Problem Set I Answer Key
... evolutionary time scale these organisms likely arose. Explain your answer, which should not be an exact time but rather in terms of before/after which evolutionary events. (3 points) Mitochondria are thought to have been engulfed by an ancestral eukaryote sometime after oxygen began accumulating ...
... evolutionary time scale these organisms likely arose. Explain your answer, which should not be an exact time but rather in terms of before/after which evolutionary events. (3 points) Mitochondria are thought to have been engulfed by an ancestral eukaryote sometime after oxygen began accumulating ...
Document
... hydrochloric acid in an open beaker. The mass of the products was found to be less than the total mass of the reactants. How should the students have conducted their experiment to reflect the law of conservation of mass? A the students should have used a less reactive metal in their experiment. B Th ...
... hydrochloric acid in an open beaker. The mass of the products was found to be less than the total mass of the reactants. How should the students have conducted their experiment to reflect the law of conservation of mass? A the students should have used a less reactive metal in their experiment. B Th ...
Energetics of the nerve terminal in relation to central nervous system
... being much greater in synaptosomes than in their membranes. There are two binding sites for ATP on the pump, with differing affinities: the K,,, on the catalytic site is low ( 10pM)whereas that on the regulatory site is much higher, > 0.5 mM [I]. It is evident from a comparison of the affinities for ...
... being much greater in synaptosomes than in their membranes. There are two binding sites for ATP on the pump, with differing affinities: the K,,, on the catalytic site is low ( 10pM)whereas that on the regulatory site is much higher, > 0.5 mM [I]. It is evident from a comparison of the affinities for ...
4. MP and MPM that contain iridoids
... established based upon the number of isoprene (or isopentane) units incorporated in the basic molecular skeleton: ...
... established based upon the number of isoprene (or isopentane) units incorporated in the basic molecular skeleton: ...
Biology EOC review
... made up of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen with a 2:1 ratio of hydrogen to oxygen plants and animals use carbohydrates for maintaining structure within the cells - Proteins Nitrogen-containing compounds made up of chains of amino acids 20 amino acids can combine to form a great variety of protein molec ...
... made up of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen with a 2:1 ratio of hydrogen to oxygen plants and animals use carbohydrates for maintaining structure within the cells - Proteins Nitrogen-containing compounds made up of chains of amino acids 20 amino acids can combine to form a great variety of protein molec ...
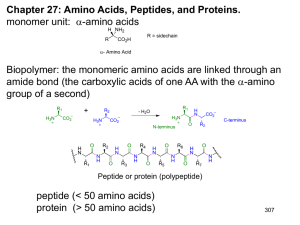
177 Chapter 26: Biomolecules: Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins
... R. Bruce Merrifield, Rockefeller University, 1984 Nobel Prize in Chemistry: “for his development of methodology for chemical synthesis on a solid matrix.” ...
... R. Bruce Merrifield, Rockefeller University, 1984 Nobel Prize in Chemistry: “for his development of methodology for chemical synthesis on a solid matrix.” ...
Cellular Respiration and Fermentation
... (2,870 kJ) of heat per mole of glucose (about 180 g). This reaction cannot happen at body temperatures. Instead, enzymes within cells lower the barrier of activation energy, allowing sugar to be oxidized in a series of steps. ...
... (2,870 kJ) of heat per mole of glucose (about 180 g). This reaction cannot happen at body temperatures. Instead, enzymes within cells lower the barrier of activation energy, allowing sugar to be oxidized in a series of steps. ...
Reece9e_Lecture_C09
... (2,870 kJ) of heat per mole of glucose (about 180 g). This reaction cannot happen at body temperatures. Instead, enzymes within cells lower the barrier of activation energy, allowing sugar to be oxidized in a series of steps. ...
... (2,870 kJ) of heat per mole of glucose (about 180 g). This reaction cannot happen at body temperatures. Instead, enzymes within cells lower the barrier of activation energy, allowing sugar to be oxidized in a series of steps. ...
CHAPTER 9 CELLULAR RESPIRATION: HARVESTING CHEMICAL
... (2,870 kJ) of heat per mole of glucose (about 180 g). This reaction cannot happen at body temperatures. Instead, enzymes within cells lower the barrier of activation energy, allowing sugar to be oxidized in a series of steps. ...
... (2,870 kJ) of heat per mole of glucose (about 180 g). This reaction cannot happen at body temperatures. Instead, enzymes within cells lower the barrier of activation energy, allowing sugar to be oxidized in a series of steps. ...
Humans as Organisms
... Carbohydrates (sometimes referred to as Starch) are required by our bodies as a source of energy. Example of food which carbohydrates can be found in are pasta, potatoes and rice. Fats are needed to insulate our bodies and to make cell membranes. They also contain fat-soluble vitamins. Example of fo ...
... Carbohydrates (sometimes referred to as Starch) are required by our bodies as a source of energy. Example of food which carbohydrates can be found in are pasta, potatoes and rice. Fats are needed to insulate our bodies and to make cell membranes. They also contain fat-soluble vitamins. Example of fo ...
Chapter 4: Chemical bonding
... c In the same family of compounds phosphorus pentachloride is used in organic chemistry to replace –OH groups with chlorine atoms. The reaction between PCl5 and ethanol results in the formation of chloroethane (C2H5Cl), phosphorus oxychloride (POCl3) and hydrogen chloride. PCl5(s) + C2H5OH(l) → C2H5 ...
... c In the same family of compounds phosphorus pentachloride is used in organic chemistry to replace –OH groups with chlorine atoms. The reaction between PCl5 and ethanol results in the formation of chloroethane (C2H5Cl), phosphorus oxychloride (POCl3) and hydrogen chloride. PCl5(s) + C2H5OH(l) → C2H5 ...
ppt - Vanderbilt University
... by treating with peptide with carboxypeptidase, then analyzing by liquid chormatography (AA Analysis). N-labeling: The peptide is first treated with 1-fluoro-2,4-dinitro benzene (Sanger’s reagent), which selectively reacts with the N-terminal amino group. The peptide is then hydrolyzed to their amin ...
... by treating with peptide with carboxypeptidase, then analyzing by liquid chormatography (AA Analysis). N-labeling: The peptide is first treated with 1-fluoro-2,4-dinitro benzene (Sanger’s reagent), which selectively reacts with the N-terminal amino group. The peptide is then hydrolyzed to their amin ...
Enzymes - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... International guidelines – name is based on the reaction they catalyse, and “ase” is added at end. ...
... International guidelines – name is based on the reaction they catalyse, and “ase” is added at end. ...
Biological Science, 5e (Freeman) Chapter 3 Protein Structure and
... Since structure correlates well with function, look for new ways to probe the complex structure of proteins in order to understand what they do and how they do it. One of the most powerful techniques in existence today is X-ray crystallography. The main difficulty with this technique is getting the ...
... Since structure correlates well with function, look for new ways to probe the complex structure of proteins in order to understand what they do and how they do it. One of the most powerful techniques in existence today is X-ray crystallography. The main difficulty with this technique is getting the ...
1 - u.arizona.edu
... Hydrogen peroxyl radical – produced by protonation of superoxide; participate in same reactions as hydroxyl radicals (less reactive) Hydrogen peroxide – central role in formation of ROS; produced from superoxide via superoxide dismutase (antioxidant) and Haber-Weiss reaction Hydroxyl radical – most ...
... Hydrogen peroxyl radical – produced by protonation of superoxide; participate in same reactions as hydroxyl radicals (less reactive) Hydrogen peroxide – central role in formation of ROS; produced from superoxide via superoxide dismutase (antioxidant) and Haber-Weiss reaction Hydroxyl radical – most ...
Practical part
... Principle. Enzymes exhibit selectivity to substrates, which is called substrate specificity. In many instances this property is the essential characteristic that renders enzymes markedly different from inorganic catalysts. The high specificity of enzymes is attributable to the conformational complem ...
... Principle. Enzymes exhibit selectivity to substrates, which is called substrate specificity. In many instances this property is the essential characteristic that renders enzymes markedly different from inorganic catalysts. The high specificity of enzymes is attributable to the conformational complem ...
3 - Suffolk County Community College
... a) will not become turgid when surrounded by pure water b) will have a faster rate of osmosis than a cell without aquaporins c) is impermeable to water d) can not survive in a terrestrial environment 27. Which of the following statement about xylem is not correct? a) xylem conducts material upward. ...
... a) will not become turgid when surrounded by pure water b) will have a faster rate of osmosis than a cell without aquaporins c) is impermeable to water d) can not survive in a terrestrial environment 27. Which of the following statement about xylem is not correct? a) xylem conducts material upward. ...
diffusion - Science @ St John`s
... partially permeable cell membrane to get into or out of a cell. Diffusion is one of the processes that allows this to happen.. ...
... partially permeable cell membrane to get into or out of a cell. Diffusion is one of the processes that allows this to happen.. ...
Fall, 2002
... carefully. If something is not clear, please ask. The exam consists of 11 problems on 4 pages with some extra credit on the fifth page. Make sure your exam is complete. The exam is worth 100 points with each of the problems labeled as to its point value. Answers should be placed in the space provide ...
... carefully. If something is not clear, please ask. The exam consists of 11 problems on 4 pages with some extra credit on the fifth page. Make sure your exam is complete. The exam is worth 100 points with each of the problems labeled as to its point value. Answers should be placed in the space provide ...
Untitled
... exhibit different degrees of interaction with charged chromatography media according to differences in their overall charge, charge density and surface charge distribution. The charged groups within a molecule that contribute to the net surface charge possess different pKa values depending on their ...
... exhibit different degrees of interaction with charged chromatography media according to differences in their overall charge, charge density and surface charge distribution. The charged groups within a molecule that contribute to the net surface charge possess different pKa values depending on their ...
Micro 260 Fall 2009 Name: ___ Allan Keys ____ Tools: You may
... A cofactor is a non-protein chemical compound that is bound to a protein and is required for the protein's biological activity. These proteins are commonly enzymes, and cofactors can be considered "helper molecules" that assist in biochemical transformations. The function of co-enzymes act as partne ...
... A cofactor is a non-protein chemical compound that is bound to a protein and is required for the protein's biological activity. These proteins are commonly enzymes, and cofactors can be considered "helper molecules" that assist in biochemical transformations. The function of co-enzymes act as partne ...
Glycogen Metabolism Gluconeogenesis
... Gα is irreversibly modified by addition of ADP-ribosyl group; Modified Gα can bind GTP but cannot hydrolyze it ). As a result, there is an excessive, nonregulated rise in the intracellular cAMP level (100 fold or more), which causes a large efflux of Na+ and water into the gut. Pertussis (whooping c ...
... Gα is irreversibly modified by addition of ADP-ribosyl group; Modified Gα can bind GTP but cannot hydrolyze it ). As a result, there is an excessive, nonregulated rise in the intracellular cAMP level (100 fold or more), which causes a large efflux of Na+ and water into the gut. Pertussis (whooping c ...
Repetitive Patterns in Proteins
... • (Retro)-Transposition -> These processes result in novel domain compositions, circularly permuted proteins (includes loss), or repetitive proteins ...
... • (Retro)-Transposition -> These processes result in novel domain compositions, circularly permuted proteins (includes loss), or repetitive proteins ...
Bioconversion Technologies
... mechanism to convert biomass into another chemical form Three different classes of thermo chemical: Combustion/burning Gasification – convert carbonaceous materials into carbon monoxide&hydrogen (syngas) Liquefaction ...
... mechanism to convert biomass into another chemical form Three different classes of thermo chemical: Combustion/burning Gasification – convert carbonaceous materials into carbon monoxide&hydrogen (syngas) Liquefaction ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.