Chapter 14 Glycolysis and the catabolism of hexoses
... called ‘ketone bodies’ that are then used in the muscle as an energy source. It is these ketone bodies that are acidic and lower the pH of the blood causing ketoacidosis ...
... called ‘ketone bodies’ that are then used in the muscle as an energy source. It is these ketone bodies that are acidic and lower the pH of the blood causing ketoacidosis ...
File - Mr. Krueger`s Biology
... Water – Helps maintain HOMEOSTASIS Polar, it has oppositely charged regions that allow soluble substances to be pulled apart (dissolved). Water and sugar are polar, oil is NONpolar. Universal Solvent – able to dissolve ALL polar molecules High Heat Capacity – water takes longer to cool down and heat ...
... Water – Helps maintain HOMEOSTASIS Polar, it has oppositely charged regions that allow soluble substances to be pulled apart (dissolved). Water and sugar are polar, oil is NONpolar. Universal Solvent – able to dissolve ALL polar molecules High Heat Capacity – water takes longer to cool down and heat ...
GPI Anchor
... 1. Proteins with a terminal Leu are modified by an isoprenyltransferase that transfers from geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate to Cys. Proteins with terminal residues, Ser, Ala, Met, or Gln are modified by another enzyme that adds farnesyl pyrophosphate to Cys. 2. Following the attachment of the isoprenyl ...
... 1. Proteins with a terminal Leu are modified by an isoprenyltransferase that transfers from geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate to Cys. Proteins with terminal residues, Ser, Ala, Met, or Gln are modified by another enzyme that adds farnesyl pyrophosphate to Cys. 2. Following the attachment of the isoprenyl ...
Topic One: Chemistry of Living Things
... C) Homeostasis is often maintained using ______________________ mechanisms. 1. Feedback mechanisms are cycles in which the product of one reaction causes another to start or stop. D) While organisms are balanced, they are not unchanging. The term used to describe the balanced state is dynamic equili ...
... C) Homeostasis is often maintained using ______________________ mechanisms. 1. Feedback mechanisms are cycles in which the product of one reaction causes another to start or stop. D) While organisms are balanced, they are not unchanging. The term used to describe the balanced state is dynamic equili ...
Characteristics of Life: • Living things have cells. o Cell:
... Living things have cells. o Cell: __________________________________ ______________________________________ o Some organisms have ______ cell, some are made up of ___________________ of cells. Living things sense and respond to change. o _____________________: maintenance of a stable internal en ...
... Living things have cells. o Cell: __________________________________ ______________________________________ o Some organisms have ______ cell, some are made up of ___________________ of cells. Living things sense and respond to change. o _____________________: maintenance of a stable internal en ...
Energy Review Questions
... Define substrate. The substrate is the molecule the enzyme binds to and changes. Describe activation energy and explain how an enzyme operates. The activation energy is the energy required to initiate a chemical reaction. Enzymes bind temporarily to one or more of the reactants of the reaction they ...
... Define substrate. The substrate is the molecule the enzyme binds to and changes. Describe activation energy and explain how an enzyme operates. The activation energy is the energy required to initiate a chemical reaction. Enzymes bind temporarily to one or more of the reactants of the reaction they ...
BIOL1003 Sample
... tails connected by glycerol. • Functions of the cell: o Cell metabolism and energy use: ! Cell metabolism: the collective chemical reactions that occur within cells. ! Energy released during metabolism i ...
... tails connected by glycerol. • Functions of the cell: o Cell metabolism and energy use: ! Cell metabolism: the collective chemical reactions that occur within cells. ! Energy released during metabolism i ...
Pyruvate Oxidation and the Krebs Cycle
... ● step 1: Acetic acid subunit of acetyl CoA is combined with oxaloacetate to form molecule of citrate ● step 2:Citrate(6-C) is rearranged to isocitrate(6-C). ● step 3:Isocitrate (6-C) is converted to -ketoglutarate (5C) by losing a CO2 and two hydrogen atoms that reduce NAD+to NADH. ● step 4:-ketogl ...
... ● step 1: Acetic acid subunit of acetyl CoA is combined with oxaloacetate to form molecule of citrate ● step 2:Citrate(6-C) is rearranged to isocitrate(6-C). ● step 3:Isocitrate (6-C) is converted to -ketoglutarate (5C) by losing a CO2 and two hydrogen atoms that reduce NAD+to NADH. ● step 4:-ketogl ...
Protein Structure - Laboratory of Molecular Modelling
... similar to those found in individual amino acids and small peptides (2) peptide bond – should be planer (3) overlaps – not permitted, pairs of atoms no closer than sum of their covalent radii (4) stabilization – have sterics that permit hydrogen bonding ...
... similar to those found in individual amino acids and small peptides (2) peptide bond – should be planer (3) overlaps – not permitted, pairs of atoms no closer than sum of their covalent radii (4) stabilization – have sterics that permit hydrogen bonding ...
МИНИСТЕРСТВО ОБРАЗОВАНИЯ И НАУКИ
... Biochemistry is the branch of science that explores the chemical processes within and related to living organisms. It is a laboratory based science that brings together biology and chemistry. By using chemical knowledge and techniques, biochemists can understand and solve biological problems 1.3 Cou ...
... Biochemistry is the branch of science that explores the chemical processes within and related to living organisms. It is a laboratory based science that brings together biology and chemistry. By using chemical knowledge and techniques, biochemists can understand and solve biological problems 1.3 Cou ...
Protein Structure
... similar to those found in individual amino acids and small peptides (2) peptide bond – should be planer (3) overlaps – not permitted, pairs of atoms no closer than sum of their covalent radii (4) stabilization – have sterics that permit hydrogen bonding ...
... similar to those found in individual amino acids and small peptides (2) peptide bond – should be planer (3) overlaps – not permitted, pairs of atoms no closer than sum of their covalent radii (4) stabilization – have sterics that permit hydrogen bonding ...
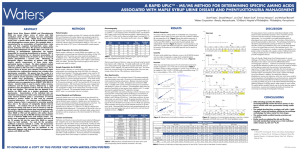
A Rapid UPLC™ MS/MS Method for Determining Specific
... metabolism which, if left untreated, can have catastrophic consequences for the child. Maple Syrup Urine Disease results from a genetic defect of the branched-chain a-keto acid dehydrogenase enzyme system. This metabolic defect is characterized by an accumulation of branched-chain α-keto acids and t ...
... metabolism which, if left untreated, can have catastrophic consequences for the child. Maple Syrup Urine Disease results from a genetic defect of the branched-chain a-keto acid dehydrogenase enzyme system. This metabolic defect is characterized by an accumulation of branched-chain α-keto acids and t ...
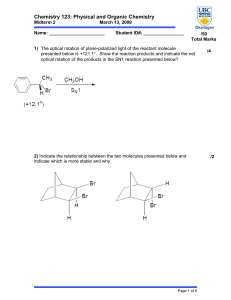
Chemistry 123: Physical and Organic Chemistry
... 17) CO2 is a greenhouse gas because…. (A) It absorbs infrared radiation (B) It has a high entropy (C) It makes plants grow better in a greenhouse (D) It has a high enthalpy of formation 18) Carbon dating is possible due to; (A) open minded rate laws (B) Irradiation of N2(g) by cosmic radiation (C) N ...
... 17) CO2 is a greenhouse gas because…. (A) It absorbs infrared radiation (B) It has a high entropy (C) It makes plants grow better in a greenhouse (D) It has a high enthalpy of formation 18) Carbon dating is possible due to; (A) open minded rate laws (B) Irradiation of N2(g) by cosmic radiation (C) N ...
The genetic code and tRNA Biochemistry 302 February 15, 2006
... •1: Used synthetic RNA triplets that would bind ribosomes and specify the binding of only certain aminoacylated-tRNAs • 2: Developed cell-free translation system using random RNA polymers prepared with polynucleotide phosphorylase (NMP)n + NDP ⇌ (NMP)n+1 + Pi ...
... •1: Used synthetic RNA triplets that would bind ribosomes and specify the binding of only certain aminoacylated-tRNAs • 2: Developed cell-free translation system using random RNA polymers prepared with polynucleotide phosphorylase (NMP)n + NDP ⇌ (NMP)n+1 + Pi ...
B3 revision part 2
... Enzymes • Enzymes are biological catalysts – they speed up a biological reaction. • Each enzyme is specific to a substrate. The substrate molecules are changed into product molecules. • Enzyme controlled reactions are affected by pH and temperature. ...
... Enzymes • Enzymes are biological catalysts – they speed up a biological reaction. • Each enzyme is specific to a substrate. The substrate molecules are changed into product molecules. • Enzyme controlled reactions are affected by pH and temperature. ...
Protein Synthesis
... By the end of this unit you will: know what transcription is know what translation is understand how proteins are made. ...
... By the end of this unit you will: know what transcription is know what translation is understand how proteins are made. ...
Biotechnology and Bioengineering 25:
... In experiments with rats, the biological value (BV) of the bacterial proteins, calculated on the basis of the total N content of the diet, was 62. The N digestibility was 90%, which indicates a good utilization of the bacterial proteins. The net protein utilization (NPU) of 56 was calculated from th ...
... In experiments with rats, the biological value (BV) of the bacterial proteins, calculated on the basis of the total N content of the diet, was 62. The N digestibility was 90%, which indicates a good utilization of the bacterial proteins. The net protein utilization (NPU) of 56 was calculated from th ...
Amino Acids - Angelo State University
... • More than 200 peptides have been identified as being essential to the body’s proper functioning. • Vasopressin and oxytocin are nonapeptide hormones secreted by the pituitary gland. Six of the amino acid residues are held in a loop by disulfide bridges formed by the oxidation of two cysteine resid ...
... • More than 200 peptides have been identified as being essential to the body’s proper functioning. • Vasopressin and oxytocin are nonapeptide hormones secreted by the pituitary gland. Six of the amino acid residues are held in a loop by disulfide bridges formed by the oxidation of two cysteine resid ...
AB Home » Focus Groups » Current »
... Translation and the Ribosome. In translation, information is transduced from polynucleotide to polypeptide. During translation, the Yin of biology connects directly with the Yang. Since the assembly principles of these two polymers are converses of each other (sidec ...
... Translation and the Ribosome. In translation, information is transduced from polynucleotide to polypeptide. During translation, the Yin of biology connects directly with the Yang. Since the assembly principles of these two polymers are converses of each other (sidec ...
Slide 1 - Killeen ISD
... Mixture – two or more compounds physically joined together – one substance (solute) dissolves in ...
... Mixture – two or more compounds physically joined together – one substance (solute) dissolves in ...
IMGT/Collier-de-Perles: a two-dimensional visualization tool for
... Amino acids can be defined and classified in a number of ways, depending on the perspective they are being examined from each time. Thereby, they can be categorized according to the functional groups of their side chains, which determine their physicochemical characteristics [1]. Taking into account ...
... Amino acids can be defined and classified in a number of ways, depending on the perspective they are being examined from each time. Thereby, they can be categorized according to the functional groups of their side chains, which determine their physicochemical characteristics [1]. Taking into account ...
Chap 4 Study Guide
... 1. bioenergetics incorporates these first and second laws 3. the cell's “universal energy carrier” 7. reactions that require energy input 10. oxidizing or reducing ________ 11. different model of the same enzyme 13. compounds mainly derived from water-soluble vitamins 15. inborn error of phenylalani ...
... 1. bioenergetics incorporates these first and second laws 3. the cell's “universal energy carrier” 7. reactions that require energy input 10. oxidizing or reducing ________ 11. different model of the same enzyme 13. compounds mainly derived from water-soluble vitamins 15. inborn error of phenylalani ...
Human Transforming Growth Factor - beta 1
... related to the products at any time. Products are not intended for human or animal diagnostic or therapeutic use but for laboratory, research or further manufacturing use only, unless otherwise specified. Statements contained herein should not be considered as a warranty of any kind, expressed or im ...
... related to the products at any time. Products are not intended for human or animal diagnostic or therapeutic use but for laboratory, research or further manufacturing use only, unless otherwise specified. Statements contained herein should not be considered as a warranty of any kind, expressed or im ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.