Composition of Muscle
... The Fourth Kind of Lipids • Cholesterol - that much maligned, essential dietary component. • Required for hormone function and cell wall integrity. • About 20% of body needs is consumed whereas, 80% is manufactured. • If we don’t eat enough, our bodies manufacture more. • Contrary to popular belief ...
... The Fourth Kind of Lipids • Cholesterol - that much maligned, essential dietary component. • Required for hormone function and cell wall integrity. • About 20% of body needs is consumed whereas, 80% is manufactured. • If we don’t eat enough, our bodies manufacture more. • Contrary to popular belief ...
Cellular Respiration: Harvesting Chemical Energy
... Products of Glycolysis • 2 Pyruvic Acids (a 3C acid) • 4 ATP ...
... Products of Glycolysis • 2 Pyruvic Acids (a 3C acid) • 4 ATP ...
Review Report
... Response: I had also thought about transaminases in this context, especially when Glu is used as an amine source because that’s a very common way of providing amino groups to metabolites. Pages 5–6 (the rest of Section 3.1): Many others have written about promiscuous enzymes and their potential role ...
... Response: I had also thought about transaminases in this context, especially when Glu is used as an amine source because that’s a very common way of providing amino groups to metabolites. Pages 5–6 (the rest of Section 3.1): Many others have written about promiscuous enzymes and their potential role ...
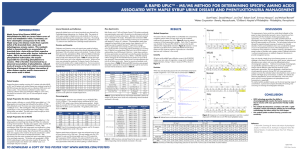
a rapid uplc™ - ms/ms method for determining specific
... Maple Syrup Urine Disease (MSUD) and Phenylketonuria (PKU) are severe inborn errors of amino acid metabolism which, if untreated, can have catastrophic consequences for the child. Maple syrup urine disease results from a genetic defect of the branched-chain α-keto acid dehydrogenase enzyme system. T ...
... Maple Syrup Urine Disease (MSUD) and Phenylketonuria (PKU) are severe inborn errors of amino acid metabolism which, if untreated, can have catastrophic consequences for the child. Maple syrup urine disease results from a genetic defect of the branched-chain α-keto acid dehydrogenase enzyme system. T ...
Lactic Acid fermentation
... Anaerobic Respiration • No oxygen present: ATP can continue to be created through glycolysis – Only 2 ATP produced – Glycolysis stops when all NAD+ is used ...
... Anaerobic Respiration • No oxygen present: ATP can continue to be created through glycolysis – Only 2 ATP produced – Glycolysis stops when all NAD+ is used ...
Document
... Many poisons and antimicrobial agents are enzyme inhibitors Can be accomplished by competitive or noncompetitive inhibitors Competitive inhibitors - compete with substrate for the active site ...
... Many poisons and antimicrobial agents are enzyme inhibitors Can be accomplished by competitive or noncompetitive inhibitors Competitive inhibitors - compete with substrate for the active site ...
Nerve activates contraction
... from body cells to the liver for breakdown; are increased by exercise, and limited coffee, smoking, and saturated fats/trans fats Healthy Ratios in the Blood ...
... from body cells to the liver for breakdown; are increased by exercise, and limited coffee, smoking, and saturated fats/trans fats Healthy Ratios in the Blood ...
DOC
... This is the final pathway of aerobic respiration. It occurs in the mitochondria. The pathway removes electrons and protons from the NADH and FADH2 molecules. FAD is Flavin Adenine Dinucleotide. It is an electron carrier like NADH. FADH2 is the reduced form that carries the electrons and protons. Ele ...
... This is the final pathway of aerobic respiration. It occurs in the mitochondria. The pathway removes electrons and protons from the NADH and FADH2 molecules. FAD is Flavin Adenine Dinucleotide. It is an electron carrier like NADH. FADH2 is the reduced form that carries the electrons and protons. Ele ...
CHAPTER OUTLINE
... Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is the genetic material of life, it is able to store information that pertains to the development, structure, and metabolic activities of the cell or organism and is stable so that it can be replicated with high accuracy during cell division and be transmitted from genera ...
... Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is the genetic material of life, it is able to store information that pertains to the development, structure, and metabolic activities of the cell or organism and is stable so that it can be replicated with high accuracy during cell division and be transmitted from genera ...
The 3 Energy Systems
... • Energy in the human body come from the breakdown of nutrients like carbohydrates, proteins and fats Food = Energy (ATP) • The end result of this breakdown is the production energy in the form of Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) ...
... • Energy in the human body come from the breakdown of nutrients like carbohydrates, proteins and fats Food = Energy (ATP) • The end result of this breakdown is the production energy in the form of Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) ...
$doc.title
... anaerobically in a validated (that is, base broth was run) PR sucrose, no color change or turbidity is observed. When a pure culture of the same bacterium is incubated anaerobically ...
... anaerobically in a validated (that is, base broth was run) PR sucrose, no color change or turbidity is observed. When a pure culture of the same bacterium is incubated anaerobically ...
Chemical Reactions - TSHSChemistry
... – Chemical reactions occur when bonds between the outermost parts of atoms are formed or broken – Chemical reactions involve changes in matter, the making of new materials with new properties, and energy changes. – Symbols represent elements, formulas describe compounds, chemical equations describe ...
... – Chemical reactions occur when bonds between the outermost parts of atoms are formed or broken – Chemical reactions involve changes in matter, the making of new materials with new properties, and energy changes. – Symbols represent elements, formulas describe compounds, chemical equations describe ...
Metabolism Part II: The tricarboxylic acid (TCA), citric acid, or Krebs
... In 1937, Hans Krehs found that citrate is readily formed from oxaloacetate and suggested that this pathway was in fact a cycle of reactions that was responsible for the aerobic oxidation of fuel molecules. Concern over whether citric acid (or more accurately the citrate ion) was the first product of ...
... In 1937, Hans Krehs found that citrate is readily formed from oxaloacetate and suggested that this pathway was in fact a cycle of reactions that was responsible for the aerobic oxidation of fuel molecules. Concern over whether citric acid (or more accurately the citrate ion) was the first product of ...
Lecture 7: Metabolic Regulation - University of California, Berkeley
... glucose by the liver enzyme also go up, which allows the liver to take care of excess glucose. If you have lots of glucose, then the liver enzyme will function much faster and take away glucose. Glucagon levels goes down in response to high [glucose]. The opposite regulation of the PFK2/FBPase-2 wil ...
... glucose by the liver enzyme also go up, which allows the liver to take care of excess glucose. If you have lots of glucose, then the liver enzyme will function much faster and take away glucose. Glucagon levels goes down in response to high [glucose]. The opposite regulation of the PFK2/FBPase-2 wil ...
Protein Synthesis Study Sheet
... Draw a nucleic acid and label its parts. What is a polymer? What are proteins made from? Give 3 examples of proteins and describe their functions? What do enzymes do? What kind of a molecule is an enzyme? Draw an amino acid molecule. Draw 2 DIFFERENT proteins. What makes them different? What is the ...
... Draw a nucleic acid and label its parts. What is a polymer? What are proteins made from? Give 3 examples of proteins and describe their functions? What do enzymes do? What kind of a molecule is an enzyme? Draw an amino acid molecule. Draw 2 DIFFERENT proteins. What makes them different? What is the ...
Polymerization Reactions - SCH4U1-CCVI
... High temperature or UV light can cause 2 of these shared (paired) electrons to become unshared (unpaired). ...
... High temperature or UV light can cause 2 of these shared (paired) electrons to become unshared (unpaired). ...
Info
... that, like carboxylic acids, the imidazole side chain of histidine can exist in two tautomeric forms, in which the N-H bond can be on either the δ or ε ring nitrogen. ...
... that, like carboxylic acids, the imidazole side chain of histidine can exist in two tautomeric forms, in which the N-H bond can be on either the δ or ε ring nitrogen. ...
Midterm 3 - Creighton Biology
... trying to trick you with these units. This is the same convention we used in class, just stated explicitly.) Black curve: ...
... trying to trick you with these units. This is the same convention we used in class, just stated explicitly.) Black curve: ...
Protein Structure Prediction Using Rosetta
... accuracy of this protocol for predicting protein structure. The primary sequence of the proteins were input to several programs for secondary structure prediction., then Rosetta created models for tertiary structure using this information. Success of the method was determined by computing the root m ...
... accuracy of this protocol for predicting protein structure. The primary sequence of the proteins were input to several programs for secondary structure prediction., then Rosetta created models for tertiary structure using this information. Success of the method was determined by computing the root m ...
Biochemistry
... Biochemistry and Molecular Biology is to study the structure and function of biological macromolecules, metabolism and its regulation, genetic information transfer and its regulation, as well as their role in life activities. With the development of the medicine, lots of wonders are being created, a ...
... Biochemistry and Molecular Biology is to study the structure and function of biological macromolecules, metabolism and its regulation, genetic information transfer and its regulation, as well as their role in life activities. With the development of the medicine, lots of wonders are being created, a ...
Lab - Week One: The Scientific Method
... chalk below the template the sequence of the replication product (make letters same size as the molecule given to you). Given the complexities of real replication, we will not be modeling unwinding, leading/lagging strand, etc. today. Have your instructor check your work before proceeding. II. Centr ...
... chalk below the template the sequence of the replication product (make letters same size as the molecule given to you). Given the complexities of real replication, we will not be modeling unwinding, leading/lagging strand, etc. today. Have your instructor check your work before proceeding. II. Centr ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.