British Journal of Dairy Sciences 3(2): 9-13, 2013
... asparagine are the storage forms of nitrogen in addition to being the starting compounds from which the backbones of amino acids are made. During acid hydrolysis steps glutamic acid and asparagine are converted to aspartic acid respectively with the liberation of ammonium ions (Onwuliri and Anekwe, ...
... asparagine are the storage forms of nitrogen in addition to being the starting compounds from which the backbones of amino acids are made. During acid hydrolysis steps glutamic acid and asparagine are converted to aspartic acid respectively with the liberation of ammonium ions (Onwuliri and Anekwe, ...
The Cell: A Microcosm of Life Multiple
... Mechanism 1: Covalent modification – no change in the abundance of a protein. Here, preexisting protein is made active or inactive by covalently modifying it (involves making or breaking covalent bonds). Examples include phosphorylation, carboxylation, glycosylation, or proenzyme activation by break ...
... Mechanism 1: Covalent modification – no change in the abundance of a protein. Here, preexisting protein is made active or inactive by covalently modifying it (involves making or breaking covalent bonds). Examples include phosphorylation, carboxylation, glycosylation, or proenzyme activation by break ...
Chapter x – title of chapter
... Mechanism 1: Covalent modification – no change in the abundance of a protein. Here, preexisting protein is made active or inactive by covalently modifying it (involves making or breaking covalent bonds). Examples include phosphorylation, carboxylation, glycosylation, or proenzyme activation by break ...
... Mechanism 1: Covalent modification – no change in the abundance of a protein. Here, preexisting protein is made active or inactive by covalently modifying it (involves making or breaking covalent bonds). Examples include phosphorylation, carboxylation, glycosylation, or proenzyme activation by break ...
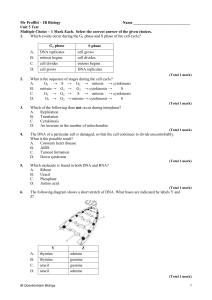
Mr Proffitt – IB Biology Name Unit 3 Test Multiple Choice – 1 Mark
... Short Answer – Various marks. Answer, to the best of your ability, the following questions. Be sure to pay attention to the number of marks available for each question! 15. The micrograph below shows an adult human stem cell. ...
... Short Answer – Various marks. Answer, to the best of your ability, the following questions. Be sure to pay attention to the number of marks available for each question! 15. The micrograph below shows an adult human stem cell. ...
chapter 13 section 2 notes
... The sequence of nucleotide bases in an mRNA molecule is a set of instructions that gives the order in which amino acids should be joined to produce a polypeptide. The forming of a protein requires the folding of one or more polypeptide chains. Ribosomes use the sequence of codons in mRNA to assemble ...
... The sequence of nucleotide bases in an mRNA molecule is a set of instructions that gives the order in which amino acids should be joined to produce a polypeptide. The forming of a protein requires the folding of one or more polypeptide chains. Ribosomes use the sequence of codons in mRNA to assemble ...
Amino Acid Student Handout 1
... that are involved in nearly all of your cellular functions. Each protein has a specific shape (structure) that enables it to carry out its specific job (function). A core idea in the life sciences is that there is a fundamental relationship between a biological structure and the function it must per ...
... that are involved in nearly all of your cellular functions. Each protein has a specific shape (structure) that enables it to carry out its specific job (function). A core idea in the life sciences is that there is a fundamental relationship between a biological structure and the function it must per ...
Final Review - Department of Chemistry ::: CALTECH
... Glycolysis -the simple sugar glucose is broken down in the cytosol Pyruvate, the product from glycolysis, is transformed into acetyl CoA in the mitochondria in preparation for the next step The citric acid cycle - where electron carriers, NADH and FADH2, are made in the mitochondria Oxidative phosph ...
... Glycolysis -the simple sugar glucose is broken down in the cytosol Pyruvate, the product from glycolysis, is transformed into acetyl CoA in the mitochondria in preparation for the next step The citric acid cycle - where electron carriers, NADH and FADH2, are made in the mitochondria Oxidative phosph ...
Schedule
... Produces evidence for the outcome and explains the outcome as a gene interaction and result from a metabolic pathway. Purple C-PWhite ccPRed C-pp Only C allele will allow colour expression. Then only P allele will convert / make to purple / pigment. In this case for all purple seeds to be produced b ...
... Produces evidence for the outcome and explains the outcome as a gene interaction and result from a metabolic pathway. Purple C-PWhite ccPRed C-pp Only C allele will allow colour expression. Then only P allele will convert / make to purple / pigment. In this case for all purple seeds to be produced b ...
2013 ProSyn PREAP
... cause of many genetic disorders and cancer. Source of genetic variability in a species (may be highly beneficial). ...
... cause of many genetic disorders and cancer. Source of genetic variability in a species (may be highly beneficial). ...
What is topline and how do you get it?
... it is not necessarily the figure listed for protein percentage that matters as much as the quality of the protein. The science bit! Protein is made up of chains of amino acids. The amino acids build up the protein molecule like building blocks. There are two types of amino acids, essential and non- ...
... it is not necessarily the figure listed for protein percentage that matters as much as the quality of the protein. The science bit! Protein is made up of chains of amino acids. The amino acids build up the protein molecule like building blocks. There are two types of amino acids, essential and non- ...
Protein Structure and Function
... primary structure a Each protein can be fragmented into peptides which are composed of aa’s. a Each aa has a unique mass to charge ratio at a given pH a Each protein therefore has a unique peptide-fingerprint a Technique: proteins->peptides->mass/charge ratio ...
... primary structure a Each protein can be fragmented into peptides which are composed of aa’s. a Each aa has a unique mass to charge ratio at a given pH a Each protein therefore has a unique peptide-fingerprint a Technique: proteins->peptides->mass/charge ratio ...
Protein Synthesis - Katy Independent School District
... cause of many genetic disorders and cancer. Source of genetic variability in a species (may be highly beneficial). ...
... cause of many genetic disorders and cancer. Source of genetic variability in a species (may be highly beneficial). ...
Lesson Overview
... Proteins are polymers of molecules called amino acids. Proteins perform many varied functions, such as controlling the rate of reactions and regulating cell processes, forming cellular structures, transporting substances into or out of cells, and helping to fight disease. ...
... Proteins are polymers of molecules called amino acids. Proteins perform many varied functions, such as controlling the rate of reactions and regulating cell processes, forming cellular structures, transporting substances into or out of cells, and helping to fight disease. ...
A1988N971500002
... certainly will improve our knowledge of chromatin functions, metabolic regulations, and transmission of external signals. Although engaged for years with this type of covalent modification of proteins, the early imprint of group activation asa basic biochemical phenomenon kept me open toother ways i ...
... certainly will improve our knowledge of chromatin functions, metabolic regulations, and transmission of external signals. Although engaged for years with this type of covalent modification of proteins, the early imprint of group activation asa basic biochemical phenomenon kept me open toother ways i ...
Judgement Statement – 2012
... Eg, offspring will be PpCc because one parent has given them Pc and the other parent has given them pC. ...
... Eg, offspring will be PpCc because one parent has given them Pc and the other parent has given them pC. ...
LS1a Fall 2014 Lab 2: Computer Modeling of Proteins with PyMOL
... acids covalently attached to each other. Different proteins have different amino acid sequences and the shape and function of a protein depends on the order and arrangement of its amino acid building blocks. In order to understand how proteins work, we must first understand what they look like. Usin ...
... acids covalently attached to each other. Different proteins have different amino acid sequences and the shape and function of a protein depends on the order and arrangement of its amino acid building blocks. In order to understand how proteins work, we must first understand what they look like. Usin ...
Exercise Physiology Study Guide-Test 1 History of Exercise
... o Sum of all chemical reactions in the body that take place in a living organism Catabolism-break down Anabolism-build up Bioenergetics-Chemical conversion of foodstuffs into biological energy Thermodynamics o Energy can be neither created nor destroyed Energy in (food)=energy out (work) + ene ...
... o Sum of all chemical reactions in the body that take place in a living organism Catabolism-break down Anabolism-build up Bioenergetics-Chemical conversion of foodstuffs into biological energy Thermodynamics o Energy can be neither created nor destroyed Energy in (food)=energy out (work) + ene ...
LECT 29 NitrogFix
... What interferes with nitrogen fixation? Oxygen is the major factor. Nitrogen fixation can take place only in the total absence of O2 How does a plant overcome oxygen interference? By synthesizing a heme protein, leghemoglobin, which like other hemoglobins, has a high affinity for binding oxygen….wh ...
... What interferes with nitrogen fixation? Oxygen is the major factor. Nitrogen fixation can take place only in the total absence of O2 How does a plant overcome oxygen interference? By synthesizing a heme protein, leghemoglobin, which like other hemoglobins, has a high affinity for binding oxygen….wh ...
Making probes/primers
... DNA synthesis using the Phosphoramidite method. •Before the start of synthesis amino groups of adenine, guanine and cytosine are derivatised by addition of benzoyl, isobutyryl and benzoyl groups respectively to prevent undesirable side reactions during chain growth. •Thymine is not treated as it ha ...
... DNA synthesis using the Phosphoramidite method. •Before the start of synthesis amino groups of adenine, guanine and cytosine are derivatised by addition of benzoyl, isobutyryl and benzoyl groups respectively to prevent undesirable side reactions during chain growth. •Thymine is not treated as it ha ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Nerve activates contraction
... Ch 2 Performance Objectives • Distinguish between organic and inorganic compounds. ...
... Ch 2 Performance Objectives • Distinguish between organic and inorganic compounds. ...
Document
... What interferes with nitrogen fixation? Oxygen is the major factor. Nitrogen fixation can take place only in the total absence of O2 How does a plant overcome oxygen interference? By synthesizing a heme protein, leghemoglobin, which like other hemoglobins, has a high affinity for binding oxygen….wh ...
... What interferes with nitrogen fixation? Oxygen is the major factor. Nitrogen fixation can take place only in the total absence of O2 How does a plant overcome oxygen interference? By synthesizing a heme protein, leghemoglobin, which like other hemoglobins, has a high affinity for binding oxygen….wh ...
Oxidation
... • Chloroplast contains a double layered membrane • Like mitochondria it contains its own DNA (plasmid) and 70s ribosomes. • Stroma- matrix similar to the cytosol of the cell ; it contains enzymes and chemicals necessary for dark reaction , some lipid molecules and starch granules. • Grana- contains ...
... • Chloroplast contains a double layered membrane • Like mitochondria it contains its own DNA (plasmid) and 70s ribosomes. • Stroma- matrix similar to the cytosol of the cell ; it contains enzymes and chemicals necessary for dark reaction , some lipid molecules and starch granules. • Grana- contains ...
The Aerobic Fate of Pyruvate
... The 2 ATP’s produced are only a small fraction of the potential energy available from glucose. Under anaerobic conditions, animals convert glucose into 2 molecules of lactate. Much of the potential energy of the glucose molecule remains untapped. Under Aerobic conditions a much more dynamic pyruvate ...
... The 2 ATP’s produced are only a small fraction of the potential energy available from glucose. Under anaerobic conditions, animals convert glucose into 2 molecules of lactate. Much of the potential energy of the glucose molecule remains untapped. Under Aerobic conditions a much more dynamic pyruvate ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.