Chapter 1 Biology Exam Study Guide
... 1. What is biology the study of? Biology is the study of life. 2. What are the 4 characteristics of life? 1. All organisms are made up of one or more cells. 2. All organisms need a source of energy for their life processes. 3. All organisms must respond to their environment. 4. Members of a species ...
... 1. What is biology the study of? Biology is the study of life. 2. What are the 4 characteristics of life? 1. All organisms are made up of one or more cells. 2. All organisms need a source of energy for their life processes. 3. All organisms must respond to their environment. 4. Members of a species ...
Study Guide
... receptor proteins (e.g., T1R2 and T1R3), are expressed inside embryonic kidney cells (Hek293t), which then respond to taste stimuli as normal taste receptors would, triggering a rise in intracellular calcium. This calcium signal can then be made visible via a calcium-dependent photoprotein, which em ...
... receptor proteins (e.g., T1R2 and T1R3), are expressed inside embryonic kidney cells (Hek293t), which then respond to taste stimuli as normal taste receptors would, triggering a rise in intracellular calcium. This calcium signal can then be made visible via a calcium-dependent photoprotein, which em ...
Benfotiamine 150 + Alpha-Lipoic Acid 300
... “mitochondrial nutrient” helps to address these aging factors.18, 19 Benfotiamine has several means of fighting the aging process. It can enhance transketolase activity by promoting tissue levels of thiamine diphosphate, leading to metabolic pathways favoring less production of Advanced Glycation En ...
... “mitochondrial nutrient” helps to address these aging factors.18, 19 Benfotiamine has several means of fighting the aging process. It can enhance transketolase activity by promoting tissue levels of thiamine diphosphate, leading to metabolic pathways favoring less production of Advanced Glycation En ...
LT AP BIO
... ATP-coupled reactions • The body couples ATP hydrolysis to endergonic processes by transferring a P to another molecule • The Phosphorylated molecule is less stable (more reactive) • This turns an endergonic reaction to an exergonic (spontaneous) reaction ...
... ATP-coupled reactions • The body couples ATP hydrolysis to endergonic processes by transferring a P to another molecule • The Phosphorylated molecule is less stable (more reactive) • This turns an endergonic reaction to an exergonic (spontaneous) reaction ...
The Respiratory System
... • Warms & moistens air • Glands that produce sticky mucus line the nasal cavity – traps dust, pollen, and other materials that were not trapped by nasal hairs – cilia sweep mucus and trapped material to the back of the throat where it can be swallowed ...
... • Warms & moistens air • Glands that produce sticky mucus line the nasal cavity – traps dust, pollen, and other materials that were not trapped by nasal hairs – cilia sweep mucus and trapped material to the back of the throat where it can be swallowed ...
Chapter 1 Biology Exam Study Guide
... 1. What is biology the study of? Biology is the study of life. 2. What are the 4 characteristics of life? 1. All organisms are made up of one or more cells. 2. All organisms need a source of energy for their life processes. 3. All organisms must respond to their environment. 4. Members of a species ...
... 1. What is biology the study of? Biology is the study of life. 2. What are the 4 characteristics of life? 1. All organisms are made up of one or more cells. 2. All organisms need a source of energy for their life processes. 3. All organisms must respond to their environment. 4. Members of a species ...
Biological membranes, cell compartments
... • The most dynamic part of cytoskeleton are microfilaments (actin filaments). • Diameter is 6nm • Formed by two linear polymers of actin subunits ...
... • The most dynamic part of cytoskeleton are microfilaments (actin filaments). • Diameter is 6nm • Formed by two linear polymers of actin subunits ...
ch24a_wcr
... • Liver can convert many molecules into those needed • Essential nutrients – Diet must provide; liver cannot synthesize – Possibly 50 molecules ...
... • Liver can convert many molecules into those needed • Essential nutrients – Diet must provide; liver cannot synthesize – Possibly 50 molecules ...
Artifact 1
... (c) An additional secondary effect of excess glu‐6‐P is that glu‐6‐P is then directed into production of triglycerides and exported for storage in adipose tissue as fat. Chronically low insulin levels that are a secondary effect of hypoglycemia amplify this production of ...
... (c) An additional secondary effect of excess glu‐6‐P is that glu‐6‐P is then directed into production of triglycerides and exported for storage in adipose tissue as fat. Chronically low insulin levels that are a secondary effect of hypoglycemia amplify this production of ...
20.2 Classification of Enzymes
... Isoenzymes As Diagnostic Tools Isoenzymes • are different forms of an enzyme that catalyze the same reaction in different cells or tissues of the body. • have quaternary structures with slight variations in the amino acids in the polypeptide subunits. There are five isoenzymes of lactate dehydrogena ...
... Isoenzymes As Diagnostic Tools Isoenzymes • are different forms of an enzyme that catalyze the same reaction in different cells or tissues of the body. • have quaternary structures with slight variations in the amino acids in the polypeptide subunits. There are five isoenzymes of lactate dehydrogena ...
Biochemistry I, Spring Term 2000 - Third Exam
... Note: The concentration difference gives the same amount of free energy difference for protons and phosphate ions. In both cases it would be favorable for the proton or the phosphate to diffuse back into the cell. In the case of the electrostatic contribution, the effect is just the opposite. Not su ...
... Note: The concentration difference gives the same amount of free energy difference for protons and phosphate ions. In both cases it would be favorable for the proton or the phosphate to diffuse back into the cell. In the case of the electrostatic contribution, the effect is just the opposite. Not su ...
Fatty acid
... form strong building materials for plants Enzymes that digest starch by hydrolyzing linkages can’t hydrolyze linkages in cellulose Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings ...
... form strong building materials for plants Enzymes that digest starch by hydrolyzing linkages can’t hydrolyze linkages in cellulose Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings ...
Homework Assignment #4
... 6. (4 pts) Indicate whether each sample of matter listed is a mixture or pure, if mixture, then indicate whether the mixture is homogeneous or heterogeneous: a) A cube of sugar is a _________________________________________ . b) Premium gasoline is a ________________________________________ . c) Tap ...
... 6. (4 pts) Indicate whether each sample of matter listed is a mixture or pure, if mixture, then indicate whether the mixture is homogeneous or heterogeneous: a) A cube of sugar is a _________________________________________ . b) Premium gasoline is a ________________________________________ . c) Tap ...
GHSGT Biology Review
... o Xylem: transports water and nutrients from the roots to the rest of the plant o Phloem: transports products of photosynthesis to the rest of the plant. ...
... o Xylem: transports water and nutrients from the roots to the rest of the plant o Phloem: transports products of photosynthesis to the rest of the plant. ...
Acid-Base balance: overview
... Weak acids good buffers since they can tilt a reaction in the other direction ...
... Weak acids good buffers since they can tilt a reaction in the other direction ...
Gateway Biology Review- Answer Key Characteristics of Living
... o Xylem: transports water and nutrients from the roots to the rest of the plant o Phloem: transports products of photosynthesis to the rest of the plant. ...
... o Xylem: transports water and nutrients from the roots to the rest of the plant o Phloem: transports products of photosynthesis to the rest of the plant. ...
Biology Review Notes Summary
... o Xylem: transports water and nutrients from the roots to the rest of the plant o Phloem: transports products of photosynthesis to the rest of the plant. ...
... o Xylem: transports water and nutrients from the roots to the rest of the plant o Phloem: transports products of photosynthesis to the rest of the plant. ...
Quiz (B) 1. Which of the following statements concerning enzyme
... a. Heterotropic effectors; some enzymes are regulated by their own product. b. Allosteric effectors always increase K0.5 c. induction or repression the enzyme synthesis, example insulin. d. Homotropic effectors; some enzymes are regulated by their own substrate. e. Covalent modification (phosphoryla ...
... a. Heterotropic effectors; some enzymes are regulated by their own product. b. Allosteric effectors always increase K0.5 c. induction or repression the enzyme synthesis, example insulin. d. Homotropic effectors; some enzymes are regulated by their own substrate. e. Covalent modification (phosphoryla ...
Ch. 17 Protein Synthesis
... Conclusion: One gene encodes one enzyme. Gene products encode both protein and RNA ...
... Conclusion: One gene encodes one enzyme. Gene products encode both protein and RNA ...
File
... Physical or chemical change? The rain turned to snow… Marty broke a class on the bathroom floor… I burned my bagel! I fried eggs for breakfast… I mixed baking soda and vinegar for science ...
... Physical or chemical change? The rain turned to snow… Marty broke a class on the bathroom floor… I burned my bagel! I fried eggs for breakfast… I mixed baking soda and vinegar for science ...
Alpha 1 Antitrypsin Deficiency
... • Liver Disease – Alpha 1 Antritrypsin secreted from the liver – The improperly folded protein cannot be secreted, and buildup causes liver damage. ...
... • Liver Disease – Alpha 1 Antritrypsin secreted from the liver – The improperly folded protein cannot be secreted, and buildup causes liver damage. ...
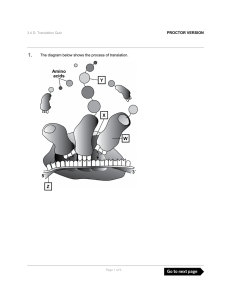
From Gene to Protein
... 4) The ribosome moves along the mRNA and adds more amino acids to the growing polypeptide or protein. 5) The process continues until the ribosome reaches one of the three stop codons on the mRNA, and then the ribosome falls off the mRNA. 6) The result is a polypeptide chain or protein that is ready ...
... 4) The ribosome moves along the mRNA and adds more amino acids to the growing polypeptide or protein. 5) The process continues until the ribosome reaches one of the three stop codons on the mRNA, and then the ribosome falls off the mRNA. 6) The result is a polypeptide chain or protein that is ready ...
Meet Your Macromolecules
... Items may require the student to apply science knowledge described in the standards from lower grades. This benchmark requires prerequisite knowledge from SC.8.P.8.5 and SC.6.L.14.3. ...
... Items may require the student to apply science knowledge described in the standards from lower grades. This benchmark requires prerequisite knowledge from SC.8.P.8.5 and SC.6.L.14.3. ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.