Nucleotide File
... A, FAD, FMN, NAD, and NADP+). In experimental biochemistry, nucleotides can be radiolabeled with radionuclides to yield radionucleotides. ...
... A, FAD, FMN, NAD, and NADP+). In experimental biochemistry, nucleotides can be radiolabeled with radionuclides to yield radionucleotides. ...
20141031093018
... Active site (and R groups of its amino acids) can lower EA and speed up a reaction by • acting as a template for substrate orientation, • stressing the substrates and stabilizing the ...
... Active site (and R groups of its amino acids) can lower EA and speed up a reaction by • acting as a template for substrate orientation, • stressing the substrates and stabilizing the ...
Chapter 9 - Cellular Respiration
... • In muscle tissues during rapid and vigorous exercise, muscle cells may be depleted of oxygen. • Muscles then switch from respiration to lacticacid fermentation. ...
... • In muscle tissues during rapid and vigorous exercise, muscle cells may be depleted of oxygen. • Muscles then switch from respiration to lacticacid fermentation. ...
CHEM523 Test 1
... 1) (10 points total) Draw the structures of and give the One and three letter abbreviations for: a) (6 points) The following three amino acids: i) A hydrophobic amino acid that would be bound in the substrate specificity pocket of chymotrypsin, ii) a polar amino acid that has an amide group on its s ...
... 1) (10 points total) Draw the structures of and give the One and three letter abbreviations for: a) (6 points) The following three amino acids: i) A hydrophobic amino acid that would be bound in the substrate specificity pocket of chymotrypsin, ii) a polar amino acid that has an amide group on its s ...
Selective and Differential Media (I) 选择和鉴别培养基
... • Require PREFORMED organic molecules like vitamins, AA, nucleic acids, carbohydrates; • In general pathogens need more PREFORMED organic molecules than non-pathogens • A simple rule of thumb: – "if humans can use something for food, many microbes will also love it". - humans are ...
... • Require PREFORMED organic molecules like vitamins, AA, nucleic acids, carbohydrates; • In general pathogens need more PREFORMED organic molecules than non-pathogens • A simple rule of thumb: – "if humans can use something for food, many microbes will also love it". - humans are ...
Threading-based Protein Structure Prediction
... – Eukaryotes (organisms with single or multiple cells. their cells have ...
... – Eukaryotes (organisms with single or multiple cells. their cells have ...
antisense orfs, codon bias and the evo lu tion of the ge netic code
... Hauptman-Woodward Institute, Buffalo, NY 14203 ...
... Hauptman-Woodward Institute, Buffalo, NY 14203 ...
GA Performance Standards
... SB3. Students will derive the relationship between single-celled and multi-celled organisms and the increasing complexity of systems. a. Explain the cycling of energy through the processes of photosynthesis and respiration. b. Compare how structures and function vary between the six kingdoms (archa ...
... SB3. Students will derive the relationship between single-celled and multi-celled organisms and the increasing complexity of systems. a. Explain the cycling of energy through the processes of photosynthesis and respiration. b. Compare how structures and function vary between the six kingdoms (archa ...
06.1 Respiration
... Respiration – a one or two stage process Stage 2 does require oxygen and releases a large amount of energy. - this process takes place in the mitochondria of the cell. Note: the rate of both processes are controlled by enzymes. ...
... Respiration – a one or two stage process Stage 2 does require oxygen and releases a large amount of energy. - this process takes place in the mitochondria of the cell. Note: the rate of both processes are controlled by enzymes. ...
Transport
... body of complex chemical compounds from smaller simpler compounds (e.g., proteins from amino acids), usually with the use of energy. ...
... body of complex chemical compounds from smaller simpler compounds (e.g., proteins from amino acids), usually with the use of energy. ...
Science Notes
... -Magnification = Length of drawing divided by Length of actual object -Chloroplast is the site of photosynthesis and manufacture of glucose -Red blood cells have cell membrane and cytoplasm that can be labelled as well -Red blood cells carry oxygen from lungs to all parts of the body. -The biconcave ...
... -Magnification = Length of drawing divided by Length of actual object -Chloroplast is the site of photosynthesis and manufacture of glucose -Red blood cells have cell membrane and cytoplasm that can be labelled as well -Red blood cells carry oxygen from lungs to all parts of the body. -The biconcave ...
Chapter 5
... • Lipids are hydrophobic because they consist mostly of hydrocarbons, which form nonpolar covalent bonds • The most biologically important lipids are fats, phospholipids, and steroids ...
... • Lipids are hydrophobic because they consist mostly of hydrocarbons, which form nonpolar covalent bonds • The most biologically important lipids are fats, phospholipids, and steroids ...
jcps 2011-2012 at-a-glance curriculu maps
... Essential Questions: What are the reactants and products of both cellular respiration and photosynthesis? How are the two processes dependent on each other? What are the key steps in each process? Why is fermentation an important cellular process? Length of Unit: 4 weeks Unit Focus Standards – Progr ...
... Essential Questions: What are the reactants and products of both cellular respiration and photosynthesis? How are the two processes dependent on each other? What are the key steps in each process? Why is fermentation an important cellular process? Length of Unit: 4 weeks Unit Focus Standards – Progr ...
ACID-BASE BALANCE
... Weak acids good buffers since they can tilt a reaction in the other direction ...
... Weak acids good buffers since they can tilt a reaction in the other direction ...
answer key
... reaction ADP + Pi ATP. Bogus! A chemical reaction that has a ΔG > 0 can proceed if it is coupled to the reverse reaction (ATP ADP + Pi). ATP synthesis does not proceed spontaneously, but ATP hydrolysis does. [This question is based on review sheet questions #32-33.] ...
... reaction ADP + Pi ATP. Bogus! A chemical reaction that has a ΔG > 0 can proceed if it is coupled to the reverse reaction (ATP ADP + Pi). ATP synthesis does not proceed spontaneously, but ATP hydrolysis does. [This question is based on review sheet questions #32-33.] ...
Membrane Protein : Integral/Peripheral
... • Diffusion of large/polar molecules with the help of a transport protein (integral membrane protein) • Stops when equilibrium is reached • Two types of Transport (Integral) Proteins – Channel proteins – Carrier proteins ...
... • Diffusion of large/polar molecules with the help of a transport protein (integral membrane protein) • Stops when equilibrium is reached • Two types of Transport (Integral) Proteins – Channel proteins – Carrier proteins ...
Protein Synthesis Overview
... whose bases are complementary to a codon on the mRNA strand. The ribosome positions the start codon to attract its anticodon, which is part of the tRNA that binds methionine. The ribosome also binds the next codon and its anticodon. ...
... whose bases are complementary to a codon on the mRNA strand. The ribosome positions the start codon to attract its anticodon, which is part of the tRNA that binds methionine. The ribosome also binds the next codon and its anticodon. ...
Proteomics techniques used to identify proteins
... Proteomics techniques used to identify proteins ...
... Proteomics techniques used to identify proteins ...
Presentation
... ATP synthesis can be uncoupled: if a different H+ diffusion channel is inserted into the mitochondrial membrane, the energy of the diffusion is lost as heat. The protein thermogenin occurs in human ...
... ATP synthesis can be uncoupled: if a different H+ diffusion channel is inserted into the mitochondrial membrane, the energy of the diffusion is lost as heat. The protein thermogenin occurs in human ...
L24_Krebs
... – One of the methyl-Hs can easily come off acetyl CoA – Gives a very reactive species that reacts with oxaloacetate ...
... – One of the methyl-Hs can easily come off acetyl CoA – Gives a very reactive species that reacts with oxaloacetate ...
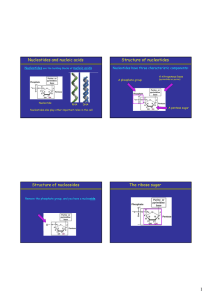
Nucleotides and nucleic acids Structure of nucleotides Structure of
... • The polynucleotide or nucleic acid backbone thus consists of alternating phosphate and pentose residues. • The bases are analogous to side chains of amino acids; they vary without changing the covalent backbone structure. • Sequence is written from the 5' to 3' end: 5'-ATGCTAGC-3' • Note that the ...
... • The polynucleotide or nucleic acid backbone thus consists of alternating phosphate and pentose residues. • The bases are analogous to side chains of amino acids; they vary without changing the covalent backbone structure. • Sequence is written from the 5' to 3' end: 5'-ATGCTAGC-3' • Note that the ...
Document
... before they reach their final form where they exhibit biological activity • N-formylmethionine in prokaryotes is _______________ • specific bonds in precursors are cleaved, as for example, preproinsulin to proinsulin to insulin • ___________ _________are removed by specific proteases of the endoplas ...
... before they reach their final form where they exhibit biological activity • N-formylmethionine in prokaryotes is _______________ • specific bonds in precursors are cleaved, as for example, preproinsulin to proinsulin to insulin • ___________ _________are removed by specific proteases of the endoplas ...
Macromolecular Structures
... All alpha proteins (138) All beta proteins (93) Alpha and beta proteins (a/b) (97) – Mainly parallel beta sheets (beta-alpha-beta units) ...
... All alpha proteins (138) All beta proteins (93) Alpha and beta proteins (a/b) (97) – Mainly parallel beta sheets (beta-alpha-beta units) ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.