Anaerobic Respiration
... The Pyruvic acid formed during Glycolysis each gain a hydrogen from NADH. The new hydrogen turn the Pyruvate into lactic acid and energy is released (which is used to form ATP). Glucose → Pyruvic acid → Lactic acid + energy ...
... The Pyruvic acid formed during Glycolysis each gain a hydrogen from NADH. The new hydrogen turn the Pyruvate into lactic acid and energy is released (which is used to form ATP). Glucose → Pyruvic acid → Lactic acid + energy ...
Bioconversion Technologies
... mechanism to convert biomass into another chemical form Three different classes of thermo chemical: Combustion/burning Gasification – convert carbonaceous materials into carbon monoxide&hydrogen (syngas) Liquefaction ...
... mechanism to convert biomass into another chemical form Three different classes of thermo chemical: Combustion/burning Gasification – convert carbonaceous materials into carbon monoxide&hydrogen (syngas) Liquefaction ...
Nitric oxide and its role in health and diabetes.
... nerve to nerve across gaps between the nerves called synapses and from peripheral nerves to the brain. 2. NOS2 is called inducible or iNOS. This enzyme generates extraordinarily high concentrations of NO, in part to kill bacteria. NOS2 (iNOS) takes several hours to be mobilized and the response is d ...
... nerve to nerve across gaps between the nerves called synapses and from peripheral nerves to the brain. 2. NOS2 is called inducible or iNOS. This enzyme generates extraordinarily high concentrations of NO, in part to kill bacteria. NOS2 (iNOS) takes several hours to be mobilized and the response is d ...
ANP 204 Main Text - National Open University of Nigeria
... glucose but for a change in the positions of OH group on carbon 2 and 4 for mannose and galactose respectively. The carbon atoms involved are ...
... glucose but for a change in the positions of OH group on carbon 2 and 4 for mannose and galactose respectively. The carbon atoms involved are ...
What are the characteristics of living things?
... What do all organisms need to survive? CONDITIONS/FACTORS FOR LIFE: 1. SOURCE OF ENERGY - needed for life processes. - light, FOOD **The SUN is the origin of almost all the energy available to all living things. ...
... What do all organisms need to survive? CONDITIONS/FACTORS FOR LIFE: 1. SOURCE OF ENERGY - needed for life processes. - light, FOOD **The SUN is the origin of almost all the energy available to all living things. ...
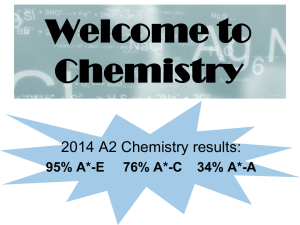
Welcome to Chemistry
... Further reaction kinetics and equilibria Acids and bases Further structure determination Organic synthesis Aromatic compounds Amines Amino Acids Enthalpy and entropy Transition metal complexes ...
... Further reaction kinetics and equilibria Acids and bases Further structure determination Organic synthesis Aromatic compounds Amines Amino Acids Enthalpy and entropy Transition metal complexes ...
Ecological speciation model
... Gram negative bacteria that ferment sugars to acids and gas. All use glycolysis Mixed acid group: ...
... Gram negative bacteria that ferment sugars to acids and gas. All use glycolysis Mixed acid group: ...
Document
... Every molecule consists of atoms that are very strongly bound to each other Degrees of freedom: atoms are the ...
... Every molecule consists of atoms that are very strongly bound to each other Degrees of freedom: atoms are the ...
electron transport chain
... • Catabolic pathways funnel electrons from many kinds of organic molecules into cellular respiration • Glycolysis accepts a wide range of carbohydrates • Proteins must be digested to amino acids; amino groups can feed glycolysis or the citric acid cycle ...
... • Catabolic pathways funnel electrons from many kinds of organic molecules into cellular respiration • Glycolysis accepts a wide range of carbohydrates • Proteins must be digested to amino acids; amino groups can feed glycolysis or the citric acid cycle ...
DNA and Cell Division
... sequence, if present in a protein-coding region, can change the amino acid sequence of the polypeptide. In other cases, mutations can alter levels of gene expression or simply be silent. In order for information in DNA to direct cellular processes, information must be transcribed (DNA→RNA) and, in m ...
... sequence, if present in a protein-coding region, can change the amino acid sequence of the polypeptide. In other cases, mutations can alter levels of gene expression or simply be silent. In order for information in DNA to direct cellular processes, information must be transcribed (DNA→RNA) and, in m ...
Location and characterization of the three carbohydrate prosthetic
... presence in protein HC of one O-glycosidic linkage and two N-glycosidic linkages, differ from those previously reported for the oq-microglobulin, which indicated the presence of three identical N-glycosidic linked carbohydrate chains without specifying their location in the polypeptide chain [19]. T ...
... presence in protein HC of one O-glycosidic linkage and two N-glycosidic linkages, differ from those previously reported for the oq-microglobulin, which indicated the presence of three identical N-glycosidic linked carbohydrate chains without specifying their location in the polypeptide chain [19]. T ...
Chapter 3 → Bioenergetics Introduction Cell Structure
... Classification of Enzymes • Oxidoreductases – Catalyze oxidation-reduction reactions • Transferases – Transfer elements of one molecule to another • Hydrolases – Cleave bonds by adding water • Lyases – Groups of elements are removed to form a double bond or added to a double bond ...
... Classification of Enzymes • Oxidoreductases – Catalyze oxidation-reduction reactions • Transferases – Transfer elements of one molecule to another • Hydrolases – Cleave bonds by adding water • Lyases – Groups of elements are removed to form a double bond or added to a double bond ...
HMT Newsletter - Human Metabolome Technologies
... Tumor cells metabolically adapt to environments of low oxygen or nutrient availability. It was found that glioma tumor cells in the pseudopalisading zones around necrotic foci highly expressed serine hydroxymethyltransferase (SHMT2) and glycine decarboxylase (GLDC). SHMT2 limited pyruvate kinase act ...
... Tumor cells metabolically adapt to environments of low oxygen or nutrient availability. It was found that glioma tumor cells in the pseudopalisading zones around necrotic foci highly expressed serine hydroxymethyltransferase (SHMT2) and glycine decarboxylase (GLDC). SHMT2 limited pyruvate kinase act ...
The following equations and constants may be useful:
... 2. In the titration of a diprotic weak acid that has two identical pKa values, an inflection point occurs: a) at the beginning of the titration. b) when two equivalents of base have been added. c) when the pH equals the pKa. d) when one-half equivalent of base has been added. 3. Which of the followi ...
... 2. In the titration of a diprotic weak acid that has two identical pKa values, an inflection point occurs: a) at the beginning of the titration. b) when two equivalents of base have been added. c) when the pH equals the pKa. d) when one-half equivalent of base has been added. 3. Which of the followi ...
AP Biology -- John Burroughs School -
... Recognize the structural formulas of the various organic molecules. (See the practice page in your binder) Explain how a phospholipid can be both hydrophilic and hydrophobic at the same time. Explain the role cholesterol plays in cell membranes. ...
... Recognize the structural formulas of the various organic molecules. (See the practice page in your binder) Explain how a phospholipid can be both hydrophilic and hydrophobic at the same time. Explain the role cholesterol plays in cell membranes. ...
Themes of Life
... a. ability to store hereditary information b. use of organelles to control cell processes c. use of cellular respiration for energy release d. ability to move in response to environmental stimuli 2. Living organisms can be classified as prokaryotes or eukaryotes. Which two structures are common to b ...
... a. ability to store hereditary information b. use of organelles to control cell processes c. use of cellular respiration for energy release d. ability to move in response to environmental stimuli 2. Living organisms can be classified as prokaryotes or eukaryotes. Which two structures are common to b ...
The DNA of microorganisms is made up of subunits called A
... microbes in a sample at a specified temperature is called the A. thermal death point (TDP). B. thermal death time (TDT). C. sporicidal time. D. death phase point. E. None of the choices are correct. ...
... microbes in a sample at a specified temperature is called the A. thermal death point (TDP). B. thermal death time (TDT). C. sporicidal time. D. death phase point. E. None of the choices are correct. ...
Major components of cells
... interactions. – The hydrophilic part makes the detergent-protein complexes soluble in aqueous solutions. ...
... interactions. – The hydrophilic part makes the detergent-protein complexes soluble in aqueous solutions. ...
How are the proteins built up
... Sometimes the secondary structures are closely related to the tertiary contacts between the different parts of the protein that are far away along the sequence (think of the β-sheet contacts, which had H-bonding between the β -strands, and the β -strands are located at different parts of the polymer ...
... Sometimes the secondary structures are closely related to the tertiary contacts between the different parts of the protein that are far away along the sequence (think of the β-sheet contacts, which had H-bonding between the β -strands, and the β -strands are located at different parts of the polymer ...
Ch 3 The Molecules of Life 20112012
... • The simplest organic compounds are hydrocarbons. – These are organic molecules containing only carbon and hydrogen atoms. – Composed of a carbon skeleton with hydrogens attached to the carbons. ...
... • The simplest organic compounds are hydrocarbons. – These are organic molecules containing only carbon and hydrogen atoms. – Composed of a carbon skeleton with hydrogens attached to the carbons. ...
What is an acid?
... Electrolytes (in solution) React to certain metals to produce hydrogen gas They can cause chemical dyes (called indicators) to change colors ...
... Electrolytes (in solution) React to certain metals to produce hydrogen gas They can cause chemical dyes (called indicators) to change colors ...
Electron transport chain
... • The electron transport chain complexes pump H+ from the matrix into the intermembrane space of the mitochondrion • H+ therefore becomes more concentrated in the ...
... • The electron transport chain complexes pump H+ from the matrix into the intermembrane space of the mitochondrion • H+ therefore becomes more concentrated in the ...
Document
... In Stage 1, the carbohydrates • begin digestion in the mouth where salivary amylase breaks down polysaccharides to smaller polysaccharides (dextrins), maltose, and some glucose. • continue digestion in the small intestine where pancreatic amylase hydrolyzes dextrins to maltose and glucose. • maltose ...
... In Stage 1, the carbohydrates • begin digestion in the mouth where salivary amylase breaks down polysaccharides to smaller polysaccharides (dextrins), maltose, and some glucose. • continue digestion in the small intestine where pancreatic amylase hydrolyzes dextrins to maltose and glucose. • maltose ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.