MS Word
... sites was compared to that published by Brugère et al.4. Assignment of contigs to chromosomes was based on known genetic markers5 and/or by hybridization of Southern blots of E. cuniculi chromosomes separated by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. Blots were hybridized using standard procedures with s ...
... sites was compared to that published by Brugère et al.4. Assignment of contigs to chromosomes was based on known genetic markers5 and/or by hybridization of Southern blots of E. cuniculi chromosomes separated by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. Blots were hybridized using standard procedures with s ...
Lipids Metabolism - GIT
... Ketone Bodies • Liver mitochondria can convert acetyl CoA derived from the oxidation of fatty acids to ketone bodies which are: 1- Acetoacetate 2- 3-hydroxybutyrate (or b-hydroxybutyrate) 3- Acetone (nonmetabolized side product) • Acetoacetate & 3-hydroxybutyrate synthesized in the liver are transp ...
... Ketone Bodies • Liver mitochondria can convert acetyl CoA derived from the oxidation of fatty acids to ketone bodies which are: 1- Acetoacetate 2- 3-hydroxybutyrate (or b-hydroxybutyrate) 3- Acetone (nonmetabolized side product) • Acetoacetate & 3-hydroxybutyrate synthesized in the liver are transp ...
CELLULAR RESPIRATION Getting energy to make atp
... Overall chemical rxn for Cellular Respiration ...
... Overall chemical rxn for Cellular Respiration ...
Quantum Mechanical Model for Information Transfer from DNA to
... Hydrogen bond sites are characterized as “donors” or “acceptors” of hydrogen. Figure 2 shows a schematic representation of the four nucleotides and their bond sites. Donor sites are marked with “1” and acceptor sites with “0”. The upper bond is the first bond. The following three assumptions about t ...
... Hydrogen bond sites are characterized as “donors” or “acceptors” of hydrogen. Figure 2 shows a schematic representation of the four nucleotides and their bond sites. Donor sites are marked with “1” and acceptor sites with “0”. The upper bond is the first bond. The following three assumptions about t ...
Peptides and proteins Chapter 36:
... acids is termed a protein. However, interleukins, cytokines, and interferon are also sometimes referred to as peptides, even though they possess a much higher molecular weight (Figure 36.2). Sometimes the distinction between the two categories relies more on the function of the molecule rather than ...
... acids is termed a protein. However, interleukins, cytokines, and interferon are also sometimes referred to as peptides, even though they possess a much higher molecular weight (Figure 36.2). Sometimes the distinction between the two categories relies more on the function of the molecule rather than ...
1 Protein Synthesis Simulation Lab This lab was originally created
... 3. Give the base sequence of the strand of mRNA read from the original DNA strand. 4. The original DNA strand serves as a template. What does the term template mean? 5. Draw the first three nucleotide sequences of the RNA molecule whose bases you determined in question 3. Remember that RNA is only h ...
... 3. Give the base sequence of the strand of mRNA read from the original DNA strand. 4. The original DNA strand serves as a template. What does the term template mean? 5. Draw the first three nucleotide sequences of the RNA molecule whose bases you determined in question 3. Remember that RNA is only h ...
Review Material
... A catalyst is a substance which increases the rate of a chemical reaction without undergoing a permanent chemical change itself in the process. Homogeneous catalysts are in the same phase as the reactants; heterogeneous catalysts are in a different phase from that of the reactants. ...
... A catalyst is a substance which increases the rate of a chemical reaction without undergoing a permanent chemical change itself in the process. Homogeneous catalysts are in the same phase as the reactants; heterogeneous catalysts are in a different phase from that of the reactants. ...
Valhalla High School
... GCTTCCTACGCTGGAACCGCGCGATTCATCGCT DNA base sequence:___________________________________________________ ...
... GCTTCCTACGCTGGAACCGCGCGATTCATCGCT DNA base sequence:___________________________________________________ ...
Summary
... Side Chains conserved in the primary sequence are in close proximity. Up until Ala 123, they also derive from similar secondary structural elements. Interestingly, the two pairs of leucines deriving from the positionally related helix of SMOA and three stranded antiparallel sheet of PHBH are still ...
... Side Chains conserved in the primary sequence are in close proximity. Up until Ala 123, they also derive from similar secondary structural elements. Interestingly, the two pairs of leucines deriving from the positionally related helix of SMOA and three stranded antiparallel sheet of PHBH are still ...
Lecture 3 Nutrient Roles in Bioenergetics
... • Oxygen is the final electron acceptor in the respiratory chain & combines with hydrogen to form water. • Strenuous Exercise – In Cond. 2 if there is inadequate O2 in the tissues or in Cond 3 if the rate of delivery of O2 is inadequate these give an imbalance between H release & acceptance by O2 ...
... • Oxygen is the final electron acceptor in the respiratory chain & combines with hydrogen to form water. • Strenuous Exercise – In Cond. 2 if there is inadequate O2 in the tissues or in Cond 3 if the rate of delivery of O2 is inadequate these give an imbalance between H release & acceptance by O2 ...
15. The Importance of Energy Changes and Electron Transfer in
... atoms. ② Configuration at carbon atom number four of pyranose ring of glucose has been inverted. - Not metabolized by the body (no calories) - Some report for its toxicity ...
... atoms. ② Configuration at carbon atom number four of pyranose ring of glucose has been inverted. - Not metabolized by the body (no calories) - Some report for its toxicity ...
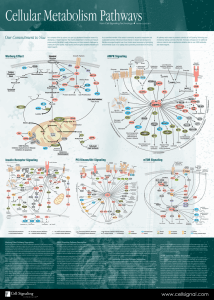
Cellular Metabolism Pathways
... distinct complexes. mTOR complex 1 (mTORC1) is composed of mTOR, Raptor, GβL (mLST8), and Deptor and is partially inhibited by rapamycin. mTORC1 integrates multiple signals reflecting the availability of growth factors, nutrients, or energy to promote either cellular growth when conditions are favor ...
... distinct complexes. mTOR complex 1 (mTORC1) is composed of mTOR, Raptor, GβL (mLST8), and Deptor and is partially inhibited by rapamycin. mTORC1 integrates multiple signals reflecting the availability of growth factors, nutrients, or energy to promote either cellular growth when conditions are favor ...
green chemistry - Catalysis Eprints database
... prominent part of our daily lives. • Chemical developments also bring new environmental problems and harmful unexpected side effects, which result in the need for ‘greener’ chemical products. • A famous example is the pesticide DDT. ...
... prominent part of our daily lives. • Chemical developments also bring new environmental problems and harmful unexpected side effects, which result in the need for ‘greener’ chemical products. • A famous example is the pesticide DDT. ...
슬라이드 1
... - The most ciritical alterations during cold acclimation are changes in lipid composition in PM a. increase of phospholipid b. decrease of glucocerebrosides c. increase of diunsaturated phospholipid d. shortening of fatty acid chain e. increase the size of head group ...
... - The most ciritical alterations during cold acclimation are changes in lipid composition in PM a. increase of phospholipid b. decrease of glucocerebrosides c. increase of diunsaturated phospholipid d. shortening of fatty acid chain e. increase the size of head group ...
PowerPoint-RNA
... 3. The ribosome attaches one amino acid to another as it moves along the mRNA molecule 4. The tRNA molecules are released after the amino acids they carry are attached to the growing chain of amino acids 5. The ribosome completes the translation when it reaches the end of the mRNA strand and the new ...
... 3. The ribosome attaches one amino acid to another as it moves along the mRNA molecule 4. The tRNA molecules are released after the amino acids they carry are attached to the growing chain of amino acids 5. The ribosome completes the translation when it reaches the end of the mRNA strand and the new ...
chapter 1 - College Test bank - get test bank and solution manual
... a. On the left side of the arrow, "2 Na" means 2 Na atoms; one Cl2 molecule contains 2 Cl atoms. On the right side 2 NaCl units contain 2 Na atoms and 2 Cl atoms. b. On the left one N2 molecule contains 2 N atoms and 3 Cl2 molecules contain 6 Cl atoms. On the right 2 NCl3 molecules contain a total o ...
... a. On the left side of the arrow, "2 Na" means 2 Na atoms; one Cl2 molecule contains 2 Cl atoms. On the right side 2 NaCl units contain 2 Na atoms and 2 Cl atoms. b. On the left one N2 molecule contains 2 N atoms and 3 Cl2 molecules contain 6 Cl atoms. On the right 2 NCl3 molecules contain a total o ...
Module 13 Enzymes and Vitamins Lecture 34 Enzymes
... example where amino acid in the active site can assist the enzyme mechanism acting as a nucleophile. Another reason why enzyme acts as catalyst is the binding process itself. The active site is not ideal shape for the substrate, but when the binding takes place the shape changes to accommodate the s ...
... example where amino acid in the active site can assist the enzyme mechanism acting as a nucleophile. Another reason why enzyme acts as catalyst is the binding process itself. The active site is not ideal shape for the substrate, but when the binding takes place the shape changes to accommodate the s ...
- WordPress.com
... A common way that cells capture the energy released during the breakdown of large molecules is to add electrons to smaller, specialized molecules that can accept them. This process of electron acceptance is otherwise known as A.biosynthesis B. Metabolism C. reduction D.Catalysis ...
... A common way that cells capture the energy released during the breakdown of large molecules is to add electrons to smaller, specialized molecules that can accept them. This process of electron acceptance is otherwise known as A.biosynthesis B. Metabolism C. reduction D.Catalysis ...
Anaerobic Energy Systems
... Few chemical reactions involved so energy can be produced quickly. summary of anaerobic energy systems ...
... Few chemical reactions involved so energy can be produced quickly. summary of anaerobic energy systems ...
Biology EOC Review Packet - Watchung Hills Regional High School
... Glucose, sucrose, startch, glycogen ...
... Glucose, sucrose, startch, glycogen ...
Metabolic Disorders
... Peroxisomal disorders (Zellweger syndrome, neonatal adrenoleukodystrophy, infantile refsum disease) ...
... Peroxisomal disorders (Zellweger syndrome, neonatal adrenoleukodystrophy, infantile refsum disease) ...
Biology formula and tips
... Tissue :- ‘A’ group of cells performing a particular function is called tissue. Organ :- A group of tissue performing a particular function is called organ. Organ System :- A group of organs performing a particular function is called organ system. Eukaryotic cell :- The cell in which nucleus is well ...
... Tissue :- ‘A’ group of cells performing a particular function is called tissue. Organ :- A group of tissue performing a particular function is called organ. Organ System :- A group of organs performing a particular function is called organ system. Eukaryotic cell :- The cell in which nucleus is well ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.