Interpretive Guide for Amino Acids
... α-Amino-N-butyric acid Low - possible increased need for the nutrients which aid in threonine metabolism from which this AA is derived. These include α-KG and B6. High - inadequate utilization of this AA for cellular energy generation. Alpha-ABA is converted to succinyl Co-A for use in the citric ac ...
... α-Amino-N-butyric acid Low - possible increased need for the nutrients which aid in threonine metabolism from which this AA is derived. These include α-KG and B6. High - inadequate utilization of this AA for cellular energy generation. Alpha-ABA is converted to succinyl Co-A for use in the citric ac ...
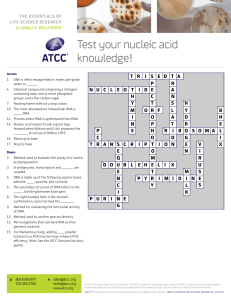
Test your nucleic acid knowledge!
... Method used to evaluate the purity of a nucleic acid preparation. ...
... Method used to evaluate the purity of a nucleic acid preparation. ...
Adv. Bio. Ch 9 Glyco and Resp
... and redox rnxs are not coupled – we round the number of ATP produced for each NADH to 3 and FADH2 2 (more like 2.5-3.3 and 1.5-2 respectively) NADH is hard to get in to the mitochondria from cytosol – shuttle to get it in varies by cell (NAD+ or FAD) – more ATP if shuttled in by NAD+ The ATP mad ...
... and redox rnxs are not coupled – we round the number of ATP produced for each NADH to 3 and FADH2 2 (more like 2.5-3.3 and 1.5-2 respectively) NADH is hard to get in to the mitochondria from cytosol – shuttle to get it in varies by cell (NAD+ or FAD) – more ATP if shuttled in by NAD+ The ATP mad ...
PowerPoint 簡報
... deficiency because pyridoxal phosphate is a coenzyme in NAD+ biosynthesis from tryptophan. ...
... deficiency because pyridoxal phosphate is a coenzyme in NAD+ biosynthesis from tryptophan. ...
Animal Productio fet level 4 sb - Macmillan Education South Africa
... 1.1.3 Classes of carbohydrates All carbohydrates consist of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. Carbohydrates are subdivided into three main classes: • monosaccharides (mono = one sugar) • disaccharides (di = two sugars) • polysaccharides (poly = many sugars). ...
... 1.1.3 Classes of carbohydrates All carbohydrates consist of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. Carbohydrates are subdivided into three main classes: • monosaccharides (mono = one sugar) • disaccharides (di = two sugars) • polysaccharides (poly = many sugars). ...
File
... membrane folds inwards to create new vesicles that remove aquaporins from the membrane. Walls of collecting duct are made less permeable, less water is reabsorbed and more water is lost from the body, decreasing water potential of blood. Describe how the light energy absorbed in photosystems is conv ...
... membrane folds inwards to create new vesicles that remove aquaporins from the membrane. Walls of collecting duct are made less permeable, less water is reabsorbed and more water is lost from the body, decreasing water potential of blood. Describe how the light energy absorbed in photosystems is conv ...
Proteomes, Genes and Junk DNA
... Oxford and Linus Pauling as the third race participant. It won them the 1962 Nobel Prize in medicine and physiology, which they shared with Maurice Wilkins. Rosalind Franklin, who had died from cancer in 1958, was largely overlooked in the credits. The stuff of Nobel prizes is now the stuff of schoo ...
... Oxford and Linus Pauling as the third race participant. It won them the 1962 Nobel Prize in medicine and physiology, which they shared with Maurice Wilkins. Rosalind Franklin, who had died from cancer in 1958, was largely overlooked in the credits. The stuff of Nobel prizes is now the stuff of schoo ...
Part I - Nutrition. I. How to obtain food: This is descriptive
... Briefly, animals need organic carbon to manufacture needed organic molecules. Another example is nitrogenous compounds - can’t fix nitrogen, so animals need to get this from diet. Important for amino acids (see below). v) essential nutrients: These are compounds the animal can not manufacture, but a ...
... Briefly, animals need organic carbon to manufacture needed organic molecules. Another example is nitrogenous compounds - can’t fix nitrogen, so animals need to get this from diet. Important for amino acids (see below). v) essential nutrients: These are compounds the animal can not manufacture, but a ...
Origin of the earth
... formation of polypeptides from amino acids. • This supported the ideas that life did need something like a clay catalyst at the beginning because the oceans were too diluted. ...
... formation of polypeptides from amino acids. • This supported the ideas that life did need something like a clay catalyst at the beginning because the oceans were too diluted. ...
Unit 2 - OCCC.edu
... A carbon atom is ________________ from pyruvate and released in ___________ The remaining two-carbon compound is _______________________, and a molecule of NAD+ is reduced to ________________________ Coenzyme ___ joins with the 2-carbon group to produce _____________________ The citric acid cycle co ...
... A carbon atom is ________________ from pyruvate and released in ___________ The remaining two-carbon compound is _______________________, and a molecule of NAD+ is reduced to ________________________ Coenzyme ___ joins with the 2-carbon group to produce _____________________ The citric acid cycle co ...
Separation of Nucleic acid constituents Nucleic acids do exist in
... Separation of Nucleic acid constituents Nucleic acids do exist in nuclei and protoplasm of biological cells and control the growth and heredity. There are two kinds of nucleic acids; DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) and RNA (ribonucleic acid). There are six kinds of nucleotides formed of sugar, phosphori ...
... Separation of Nucleic acid constituents Nucleic acids do exist in nuclei and protoplasm of biological cells and control the growth and heredity. There are two kinds of nucleic acids; DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) and RNA (ribonucleic acid). There are six kinds of nucleotides formed of sugar, phosphori ...
Answers to Exam 2 multiple choice and TF questions
... 9. T F Only aerobic organisms use glycolysis to degrade sugars, suggesting that glycolysis evolved rather recently. 10. T F Some thermodynamically favorable (spontaneous) reactions that occur in cells require a catalyst but most do not. 11. T F Oxidation of a molecule requires the removal of electro ...
... 9. T F Only aerobic organisms use glycolysis to degrade sugars, suggesting that glycolysis evolved rather recently. 10. T F Some thermodynamically favorable (spontaneous) reactions that occur in cells require a catalyst but most do not. 11. T F Oxidation of a molecule requires the removal of electro ...
G Protein Coupled Receptors
... Simple Methods for Predicting the Secondary Structure of Globular Proteins J. Garnier, D.J. Osguthorpe and B Robson Journal of Molecular Biology (1978); 120, 97-120 ...
... Simple Methods for Predicting the Secondary Structure of Globular Proteins J. Garnier, D.J. Osguthorpe and B Robson Journal of Molecular Biology (1978); 120, 97-120 ...
Slide 1
... -have more energy per gram than carbohydrates or proteins (~2x as much) -fatty acid chains are oxidized and broken into smaller 2 carbon chains -the 2 carbon chains are converted into acetyl CoA to enter the Kreb’s cycle B. Proteins -must be converted into individual amino acids -excess amino acids ...
... -have more energy per gram than carbohydrates or proteins (~2x as much) -fatty acid chains are oxidized and broken into smaller 2 carbon chains -the 2 carbon chains are converted into acetyl CoA to enter the Kreb’s cycle B. Proteins -must be converted into individual amino acids -excess amino acids ...
What is the purpose of mitosis?
... • some variations have an adaptive value because they give a survival advantage • the survivors pass on their characteristics to their offspring and these adaptations increase in the population ...
... • some variations have an adaptive value because they give a survival advantage • the survivors pass on their characteristics to their offspring and these adaptations increase in the population ...
M2 L7 - Energy Systems
... The aerobic system produces ATP by breaking down carbohydrate, fat and protein in the presence of oxygen ...
... The aerobic system produces ATP by breaking down carbohydrate, fat and protein in the presence of oxygen ...
general medicine
... compounds – glucose, amino acids, uric acid, tubular proteinuria), the term fractional excretion E/F. 57 Transport processes in loop of Henle, distal tubulus and collecting duct. Main types of diuretics and principle of their effect. 58 Endocrine functions of kidney (erythropoetin, rennin-angiotensi ...
... compounds – glucose, amino acids, uric acid, tubular proteinuria), the term fractional excretion E/F. 57 Transport processes in loop of Henle, distal tubulus and collecting duct. Main types of diuretics and principle of their effect. 58 Endocrine functions of kidney (erythropoetin, rennin-angiotensi ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.