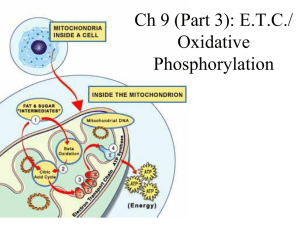
Ch 9: E.T.C./ Oxidative Phosphorylation
... • the groups along the chain alternate between reduced & oxidized states as they accept and donate electrons • each successive group is more electronegative than the group before it, so the electrons are “pulled downhill” towards OXYGEN (the final electron carrier!) ...
... • the groups along the chain alternate between reduced & oxidized states as they accept and donate electrons • each successive group is more electronegative than the group before it, so the electrons are “pulled downhill” towards OXYGEN (the final electron carrier!) ...
Name: ______ Date: Period: ATP, Photosynthesis and Cellular
... http://www.biology.iupui.edu/biocourses/N100/2k4ch7respirationnotes.html 29. What is the definition of Cellular Respiration?(in purple) 30. What happens during cellular respiration? 31. What’s the equation for Cellular Respiration? Stages of Cellular respiration. http://www.essortment.com/understand ...
... http://www.biology.iupui.edu/biocourses/N100/2k4ch7respirationnotes.html 29. What is the definition of Cellular Respiration?(in purple) 30. What happens during cellular respiration? 31. What’s the equation for Cellular Respiration? Stages of Cellular respiration. http://www.essortment.com/understand ...
Are Aggregates of Enzyme Molecules More Effective than Individual
... Citation: Pundir CS (2016) Are Aggregates of Enzyme Molecules More Effective than Individual Enzyme Molecules? Mol Enz Drug Tar 2:2 ...
... Citation: Pundir CS (2016) Are Aggregates of Enzyme Molecules More Effective than Individual Enzyme Molecules? Mol Enz Drug Tar 2:2 ...
bch2ibm: molecular biology end of semester 1 exam notes 2014
... -‐ One side of the adaptor could bind a specific AA to it, while the other side recognises the nucleotide sequence in mRNA. -‐ Molecule now called tRNA ...
... -‐ One side of the adaptor could bind a specific AA to it, while the other side recognises the nucleotide sequence in mRNA. -‐ Molecule now called tRNA ...
Self Assessment Chapter 2, part 2 - CM
... • Carbohydrates, composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, function primarily as fuel; some limited structural roles • Monosaccharides – consist of 3 to 7 carbons; monomers from which all carbohydrates are made; glucose, fructose, galactose, ribose, and dexoyribose are most abundant monosaccharides ...
... • Carbohydrates, composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, function primarily as fuel; some limited structural roles • Monosaccharides – consist of 3 to 7 carbons; monomers from which all carbohydrates are made; glucose, fructose, galactose, ribose, and dexoyribose are most abundant monosaccharides ...
File
... C) Ubiquinone of the electron transport chain D) Cytochrome of the electron transport chain E) NADH channel ...
... C) Ubiquinone of the electron transport chain D) Cytochrome of the electron transport chain E) NADH channel ...
Lecture PowerPoint
... Cells: fundamental units of all living organisms. Cells are specialized to specific functions in the body. There is a division of labor. Some cells produce mineral for bone, some cells produce protein for muscle contraction, etc. Tissues: Tissues are groups of similar cells that function together. T ...
... Cells: fundamental units of all living organisms. Cells are specialized to specific functions in the body. There is a division of labor. Some cells produce mineral for bone, some cells produce protein for muscle contraction, etc. Tissues: Tissues are groups of similar cells that function together. T ...
First Trimester Kevin Hoffmeyer`s Biology
... 1. Describe the steps of the scientific method. 2. What is a hypothesis? 3. What is a control or control group? 4. What is an independent variable? Dependent variable? Chapter 4: Chemistry of Life 1. What are the three particles that make up an atom? Location? Charge? 2. What is an ion? Give an exam ...
... 1. Describe the steps of the scientific method. 2. What is a hypothesis? 3. What is a control or control group? 4. What is an independent variable? Dependent variable? Chapter 4: Chemistry of Life 1. What are the three particles that make up an atom? Location? Charge? 2. What is an ion? Give an exam ...
Genes and Gene Action
... types of amino acids. The order in which the amino acids are joined determines which protein is made. Every different protein has a unique sequence of amino acids. This sequence determines the shape of a protein molecule. It is the shape of the protein that allows the molecule to do its work in the ...
... types of amino acids. The order in which the amino acids are joined determines which protein is made. Every different protein has a unique sequence of amino acids. This sequence determines the shape of a protein molecule. It is the shape of the protein that allows the molecule to do its work in the ...
Carbohydrate metabolism File
... i) Glycogenesis in which the excess glucose is converted into glycogen as a cellular storage compound. ii) Glycogenolysis involves the breakdown of glycogen into glucose, which provides a glucose supply for glucosedependent tissues. 2. Oxidative degradation to CO2 i)Glycolysis is the pathway in whic ...
... i) Glycogenesis in which the excess glucose is converted into glycogen as a cellular storage compound. ii) Glycogenolysis involves the breakdown of glycogen into glucose, which provides a glucose supply for glucosedependent tissues. 2. Oxidative degradation to CO2 i)Glycolysis is the pathway in whic ...
MACRONUTRIENT FOUNDATIONS
... Protein is STRUCTURE • Protein plays a big role in keeping the body functioning properly, and a healthy, nourished body is one that can perform at the highest levels. • In our bodies, protein makes up tissues (including muscle), enzymes (which help facilitate reactions in the body, e.g., metabolism ...
... Protein is STRUCTURE • Protein plays a big role in keeping the body functioning properly, and a healthy, nourished body is one that can perform at the highest levels. • In our bodies, protein makes up tissues (including muscle), enzymes (which help facilitate reactions in the body, e.g., metabolism ...
Glycolipids and Glyc..
... composition of the saccharide moiety is cell type specific, depends on the developmental stage of the organism, or can change with the oncogenic state of a cell. The central and peripheral nervous systems are rich in many specialized lipids, but have a very low percentage of triglycerides (fat). Bra ...
... composition of the saccharide moiety is cell type specific, depends on the developmental stage of the organism, or can change with the oncogenic state of a cell. The central and peripheral nervous systems are rich in many specialized lipids, but have a very low percentage of triglycerides (fat). Bra ...
6.2, 6.4, H.5, H.6 KEY Summative Test 2014
... 2. altitude has little effect as the values for 0 m normoxia and 5260 m normoxia are very similar / normoxia is the (more) important factor (at both altitudes); 3. O2 levels are significant as values for 0 m hypoxia and 5260 m hypoxia are very similar/much lower than for normoxia; 4. O2 levels ...
... 2. altitude has little effect as the values for 0 m normoxia and 5260 m normoxia are very similar / normoxia is the (more) important factor (at both altitudes); 3. O2 levels are significant as values for 0 m hypoxia and 5260 m hypoxia are very similar/much lower than for normoxia; 4. O2 levels ...
Codon - Cloudfront.net
... DNA and Translation • Gene: section of DNA that creates a specific protein – Approx 25,000 human genes • Proteins are used to build cells and tissue • Protein synthesis involves two processes: 1) Transcription 2) Translation ...
... DNA and Translation • Gene: section of DNA that creates a specific protein – Approx 25,000 human genes • Proteins are used to build cells and tissue • Protein synthesis involves two processes: 1) Transcription 2) Translation ...
Protein Synthesis Notes
... chain is 100+ amino acids long. 5. When a stop codon is reached, translation ends and the polypeptide (protein) is released. 6. The polypeptide’s a.a. sequence will determine how the protein folds into a 3-D functional shape. http://nobelprize.org/educational/medicine/dna/b/translation/translation_a ...
... chain is 100+ amino acids long. 5. When a stop codon is reached, translation ends and the polypeptide (protein) is released. 6. The polypeptide’s a.a. sequence will determine how the protein folds into a 3-D functional shape. http://nobelprize.org/educational/medicine/dna/b/translation/translation_a ...
oxidation
... 6.15 Cells use many kinds of organic molecules as fuel for cellular respiration Although glucose is considered to be the primary source of sugar for respiration and fermentation, ATP is generated using – carbohydrates, – fats, and – proteins. ...
... 6.15 Cells use many kinds of organic molecules as fuel for cellular respiration Although glucose is considered to be the primary source of sugar for respiration and fermentation, ATP is generated using – carbohydrates, – fats, and – proteins. ...
Review Ribosome-independent Peptide Synthesis in Nature and
... Ala-Met, and Thr-Phe, respectively, were also reported (44). Obviously, the direct fermentation method is the most cost-effective for dipeptide manufacturing since it dose not need even the substrate amino acids. However, there has been little insight into balancing two metabolic fluxes or the intra ...
... Ala-Met, and Thr-Phe, respectively, were also reported (44). Obviously, the direct fermentation method is the most cost-effective for dipeptide manufacturing since it dose not need even the substrate amino acids. However, there has been little insight into balancing two metabolic fluxes or the intra ...
Unit 04 Lecture Notes - Roderick Anatomy and Physiology
... • I know what DNA is and why it is important to cells. • I know can explain how information is transmitted from parents to offspring. • I know all DNA in a cell is known as a person’s ...
... • I know what DNA is and why it is important to cells. • I know can explain how information is transmitted from parents to offspring. • I know all DNA in a cell is known as a person’s ...
"Introduction to Microbial Physiology". In: Microbial Physiology
... cells is a lipid bilayer composed of phospholipids, glycolipids, and a variety of proteins. The proteins in the cytoplasmic membrane may extend through its entire thickness. Some of these proteins provide structural support to the membrane while others function in the transport of sugars, amino acid ...
... cells is a lipid bilayer composed of phospholipids, glycolipids, and a variety of proteins. The proteins in the cytoplasmic membrane may extend through its entire thickness. Some of these proteins provide structural support to the membrane while others function in the transport of sugars, amino acid ...
lect5
... Urea - major nitrogen excretion product. NH4+ - produced in the kidney by deamination of glutamine. Reduces body acidity because the process removes protons. ...
... Urea - major nitrogen excretion product. NH4+ - produced in the kidney by deamination of glutamine. Reduces body acidity because the process removes protons. ...
CH_17_6_Genetic_Mutations
... When a mutation causes a change in the amino acid sequence the structure of the resulting protein may be severely altered, causing loss of its biological activity. Altered enzymes cannot catalyze reactions, and possible toxins may accumulate in the body and may be lethal. When this condition is here ...
... When a mutation causes a change in the amino acid sequence the structure of the resulting protein may be severely altered, causing loss of its biological activity. Altered enzymes cannot catalyze reactions, and possible toxins may accumulate in the body and may be lethal. When this condition is here ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.























