Alternative Pathways to Cellular Respiration!
... cycle cannot fuction thus photosynthesis cannot occur. When CO2 levels are low and rubisco has trouble finding it the CO2 travels through the stomata into the mesophyll cell and PEP carboxylase finds it and gives the CO2 to rubisco Once the rubsico has the CO2 it travels to the bundlesheath cell, wh ...
... cycle cannot fuction thus photosynthesis cannot occur. When CO2 levels are low and rubisco has trouble finding it the CO2 travels through the stomata into the mesophyll cell and PEP carboxylase finds it and gives the CO2 to rubisco Once the rubsico has the CO2 it travels to the bundlesheath cell, wh ...
Name - Humble ISD
... What many people do not realize, however, is that the evolution of a species is a continuous process whit no definite end. Modern plants and animals- and, of course, humans- are subject to the forces of natural selection today, just as they were millions of years ago. In this activity, you will stud ...
... What many people do not realize, however, is that the evolution of a species is a continuous process whit no definite end. Modern plants and animals- and, of course, humans- are subject to the forces of natural selection today, just as they were millions of years ago. In this activity, you will stud ...
The CENTRAL DOGMA Make a Protein – Transcription and
... 4. Bond your polypeptide. Tape your amino acids together in the correct order as coded for in your mRNA strand. Don’t forget to bond your start and stop codons at the beginning and the end of your new, polypeptide. Tape the polypeptide into your notebook. 5. Get your polypeptide checked. Get a stamp ...
... 4. Bond your polypeptide. Tape your amino acids together in the correct order as coded for in your mRNA strand. Don’t forget to bond your start and stop codons at the beginning and the end of your new, polypeptide. Tape the polypeptide into your notebook. 5. Get your polypeptide checked. Get a stamp ...
DNA, RNA and Protein Power Point
... codes for a single amino acid 2. With 4 different types of nucleotides in triplet codes, 64 combinations are possible a) 61 of the codons code for 20 amino acids b) 3 codons signal a stop- Identifies the end of a ...
... codes for a single amino acid 2. With 4 different types of nucleotides in triplet codes, 64 combinations are possible a) 61 of the codons code for 20 amino acids b) 3 codons signal a stop- Identifies the end of a ...
lecture notes endomembrane system 4
... and those on the plasma membrane therefore have the carbohydrate facing the outside of the cell. 14. What is the purpose of glycosylation? There is an important difference between the construction of an oligosaccharide and other large molecules such as DNA, RNA and protein. ...
... and those on the plasma membrane therefore have the carbohydrate facing the outside of the cell. 14. What is the purpose of glycosylation? There is an important difference between the construction of an oligosaccharide and other large molecules such as DNA, RNA and protein. ...
respiration - sandsbiochem
... Autotrophs transform it into chemical E O2 released as byproduct Cells use some of chemical E in organic molecules to make ATP ...
... Autotrophs transform it into chemical E O2 released as byproduct Cells use some of chemical E in organic molecules to make ATP ...
Homework # 9 Citric Acid Cycle, electron transport Chain, and
... Alcohol is the favorite mood-altering drug in the United States and its effects, both pleasant and unpleasant, are well-known. What may not be well known is the fact that alcohol is a toxic drug that produces pathological changes (cirrhosis) in liver tissue and can cause death. Alcohol is readily ab ...
... Alcohol is the favorite mood-altering drug in the United States and its effects, both pleasant and unpleasant, are well-known. What may not be well known is the fact that alcohol is a toxic drug that produces pathological changes (cirrhosis) in liver tissue and can cause death. Alcohol is readily ab ...
Intermediary Metabolism-II SECTION A What are ketogenic amino
... Discuss the role of carnitine. What are chylomicrons? How are water insoluble triacylglycerol and cholesterol transported in the aqueous medium of blood? Expalin fatty acid synthetase enzyme complex components. What is the effect of dietary cholesterol on the cholesterol biosynthesis? When does acet ...
... Discuss the role of carnitine. What are chylomicrons? How are water insoluble triacylglycerol and cholesterol transported in the aqueous medium of blood? Expalin fatty acid synthetase enzyme complex components. What is the effect of dietary cholesterol on the cholesterol biosynthesis? When does acet ...
CH_16_2_Functions_Proteins
... • has charged NH3+ and COO– groups • forms when both the –NH2 and the –COOH groups in an amino acid ionize in solution • has equal + and – charges and called a dipolar ion O ...
... • has charged NH3+ and COO– groups • forms when both the –NH2 and the –COOH groups in an amino acid ionize in solution • has equal + and – charges and called a dipolar ion O ...
EOC Warm-up Review Part I and II
... 20. Which statement best describes cellular respiration? A. It occurs in animal cells but not in plant cells. B. It converts energy in glucose into a more usable form of energy. C. It uses carbon dioxide and produces oxygen. D. It stores energy in food molecules. ...
... 20. Which statement best describes cellular respiration? A. It occurs in animal cells but not in plant cells. B. It converts energy in glucose into a more usable form of energy. C. It uses carbon dioxide and produces oxygen. D. It stores energy in food molecules. ...
Organic Acids - The Nest Group, Inc.
... Organic acids are hydrophilic compounds with acidic properties where the carboxylic acids are predominant. Organic acids are generally weak acids that do not dissociate completely in water and they are present in every meal we eat. Organic acids are also used in food preservation because they can pe ...
... Organic acids are hydrophilic compounds with acidic properties where the carboxylic acids are predominant. Organic acids are generally weak acids that do not dissociate completely in water and they are present in every meal we eat. Organic acids are also used in food preservation because they can pe ...
Gene action
... General idea: the closer the relationship between two species, the more similar their DNA code will be Therefore, by finding out the genome of many species, we can not only work out relationships, but also identify the rise of different alleles! ...
... General idea: the closer the relationship between two species, the more similar their DNA code will be Therefore, by finding out the genome of many species, we can not only work out relationships, but also identify the rise of different alleles! ...
Communication, Homeostasis
... in complex organic molecules such as glucose by photosynthesis by photoautotrophs. o The complex organic molecules are only potential stores of energy. o For their energy to be realised and used it must be converted into another form ATP. o The metabolic process of Respiration converts these organic ...
... in complex organic molecules such as glucose by photosynthesis by photoautotrophs. o The complex organic molecules are only potential stores of energy. o For their energy to be realised and used it must be converted into another form ATP. o The metabolic process of Respiration converts these organic ...
Seminario Tunable electronic properties of self
... In novel organic optoelectronics applications, the device efficiency depends crucially on the energy barrier that controls charge carrier injection at molecule/electrode interfaces. These processes are determined by the chemical interaction between the deposited species and the inorganic surface, as ...
... In novel organic optoelectronics applications, the device efficiency depends crucially on the energy barrier that controls charge carrier injection at molecule/electrode interfaces. These processes are determined by the chemical interaction between the deposited species and the inorganic surface, as ...
electron transport chain
... We would not make enough ATP to meet our energy requirements We would not have enough enzymes to catalyze reactions. We would not be able to perform lactic acid fermentation. We would not be able to synthesize organic molecules from inorganic molecules. We would not be affected because we can switch ...
... We would not make enough ATP to meet our energy requirements We would not have enough enzymes to catalyze reactions. We would not be able to perform lactic acid fermentation. We would not be able to synthesize organic molecules from inorganic molecules. We would not be affected because we can switch ...
Chapter 13 Notes
... oxidation. Iron is gaining back electrons it had lost to become a free element so it is undergoing reduction. This is called an oxidation-reduction reaction or redox for short. Although this type of reaction is named for oxygen, many other elements undergo redox reactions with each other without oxy ...
... oxidation. Iron is gaining back electrons it had lost to become a free element so it is undergoing reduction. This is called an oxidation-reduction reaction or redox for short. Although this type of reaction is named for oxygen, many other elements undergo redox reactions with each other without oxy ...
Peptides and Protein Primary Structure
... • Each R-group has its own chemical character (steric volume and shape, hydrophobicity, hydrophilicity, charge, etc.) • Adjacent R-groups interact with each other. • This interaction leads to the discrete f,y angles about each alpha carbon. • The collective effect of these f,y angles gives rise to s ...
... • Each R-group has its own chemical character (steric volume and shape, hydrophobicity, hydrophilicity, charge, etc.) • Adjacent R-groups interact with each other. • This interaction leads to the discrete f,y angles about each alpha carbon. • The collective effect of these f,y angles gives rise to s ...
H_355605_Nenova, Bulgaria.fm
... produce them when needed. The nutrition value of sunflower protein is determined by the good balance of the essential amino acids contained in it. Each amino acid plays a specific biological role (Ribarova, 1987). Lysine is one of the three most important essential amino acids (the other two are try ...
... produce them when needed. The nutrition value of sunflower protein is determined by the good balance of the essential amino acids contained in it. Each amino acid plays a specific biological role (Ribarova, 1987). Lysine is one of the three most important essential amino acids (the other two are try ...
Lecture 10 Protein Tertiary (3D) Structure
... PDB • Database of molecular structures – Obtained by crystallography or NMR – Carefully curated and validated ...
... PDB • Database of molecular structures – Obtained by crystallography or NMR – Carefully curated and validated ...
Gluconeogenesis - Assignment Point
... cycle can also be used for gluconeogenesis. Amino acids, after their amino group has been removed, feed into parts of the citric acid cycle, and can thus can generate glucose in this pathway. • Fatty acids cannot be turned into glucose, as they are broken down into the two carbon acetyl CoA. (Howeve ...
... cycle can also be used for gluconeogenesis. Amino acids, after their amino group has been removed, feed into parts of the citric acid cycle, and can thus can generate glucose in this pathway. • Fatty acids cannot be turned into glucose, as they are broken down into the two carbon acetyl CoA. (Howeve ...
HH-Unit-1-PPQs - Dalkeith High School
... i) Use the information form the table above to determine the DNA base sequence which would code for this molecule. ...
... i) Use the information form the table above to determine the DNA base sequence which would code for this molecule. ...
full - screen version here
... smaller molecules are forced through porous membranes. Hydrostatic pressure is important in the body. Example: molecules leaving blood capillaries ...
... smaller molecules are forced through porous membranes. Hydrostatic pressure is important in the body. Example: molecules leaving blood capillaries ...
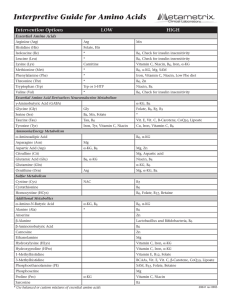
Interpretive Guide for Amino Acids
... α-Amino-N-butyric acid Low - possible increased need for the nutrients which aid in threonine metabolism from which this AA is derived. These include α-KG and B6. High - inadequate utilization of this AA for cellular energy generation. Alpha-ABA is converted to succinyl Co-A for use in the citric ac ...
... α-Amino-N-butyric acid Low - possible increased need for the nutrients which aid in threonine metabolism from which this AA is derived. These include α-KG and B6. High - inadequate utilization of this AA for cellular energy generation. Alpha-ABA is converted to succinyl Co-A for use in the citric ac ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.