The Stereochemistry of Enzymatic Transamination“
... was about 500. Pyridoxal and pyridoxamine were separated and purified by the method of Peterson and Sober (1954). Preparation of Deuteriopyridoxamine. Pyridoxaminepyridoxal (3:l) mixtures in D20 at p D 4-5 were allowed t o stand at room temperature for several days. The mixtures were freeze dried, t ...
... was about 500. Pyridoxal and pyridoxamine were separated and purified by the method of Peterson and Sober (1954). Preparation of Deuteriopyridoxamine. Pyridoxaminepyridoxal (3:l) mixtures in D20 at p D 4-5 were allowed t o stand at room temperature for several days. The mixtures were freeze dried, t ...
Synthesis of RNA - Stamm revision
... accompanying product sheets. In general, the modified phosphoramidites are applied as 100 mM solutions in dry acetonitrile. At least 10 equivalents of modified amidites are used and coupling times are set for up to 12 minutes. It is advisable to use phosphoramidites with nucleobase protecting groups ...
... accompanying product sheets. In general, the modified phosphoramidites are applied as 100 mM solutions in dry acetonitrile. At least 10 equivalents of modified amidites are used and coupling times are set for up to 12 minutes. It is advisable to use phosphoramidites with nucleobase protecting groups ...
11 myp covalent bonding
... Chemical Bond • But depending on the composition of the substance, the bond between atoms in a compound is classified as either covalent, ionic or metallic. – The chemical bond in compounds made up only of non-metals is referred to as covalent bond. • We will consider covalent bonds, and look at ho ...
... Chemical Bond • But depending on the composition of the substance, the bond between atoms in a compound is classified as either covalent, ionic or metallic. – The chemical bond in compounds made up only of non-metals is referred to as covalent bond. • We will consider covalent bonds, and look at ho ...
Problem Set 1
... Because it targeted a different enzyme than the other NSAIDs listed above, it was hoped that it would cause fewer gastrointestinal side effects while having comparable (or better) anti-inflammatory activity. ...
... Because it targeted a different enzyme than the other NSAIDs listed above, it was hoped that it would cause fewer gastrointestinal side effects while having comparable (or better) anti-inflammatory activity. ...
Chapter 3 Stoichiometry: Ratios of Combination
... and sometimes O) are carried using an apparatus like the one below ...
... and sometimes O) are carried using an apparatus like the one below ...
PDF - FEMS Microbiology Letters
... and, in an attempt to discover whether both compounds act as substrates for the same enzyme or whether a separate enzyme is involved, he concluded that it seems highly probable that only one enzyme is involved in both decarboxylations (Epps, 1944). Finally in 1948, McGilvery and Cohen, in the course ...
... and, in an attempt to discover whether both compounds act as substrates for the same enzyme or whether a separate enzyme is involved, he concluded that it seems highly probable that only one enzyme is involved in both decarboxylations (Epps, 1944). Finally in 1948, McGilvery and Cohen, in the course ...
Structure and function of haemoglobin: II. Some
... If residues forming part of an ec-helix are defined as having their oc-carbonyl , or their cc-iminc groups or both, hydrogen-bonded within the helix, then model building shows that proline can occur in site s 1, 2, 3 or n 1 of an «-helix containing n residues. Prolines are in fact observed in all th ...
... If residues forming part of an ec-helix are defined as having their oc-carbonyl , or their cc-iminc groups or both, hydrogen-bonded within the helix, then model building shows that proline can occur in site s 1, 2, 3 or n 1 of an «-helix containing n residues. Prolines are in fact observed in all th ...
A structural determinant in the uracil DNA glycosylase superfamily
... apply a multitude of catalytic elements to catalyze the breakage of the glycosidic bond associated with pyrimidine and purine deaminated bases (3,12,16). Two important motifs have been identified in the UDG superfamily, in which motif 1 contains residues that form the base recognition pocket and a w ...
... apply a multitude of catalytic elements to catalyze the breakage of the glycosidic bond associated with pyrimidine and purine deaminated bases (3,12,16). Two important motifs have been identified in the UDG superfamily, in which motif 1 contains residues that form the base recognition pocket and a w ...
File
... production; HNO3: important industrial chemical, used to form nitrogen-based explosives, strong acid and a very strong oxidizing agent. ...
... production; HNO3: important industrial chemical, used to form nitrogen-based explosives, strong acid and a very strong oxidizing agent. ...
2015 International Practice Exam: Chemistry
... never discuss these specific multiple-choice questions at any time in any form with anyone, including your teacher and other students. If you disclose these questions through any means, your AP Exam score will be canceled. . . . You must complete the answer sheet using a No. 2 pencil only. Mark all ...
... never discuss these specific multiple-choice questions at any time in any form with anyone, including your teacher and other students. If you disclose these questions through any means, your AP Exam score will be canceled. . . . You must complete the answer sheet using a No. 2 pencil only. Mark all ...
Expression and activity of hexokinase in the early mouse embryo
... 1982). Hexokinase I has been the most extensively studied (largely in the rat) and is the only isoenzyme whose DNA sequence is available for mouse, derived from tumour tissue (Arora et al., 1990). The gene consists of two structural halves, both coding for proteins containing an ATP and a glucose bi ...
... 1982). Hexokinase I has been the most extensively studied (largely in the rat) and is the only isoenzyme whose DNA sequence is available for mouse, derived from tumour tissue (Arora et al., 1990). The gene consists of two structural halves, both coding for proteins containing an ATP and a glucose bi ...
BIOL 1322 General Nutrition
... Identify the essential fatty acids; their role in improving health; why they are essential Identify the 9 essential amino acids and why they are essential; what makes a complete protein; what foods are complete proteins Be able to determine the following from a fatty acid diagram: number of carbons, ...
... Identify the essential fatty acids; their role in improving health; why they are essential Identify the 9 essential amino acids and why they are essential; what makes a complete protein; what foods are complete proteins Be able to determine the following from a fatty acid diagram: number of carbons, ...
Stabilization by GroEL, a Molecular Chaperone, and a Periplasmic
... partment can be compared to the lumen of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) in eukaryotic cells. Many proteins are found in the periplasm, but the physiological functions of only a few such proteins are known. Furthermore, the periplasm of Escherichia coli has been of great interest with respect to the ...
... partment can be compared to the lumen of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) in eukaryotic cells. Many proteins are found in the periplasm, but the physiological functions of only a few such proteins are known. Furthermore, the periplasm of Escherichia coli has been of great interest with respect to the ...
BIOL 1322 General Nutrition
... Identify the essential fatty acids; their role in improving health; why they are essential Identify the 9 essential amino acids and why they are essential; what makes a complete protein; what foods are complete proteins Be able to determine the following from a fatty acid diagram: number of carbons, ...
... Identify the essential fatty acids; their role in improving health; why they are essential Identify the 9 essential amino acids and why they are essential; what makes a complete protein; what foods are complete proteins Be able to determine the following from a fatty acid diagram: number of carbons, ...
The Early Interaction of the Outer Membrane Protein PhoE with
... them, the peptidyl-prolyl isomerases (FkpA, SurA, RotA, and PpiD) carry out the isomerization around the Xaa-Pro peptide bond. In addition to the isomerase activity the FkpA and SurA proteins were found to posses chaperone activity (11, 12). The second type of folding catalysts are the protein disul ...
... them, the peptidyl-prolyl isomerases (FkpA, SurA, RotA, and PpiD) carry out the isomerization around the Xaa-Pro peptide bond. In addition to the isomerase activity the FkpA and SurA proteins were found to posses chaperone activity (11, 12). The second type of folding catalysts are the protein disul ...
Beta-lactam antibiotics
... β-Lactams can easily penetrate Gram (+) bacteria, but the outer cell membrane of Gram (-) bacteria prevents diffusion of the drug. βLactams can be modified to make use of import porins in the cell membrane. β-Lactams also have difficulty penetrating human cell membranes, making them ineffective agai ...
... β-Lactams can easily penetrate Gram (+) bacteria, but the outer cell membrane of Gram (-) bacteria prevents diffusion of the drug. βLactams can be modified to make use of import porins in the cell membrane. β-Lactams also have difficulty penetrating human cell membranes, making them ineffective agai ...
Cloning and Characterization of Human Urocortin
... seenfor rat Ucn and r/hCRF (Table 1). As has been noted for CRF (19), coincubation with CRP-BP prevents the releaseof ACTH by humanUcn (Fig. 3). The actionsand distribution of CRF-BP have led us to suggest that CRF-BP may serve lo temporally and anatomically limit the action of Ucn. Furthermore, bio ...
... seenfor rat Ucn and r/hCRF (Table 1). As has been noted for CRF (19), coincubation with CRP-BP prevents the releaseof ACTH by humanUcn (Fig. 3). The actionsand distribution of CRF-BP have led us to suggest that CRF-BP may serve lo temporally and anatomically limit the action of Ucn. Furthermore, bio ...
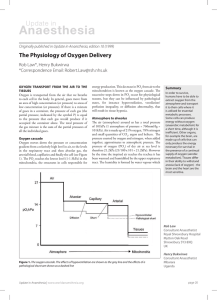
The Physiology of Oxygen Delivery
... pressure of oxygen (PO2) of dry air at sea level is therefore 21.2kPa (21/100 x 101 = 21.2kPa). However by the time the inspired air reaches the trachea it has been warmed and humidified by the upper respiratory tract. The humidity is formed by water vapour which ...
... pressure of oxygen (PO2) of dry air at sea level is therefore 21.2kPa (21/100 x 101 = 21.2kPa). However by the time the inspired air reaches the trachea it has been warmed and humidified by the upper respiratory tract. The humidity is formed by water vapour which ...
Immunoblot Detection of Proteins That Contain Cysteine
... Prxs was identified in yeast (6) and mammals (7) and was named sulfiredoxin (Srx). Reduction by Srx is specific to 2-Cys Prxs; the sulfinic forms of Prx V and Prx VI are thus not reduced by Srx (8). Moreover, Srx acts on neither the sulfinic form of GAPDH nor DJ-1 (8). This specificity is due to the ...
... Prxs was identified in yeast (6) and mammals (7) and was named sulfiredoxin (Srx). Reduction by Srx is specific to 2-Cys Prxs; the sulfinic forms of Prx V and Prx VI are thus not reduced by Srx (8). Moreover, Srx acts on neither the sulfinic form of GAPDH nor DJ-1 (8). This specificity is due to the ...
Biotechnology and Bioengineering
... and a 957 bp DNA fragment that includes the SalI restriction site downstream of codon F176 was amplified using primers F176-front and ToMO-SalI-rear (Table I). Similarly, to perform saturation mutagenesis at TouA position F196, a 763 bp DNA fragment was amplified using primers ToMO-KpnI-front and F1 ...
... and a 957 bp DNA fragment that includes the SalI restriction site downstream of codon F176 was amplified using primers F176-front and ToMO-SalI-rear (Table I). Similarly, to perform saturation mutagenesis at TouA position F196, a 763 bp DNA fragment was amplified using primers ToMO-KpnI-front and F1 ...
Unit F214
... muscle cells do not have enough oxygen / O2 is not available during anaerobic respiration / O2 is sufficient in hepatocytes ; ...
... muscle cells do not have enough oxygen / O2 is not available during anaerobic respiration / O2 is sufficient in hepatocytes ; ...
Unexpected similarities between the
... organic acids (chenodeoxycholic acid, glyceric acid), six methylated amino acids including dimethyl-proline, eight other amino acid derivatives including creatine, creatinine, and taurine, and ten carnitines. Thus, 24 of 32 compounds are derived from three categories, namely, methylated amino acids, ...
... organic acids (chenodeoxycholic acid, glyceric acid), six methylated amino acids including dimethyl-proline, eight other amino acid derivatives including creatine, creatinine, and taurine, and ten carnitines. Thus, 24 of 32 compounds are derived from three categories, namely, methylated amino acids, ...
Metabolism of acyl‐lipids in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii
... microalgae has been deduced from well characterized pathways of fungi and land plants, but recent advances in molecular and genetic analyses of microalgae have uncovered unique features, pointing out the necessity to study lipid metabolism in microalgae themselves. In the past 10 years, in addition ...
... microalgae has been deduced from well characterized pathways of fungi and land plants, but recent advances in molecular and genetic analyses of microalgae have uncovered unique features, pointing out the necessity to study lipid metabolism in microalgae themselves. In the past 10 years, in addition ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.