend in climbing up a mountain? How much energy is needed to pull RNA into a viral capsid? 2. Forces and en ...
Powering the Cell: Cellular Respiration
... Scientists think that glycolysis evolved before the other stages of cellular respiration. This is because the other stages need oxygen, whereas glycolysis does not, and there was no oxygen in Earth’s atmosphere when life first evolved about 3.5 to 4 billion years ago. Cellular respiration that proce ...
... Scientists think that glycolysis evolved before the other stages of cellular respiration. This is because the other stages need oxygen, whereas glycolysis does not, and there was no oxygen in Earth’s atmosphere when life first evolved about 3.5 to 4 billion years ago. Cellular respiration that proce ...
12.3 The Citric Acid Cycle Oxidizes AcetylCoA
... The Citric Acid Cycle Can Be a Multistep Catalyst • Oxaloacetate is regenerated • The cycle is a mechanism for oxidizing acetyl CoA to CO2 by NAD+ and Q • The cycle itself is not a pathway for a net degradation of any cycle intermediates • Cycle intermediates can be shared with other pathways, whic ...
... The Citric Acid Cycle Can Be a Multistep Catalyst • Oxaloacetate is regenerated • The cycle is a mechanism for oxidizing acetyl CoA to CO2 by NAD+ and Q • The cycle itself is not a pathway for a net degradation of any cycle intermediates • Cycle intermediates can be shared with other pathways, whic ...
Amino Acids And Central Fatigue.
... changes in brain monoamine metabolism and the influence of specific amino acids on fatigue. Several studies in experimental animals have shown that physical exercise increases the synthesis and metabolism of brain 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT). Support for the involvement of 5-HT in fatigue can be foun ...
... changes in brain monoamine metabolism and the influence of specific amino acids on fatigue. Several studies in experimental animals have shown that physical exercise increases the synthesis and metabolism of brain 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT). Support for the involvement of 5-HT in fatigue can be foun ...
INF115 Compulsory Exercise 1 The Genetic Code DNA is
... Proteins are one of the main constituents of living organisms, they perform a wide variety of functions and make up about 20% of the human body (which is quite considerable if you consider that water alone accounts for another 60%). Proteins are composed o ...
... Proteins are one of the main constituents of living organisms, they perform a wide variety of functions and make up about 20% of the human body (which is quite considerable if you consider that water alone accounts for another 60%). Proteins are composed o ...
PFK-2
... Gluconeogenesis • Mechanism to maintain adequate glucose levels in tissues, especially in brain (brain uses 120 g of the 160g of glucose needed daily). Erythrocytes also require glucose. • Occurs exclusively in liver (90%) and kidney (10%) • Glucose is synthesized from non-carbohydrate precursors d ...
... Gluconeogenesis • Mechanism to maintain adequate glucose levels in tissues, especially in brain (brain uses 120 g of the 160g of glucose needed daily). Erythrocytes also require glucose. • Occurs exclusively in liver (90%) and kidney (10%) • Glucose is synthesized from non-carbohydrate precursors d ...
The Nature of Matter
... • Valence electrons determine the chemical nature of an atom • Smallest subatomic particle ...
... • Valence electrons determine the chemical nature of an atom • Smallest subatomic particle ...
Islamic University of Gaza Advanced Biochemistry Faculty of
... E. Why does citric acid cycle only operate when there is oxygen present? Be sure to include the regulatory mechanisms of the cycle in your discussion. (2 points) Answer: Although the Krebs cycle does not directly require oxygen, it can only take place when oxygen is present because it relies on by- ...
... E. Why does citric acid cycle only operate when there is oxygen present? Be sure to include the regulatory mechanisms of the cycle in your discussion. (2 points) Answer: Although the Krebs cycle does not directly require oxygen, it can only take place when oxygen is present because it relies on by- ...
1. Proteins Are Informational and Functional Biological Polymers
... substances such as ions, oxygen, glucose, lipids, and many other molecules, often from one cellular environment to another. Some proteins convert, transport and store energy, for example in photosynthesis or in converting light to chemical signals in the eye. Some proteins form channels and gates, e ...
... substances such as ions, oxygen, glucose, lipids, and many other molecules, often from one cellular environment to another. Some proteins convert, transport and store energy, for example in photosynthesis or in converting light to chemical signals in the eye. Some proteins form channels and gates, e ...
Extraction of RNA File
... strands of DNA by some enzymes in order to transcription the genetic material from DNA to RNA and used the one strand of DNA as a template creating the m RNA strand by help of RNA polymerase after thtat the mRNA will be leaving the nucleus to cytoplasm where Ribosomes found. 5) The second step inclu ...
... strands of DNA by some enzymes in order to transcription the genetic material from DNA to RNA and used the one strand of DNA as a template creating the m RNA strand by help of RNA polymerase after thtat the mRNA will be leaving the nucleus to cytoplasm where Ribosomes found. 5) The second step inclu ...
Chapter 9
... Catabolic pathways funnel electrons from many kinds of organic molecules into cellular respiration ...
... Catabolic pathways funnel electrons from many kinds of organic molecules into cellular respiration ...
Spring 97, Exam 1
... (b; 8 pts) Draw in three residues of the antiparallel b-sheet partner below the extended polypeptide chain drawn here. Include backbone hydrogen bonds and indicate where the next strand (i.e. if you were to draw a third one) would H-bond. Indicate side chains with R. Indicate the N terminus and the ...
... (b; 8 pts) Draw in three residues of the antiparallel b-sheet partner below the extended polypeptide chain drawn here. Include backbone hydrogen bonds and indicate where the next strand (i.e. if you were to draw a third one) would H-bond. Indicate side chains with R. Indicate the N terminus and the ...
In vitro RNA-peptide co-evolution system for screening ATP
... Introduction: The advent of biological polymers was a key step for the emergence of life. Modern organisms use proteins to achieve energy harvest and transfer in various ways to sustain structural organization through reproduction of molecules. Whereas “evolvability” of the biological system is main ...
... Introduction: The advent of biological polymers was a key step for the emergence of life. Modern organisms use proteins to achieve energy harvest and transfer in various ways to sustain structural organization through reproduction of molecules. Whereas “evolvability” of the biological system is main ...
A chemical modified version of the second messenger
... Second messengers are small molecules that transmit signals in the cell. A single second messenger typically interacts with several signalling proteins. "Even though this may give the impression of promiscuity, the interactions are in fact highly specific" Assistant Professor Rehmann from the Univer ...
... Second messengers are small molecules that transmit signals in the cell. A single second messenger typically interacts with several signalling proteins. "Even though this may give the impression of promiscuity, the interactions are in fact highly specific" Assistant Professor Rehmann from the Univer ...
Translation Definition - Mr. Barrow's Science Center
... The actual process of protein synthesis where mRNA, made during transcription, leaves the nucleus, through nuclear pores located on the nuclear envelope, and attaches to a ribosome The production of a polypeptide (protein) whose amino acid sequence is derived from codon sequences Put a star next to ...
... The actual process of protein synthesis where mRNA, made during transcription, leaves the nucleus, through nuclear pores located on the nuclear envelope, and attaches to a ribosome The production of a polypeptide (protein) whose amino acid sequence is derived from codon sequences Put a star next to ...
Document
... The genome of any organism contains all the information for making that organism. The information is encoded in various types of genes that are transcribed into 4 types of RNA: mRNA - Messenger RNA: Encodes amino acid sequence of a polypeptide tRNA - Transfer RNA: Brings amino acids to ribosomes du ...
... The genome of any organism contains all the information for making that organism. The information is encoded in various types of genes that are transcribed into 4 types of RNA: mRNA - Messenger RNA: Encodes amino acid sequence of a polypeptide tRNA - Transfer RNA: Brings amino acids to ribosomes du ...
Slide 1
... get recharged, ADP (used battery) needs energy from the breakdown of carbohydrate, fat, and protein to make ATP (recharged battery). ...
... get recharged, ADP (used battery) needs energy from the breakdown of carbohydrate, fat, and protein to make ATP (recharged battery). ...
Transcription and Translation notes We often talk about how DNA is
... Transcription and Translation notes We often talk about how DNA is the blue print of an organism. At this point, we know that DNA is found in the nucleus of a cell, and that DNA can be re ...
... Transcription and Translation notes We often talk about how DNA is the blue print of an organism. At this point, we know that DNA is found in the nucleus of a cell, and that DNA can be re ...
C 6 H 12 O 6 + O 6 CO 2 + H 2 O + ATP
... Glycolysis is the break down of glucose into 2 pyruvate. How many ATP molecules are needed to start this reaction? zero, one, two or four ...
... Glycolysis is the break down of glucose into 2 pyruvate. How many ATP molecules are needed to start this reaction? zero, one, two or four ...
The Central Dogma of Genetics
... instructions (coded in DNA) from the nucleus into the cytoplasm. mRNA molecules are often called transcripts. • Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) – a structural component of ribosomes (the complexes that are involved in assembling proteins based upon information in mRNA templates) • Transfer RNA (tRNA) – acts as ...
... instructions (coded in DNA) from the nucleus into the cytoplasm. mRNA molecules are often called transcripts. • Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) – a structural component of ribosomes (the complexes that are involved in assembling proteins based upon information in mRNA templates) • Transfer RNA (tRNA) – acts as ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.