Metabolism of acyl‐lipids in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii
... microalgae has been deduced from well characterized pathways of fungi and land plants, but recent advances in molecular and genetic analyses of microalgae have uncovered unique features, pointing out the necessity to study lipid metabolism in microalgae themselves. In the past 10 years, in addition ...
... microalgae has been deduced from well characterized pathways of fungi and land plants, but recent advances in molecular and genetic analyses of microalgae have uncovered unique features, pointing out the necessity to study lipid metabolism in microalgae themselves. In the past 10 years, in addition ...
Unexpected similarities between the
... organic acids (chenodeoxycholic acid, glyceric acid), six methylated amino acids including dimethyl-proline, eight other amino acid derivatives including creatine, creatinine, and taurine, and ten carnitines. Thus, 24 of 32 compounds are derived from three categories, namely, methylated amino acids, ...
... organic acids (chenodeoxycholic acid, glyceric acid), six methylated amino acids including dimethyl-proline, eight other amino acid derivatives including creatine, creatinine, and taurine, and ten carnitines. Thus, 24 of 32 compounds are derived from three categories, namely, methylated amino acids, ...
Bin Presentation(sulfonic)3 - Indiana University Bloomington
... liver membranes [1, 4 and 5] were demonstrated to have appreciable cAMP activity that varied between 38100% of maximal in these engineered cells that over-express the glucagon receptor. We found that homocysteic acid can function as a substitute for Glu9 in glucagon structurefunction relationships, ...
... liver membranes [1, 4 and 5] were demonstrated to have appreciable cAMP activity that varied between 38100% of maximal in these engineered cells that over-express the glucagon receptor. We found that homocysteic acid can function as a substitute for Glu9 in glucagon structurefunction relationships, ...
Bio 1305--Modern Concepts of Bioscience
... 8. Describe the unique properties, building block molecules, and biological importance of the three groups of lipids: fats, phospholipids, and steroids 9. Distinguish between saturated and unsaturated fat and list some unique emergent properties that are a consequence of these structural differences ...
... 8. Describe the unique properties, building block molecules, and biological importance of the three groups of lipids: fats, phospholipids, and steroids 9. Distinguish between saturated and unsaturated fat and list some unique emergent properties that are a consequence of these structural differences ...
Analysis of the Role of Mitochondria of Sake in Fermentation Technologies
... Since sake yeast belongs to Saccharomyces cerevisiae (Akao et al. 2011), it is a facultative anaerobe, just as S. cerevisiae and can grow both with and without molecular oxygen. During respiration, namely, in the presence of oxygen and in the absence of fermentable sugars, sake yeast uses mitochondr ...
... Since sake yeast belongs to Saccharomyces cerevisiae (Akao et al. 2011), it is a facultative anaerobe, just as S. cerevisiae and can grow both with and without molecular oxygen. During respiration, namely, in the presence of oxygen and in the absence of fermentable sugars, sake yeast uses mitochondr ...
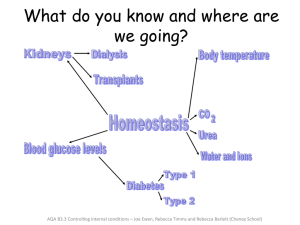
2301-B3.3 Controlling conditions lesson templates
... Urea is made in the liver. Urine is produced by the kidneys. Urine contains urea. Why is urea produced? Urea is the major organic component of human urine. This is because it is at the end of chain of reactions which break down the amino acids that make up proteins. These amino acids are metabolised ...
... Urea is made in the liver. Urine is produced by the kidneys. Urine contains urea. Why is urea produced? Urea is the major organic component of human urine. This is because it is at the end of chain of reactions which break down the amino acids that make up proteins. These amino acids are metabolised ...
Molecular characterization of carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1C Esther Gratacòs i Batlle
... WARNING. On having consulted this thesis you’re accepting the following use conditions: Spreading this thesis by the TDX (www.tesisenxarxa.net) service has been authorized by the titular of the intellectual property rights only for private uses placed in investigation and teaching activities. Reprod ...
... WARNING. On having consulted this thesis you’re accepting the following use conditions: Spreading this thesis by the TDX (www.tesisenxarxa.net) service has been authorized by the titular of the intellectual property rights only for private uses placed in investigation and teaching activities. Reprod ...
Purification and Characterization of
... 214 6 12.6 kD, suggesting a tetrameric structure for this catalyst. Because H. carterae PRK activity was insensitive to NADH but was stimulated by dithiothreitol, it appears that the enzyme may require a thioredoxin/ferredoxin rather than a metabolite mode of regulation. Kinetic analysis of this enz ...
... 214 6 12.6 kD, suggesting a tetrameric structure for this catalyst. Because H. carterae PRK activity was insensitive to NADH but was stimulated by dithiothreitol, it appears that the enzyme may require a thioredoxin/ferredoxin rather than a metabolite mode of regulation. Kinetic analysis of this enz ...
risk and technical assessment report
... β-galactosidic bonds in sugars such as lactose. Under conditions of high lactose concentrations the enzyme will use lactose as an alternative acceptor to water resulting in the formation of galacto-oligosaccharides (GOS). The enzyme may perform both hydrolysis and polymerisation with the equilibrium ...
... β-galactosidic bonds in sugars such as lactose. Under conditions of high lactose concentrations the enzyme will use lactose as an alternative acceptor to water resulting in the formation of galacto-oligosaccharides (GOS). The enzyme may perform both hydrolysis and polymerisation with the equilibrium ...
A1121 SD1 - Food Standards Australia New Zealand
... Using the enzyme during processing to produce meat and fish extracts is claimed to improve the taste, yield, nutritional content and physical properties. ...
... Using the enzyme during processing to produce meat and fish extracts is claimed to improve the taste, yield, nutritional content and physical properties. ...
14steriod
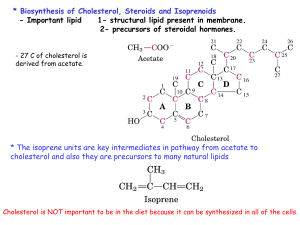
... - Bile consist of a watery mixture of organic and inorganic compounds. Bile can go from the liver directly to the intestine or to be stored at bilary gland. - The most common bile acid : Cholic and Chenodeoxycholic acid. - Bile acids are not fully ionized at pH = 7 because they have pKa = 6, (they a ...
... - Bile consist of a watery mixture of organic and inorganic compounds. Bile can go from the liver directly to the intestine or to be stored at bilary gland. - The most common bile acid : Cholic and Chenodeoxycholic acid. - Bile acids are not fully ionized at pH = 7 because they have pKa = 6, (they a ...
S17 Cholesterol And Steroids Biosynthesis
... - Bile consist of a watery mixture of organic and inorganic compounds. Bile can go from the liver directly to the intestine or to be stored at bilary gland. - The most common bile acid : Cholic and Chenodeoxycholic acid. - Bile acids are not fully ionized at pH = 7 because they have pKa = 6, (they a ...
... - Bile consist of a watery mixture of organic and inorganic compounds. Bile can go from the liver directly to the intestine or to be stored at bilary gland. - The most common bile acid : Cholic and Chenodeoxycholic acid. - Bile acids are not fully ionized at pH = 7 because they have pKa = 6, (they a ...
Document
... 6. Exchange of materials:- There is a regular exchange of materials between the living organisms and their environment. Living beings obtain nutrients, water and oxygen from their environment. They give out undigested materials, carbon dioxide and waste products. Single-celled organisms have the ent ...
... 6. Exchange of materials:- There is a regular exchange of materials between the living organisms and their environment. Living beings obtain nutrients, water and oxygen from their environment. They give out undigested materials, carbon dioxide and waste products. Single-celled organisms have the ent ...
An Introduction to Chemical Science
... any school or college in the country. During the present year the author personally supervises the work of more than 180 different pupils in chemistry. This enables him not only to assure himself that the experiments of the book are practical, but that the directions for performing them are ample. I ...
... any school or college in the country. During the present year the author personally supervises the work of more than 180 different pupils in chemistry. This enables him not only to assure himself that the experiments of the book are practical, but that the directions for performing them are ample. I ...
Salai guggal, the oleogum resin of the Boswellia serrata has been
... vitamins are essential for converting carbohydrates into energy, by burning glucose. Insulin is a hormone excreted by the pancreas which mainly functions to regulate the blood sugar level. Insulin therefore plays an important role in the carbohydrate metabolism. Each insulin molecule consists of two ...
... vitamins are essential for converting carbohydrates into energy, by burning glucose. Insulin is a hormone excreted by the pancreas which mainly functions to regulate the blood sugar level. Insulin therefore plays an important role in the carbohydrate metabolism. Each insulin molecule consists of two ...
Energy systems and interplay of energy systems
... Fats are the most concentrated form of energy for ATP resynthesis. Gram for gram, fats provide more energy than carbohydrates, with fats providing about 9 kilocalories per gram whereas carbohydrates provide about 4 kilocalories per gram. Despite this, fats are primarily used during rest and low-inte ...
... Fats are the most concentrated form of energy for ATP resynthesis. Gram for gram, fats provide more energy than carbohydrates, with fats providing about 9 kilocalories per gram whereas carbohydrates provide about 4 kilocalories per gram. Despite this, fats are primarily used during rest and low-inte ...
Chemical Modifications and Kinetic Study of Ribonuclease Sa Active
... According to Takahashi (1968) phenylglyoxal, a specific reagent for arginine, inactivates ribonuclease Ti. He found that phenylglyoxal blocks Arg 77 which binds the anionic phosphate group of the substrate (Takahashi 1970). In contrary to RNase Ti, the activity of ribonuclease Sa is not affected by ...
... According to Takahashi (1968) phenylglyoxal, a specific reagent for arginine, inactivates ribonuclease Ti. He found that phenylglyoxal blocks Arg 77 which binds the anionic phosphate group of the substrate (Takahashi 1970). In contrary to RNase Ti, the activity of ribonuclease Sa is not affected by ...
uncorrected page proofs
... Fats are the most concentrated form of energy for ATP resynthesis. Gram for gram, fats provide more energy than carbohydrates, with fats providing about 9 kilocalories per gram whereas carbohydrates provide about 4 kilocalories per gram. Despite this, fats are primarily used during rest and low-inte ...
... Fats are the most concentrated form of energy for ATP resynthesis. Gram for gram, fats provide more energy than carbohydrates, with fats providing about 9 kilocalories per gram whereas carbohydrates provide about 4 kilocalories per gram. Despite this, fats are primarily used during rest and low-inte ...
Effects of Heat Stress and Dietary Tryptophan on Performance and
... Within dietary Trp levels, means with different superscript letters were significantly different (p<0.05). p<0.05. NS: Not significant. ...
... Within dietary Trp levels, means with different superscript letters were significantly different (p<0.05). p<0.05. NS: Not significant. ...
Package `PPInfer`
... Description Interactions between proteins occur in many, if not most, biological processes. Most proteins perform their functions in networks associated with other proteins and other biomolecules. This fact has motivated the development of a variety of experimental methods for the identification of ...
... Description Interactions between proteins occur in many, if not most, biological processes. Most proteins perform their functions in networks associated with other proteins and other biomolecules. This fact has motivated the development of a variety of experimental methods for the identification of ...
Lipotoxicity in steatohepatitis occurs despite an increase in
... We controlled the experimentwide false discovery rate at Q ⬍ 0.05 (2). We next examined overall patterns in classes of metabolites (DAGs, Cer, organic acids, amino acids, and acylcarnitines) by summarizing each class of metabolites using a principal-components analysis on z-scored data (pcaMethods p ...
... We controlled the experimentwide false discovery rate at Q ⬍ 0.05 (2). We next examined overall patterns in classes of metabolites (DAGs, Cer, organic acids, amino acids, and acylcarnitines) by summarizing each class of metabolites using a principal-components analysis on z-scored data (pcaMethods p ...
Time-Resolved Transcriptome Analysis of Bacillus subtilis
... source, were used. The products of CAA-regulated genes are involved in various metabolic pathways, including nitrogen metabolism [16,17], the development of competence [18], and chemotaxis [19]. The CodY protein has been found to play a key role in mediating the CAA-dependent regulation. However, th ...
... source, were used. The products of CAA-regulated genes are involved in various metabolic pathways, including nitrogen metabolism [16,17], the development of competence [18], and chemotaxis [19]. The CodY protein has been found to play a key role in mediating the CAA-dependent regulation. However, th ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.