Problem Set 2
... (c) Now, you need to identify which nucleotide composition belongs to which species. To do this, you use a small amount of DNA that is still labeled as being from Species M or Species I. To determine which species has which nucleotide composition, you do a DNA re-naturing experiment. Below is the o ...
... (c) Now, you need to identify which nucleotide composition belongs to which species. To do this, you use a small amount of DNA that is still labeled as being from Species M or Species I. To determine which species has which nucleotide composition, you do a DNA re-naturing experiment. Below is the o ...
Respiration and Metabolism
... _____________major component of cell membranes; Acts as surfactant ...
... _____________major component of cell membranes; Acts as surfactant ...
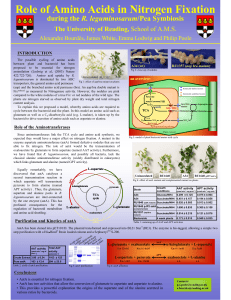
Role of Amino Acids in Nitrogen Fixation
... Since aminotransferases link the TCA cycle and amino acid synthesis, we expected they would have a major effect on nitrogen fixation. A mutant in the enzyme aspartate aminotransferase (aatA) formed defective nodules that are not able to fix nitrogen. The role of aatA would be the transamination of o ...
... Since aminotransferases link the TCA cycle and amino acid synthesis, we expected they would have a major effect on nitrogen fixation. A mutant in the enzyme aspartate aminotransferase (aatA) formed defective nodules that are not able to fix nitrogen. The role of aatA would be the transamination of o ...
7. Metabolism
... a) people follow a high-carbohydrate, low-fat diet. b) oxaloacetate builds up and TCA cycle activity increases. c) acetyl CoA is blocked from entering the TCA cycle. d) All of the above can prompt the production of ketones. ...
... a) people follow a high-carbohydrate, low-fat diet. b) oxaloacetate builds up and TCA cycle activity increases. c) acetyl CoA is blocked from entering the TCA cycle. d) All of the above can prompt the production of ketones. ...
Cellular Respiration
... • When the cell needs energy, ATP provides it by donating an energy-rich phosphate – re-forming the ADP molecule. energy-rich ...
... • When the cell needs energy, ATP provides it by donating an energy-rich phosphate – re-forming the ADP molecule. energy-rich ...
Central Dogma of Biology - Marengo Community Middle School
... Transcription and translation are the two main processes linking gene to protein: an overview • Genes provide the instructions for making specific proteins. • The bridge between DNA and protein synthesis is RNA. • RNA is chemically similar to DNA, except that it contains ribose as its sugar and sub ...
... Transcription and translation are the two main processes linking gene to protein: an overview • Genes provide the instructions for making specific proteins. • The bridge between DNA and protein synthesis is RNA. • RNA is chemically similar to DNA, except that it contains ribose as its sugar and sub ...
Chemistry of Water Notes
... A. Nitrogen is essential in producing amino acids (building blocks of proteins) B. Organic Nitrogen exists in three forms and requires bacteria in order to transfer among the three. C. Nitrate (NO3), Nitrite (NO2), and Ammonia (NH3) ...
... A. Nitrogen is essential in producing amino acids (building blocks of proteins) B. Organic Nitrogen exists in three forms and requires bacteria in order to transfer among the three. C. Nitrate (NO3), Nitrite (NO2), and Ammonia (NH3) ...
Expanding the Genetic Code with Unnatural Amino Acids
... groups can form tightly networked connections through noncovalent, ionic, hydrogen bonds and van der Waals interactions. These functional groups also form regions that are hydrophobic and hydrophilic. Furthermore, the sequence of amino acids determines how proteins will fold and interact.1 Proteins ...
... groups can form tightly networked connections through noncovalent, ionic, hydrogen bonds and van der Waals interactions. These functional groups also form regions that are hydrophobic and hydrophilic. Furthermore, the sequence of amino acids determines how proteins will fold and interact.1 Proteins ...
Introduction to genome biology
... us much about how the organism functions as a biological system. • We need to study how different gene products interact to produce various components. • Most important activities are not the result of a single molecule but depend on the coordinated effects of multiple molecules. ...
... us much about how the organism functions as a biological system. • We need to study how different gene products interact to produce various components. • Most important activities are not the result of a single molecule but depend on the coordinated effects of multiple molecules. ...
SUBSTRATE CYCLING (see Voet and Voet)
... Lactic acid which is transported out of the cell is carried away by the blood. Normal blood lactic acid concentration is maintained at ~ 1.2 mM or less., but may increase to greater than 5mM under conditions of lactic acidosis. When blood flow is inadequate, such as during heavy exercise of skeletal ...
... Lactic acid which is transported out of the cell is carried away by the blood. Normal blood lactic acid concentration is maintained at ~ 1.2 mM or less., but may increase to greater than 5mM under conditions of lactic acidosis. When blood flow is inadequate, such as during heavy exercise of skeletal ...
here
... similarity of percent identity. One often reads: sequence A and B are 70% homologous. To an evolutionary biologist this sounds as wrong as 70% pregnant. ...
... similarity of percent identity. One often reads: sequence A and B are 70% homologous. To an evolutionary biologist this sounds as wrong as 70% pregnant. ...
1 07 Cells in Their - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... Three “membranes” — glass, wire or plastic mesh, and cloth. ...
... Three “membranes” — glass, wire or plastic mesh, and cloth. ...
2012-ISB-symposium
... exploration of mass spectrometry detected peptides and their structural locations. Studying patterns of peptide location across a protein can be used for many purposes: exploring PTM (post translational modification) locations with respect to putative protein active sites and protein-protein interac ...
... exploration of mass spectrometry detected peptides and their structural locations. Studying patterns of peptide location across a protein can be used for many purposes: exploring PTM (post translational modification) locations with respect to putative protein active sites and protein-protein interac ...
Nucleic Acids
... To summarize protein synthesis: • A mRNA attaches to a ribosome. • tRNA molecules bonded to specific amino acids attach to the codons on mRNA. • Peptide bonds form between an amino acid and the peptide chain. • The ribosome shifts to each codon on the mRNA until it reach the STOP codon. • The polype ...
... To summarize protein synthesis: • A mRNA attaches to a ribosome. • tRNA molecules bonded to specific amino acids attach to the codons on mRNA. • Peptide bonds form between an amino acid and the peptide chain. • The ribosome shifts to each codon on the mRNA until it reach the STOP codon. • The polype ...
UNIT 3 – PHOTOSYNTHESIS AND CELLULAR RESPIRATION
... catabolic and anabolic pathways. Most of our food calories are obtained by eating fats, proteins and various carbohydrates. Polysaccharides are digested first that can join the process of glycolysis directly. Proteins are first broken down into amino acids which are mostly used to build new pr ...
... catabolic and anabolic pathways. Most of our food calories are obtained by eating fats, proteins and various carbohydrates. Polysaccharides are digested first that can join the process of glycolysis directly. Proteins are first broken down into amino acids which are mostly used to build new pr ...
Nucleic Acids - notescentre.com
... To summarize protein synthesis: • A mRNA attaches to a ribosome. • tRNA molecules bonded to specific amino acids attach to the codons on mRNA. • Peptide bonds form between an amino acid and the peptide chain. • The ribosome shifts to each codon on the mRNA until it reach the STOP codon. • The polype ...
... To summarize protein synthesis: • A mRNA attaches to a ribosome. • tRNA molecules bonded to specific amino acids attach to the codons on mRNA. • Peptide bonds form between an amino acid and the peptide chain. • The ribosome shifts to each codon on the mRNA until it reach the STOP codon. • The polype ...
Cellular Respiration - Ursuline High School
... c: is one of the proteins of the electron transport chain… often used by geneticists to determine relatedness… exists in all ...
... c: is one of the proteins of the electron transport chain… often used by geneticists to determine relatedness… exists in all ...
Lesson - ACS Distance Education (UK)
... ATP through this system, hence the lactic acid system may start to be used, resulting in a build up of lactic acid OR the ATP-PC system may be used resulting in a depletion of phosphocreatine in the muscles. After completing exercise, there may be a lactic acid build up, and if so, the body needs to ...
... ATP through this system, hence the lactic acid system may start to be used, resulting in a build up of lactic acid OR the ATP-PC system may be used resulting in a depletion of phosphocreatine in the muscles. After completing exercise, there may be a lactic acid build up, and if so, the body needs to ...
Fatty acid synthesis
... when blood glucose is high. Thus excess glucose is stored as fat. Transcription factors that that mediate the stimulatory effect of insulin include USFs (upstream stimulatory factors) and SREBP-1. SREBPs (sterol response element binding proteins) were first identified for their role in regulating ch ...
... when blood glucose is high. Thus excess glucose is stored as fat. Transcription factors that that mediate the stimulatory effect of insulin include USFs (upstream stimulatory factors) and SREBP-1. SREBPs (sterol response element binding proteins) were first identified for their role in regulating ch ...
Cellular Respiration: Harvesting Chemical Energy
... c: is one of the proteins of the electron transport chain… often used by geneticists to determine relatedness… exists in all ...
... c: is one of the proteins of the electron transport chain… often used by geneticists to determine relatedness… exists in all ...
review for the biology regents exam
... • Lipids are a source of stored energy for the body • Enzymes can break down lipids into fatty acids and glycerol ...
... • Lipids are a source of stored energy for the body • Enzymes can break down lipids into fatty acids and glycerol ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.