Chapter 2 DNA to end Extended Response
... DNA polymerase I removes the RNA primers and replaces them with DNA; DNA ligase joins Okazaki fragments; as deoxynucleoside triphosphate joins with growing DNA chain, two phosphates broken off releasing energy to form bond; Accept any of the points above shown on an annotated diagram. ...
... DNA polymerase I removes the RNA primers and replaces them with DNA; DNA ligase joins Okazaki fragments; as deoxynucleoside triphosphate joins with growing DNA chain, two phosphates broken off releasing energy to form bond; Accept any of the points above shown on an annotated diagram. ...
NNI086 - Nestlé Nutrition Institute
... immunomodulatory peptides promoting beneficial effects. Extensively hydrolyzed infant formulas result from a different production process leading to very short peptides, which have almost lost their allergenic properties. These infant formulas have been designed for therapeutic applications, offerin ...
... immunomodulatory peptides promoting beneficial effects. Extensively hydrolyzed infant formulas result from a different production process leading to very short peptides, which have almost lost their allergenic properties. These infant formulas have been designed for therapeutic applications, offerin ...
Mechanisms of Enzyme Regulation • Substrate concentration
... Allosteric regulation of metabolic pathways. The activity of enzymes that catalyze key regulatory reactions (committed steps) of metabolic pathways are often subject to allosteric regulation. Their activity can be modulated by the binding of allosteric effectors to a site on the enzyme that is dist ...
... Allosteric regulation of metabolic pathways. The activity of enzymes that catalyze key regulatory reactions (committed steps) of metabolic pathways are often subject to allosteric regulation. Their activity can be modulated by the binding of allosteric effectors to a site on the enzyme that is dist ...
OMNI kit - EnzyPep
... Because omniligase-1 has such a broad specificity, the acyl donor (ester) fragment normally requires N-terminal protection to prevent formation of cyclic peptides or polymers. The use of a phenylacetyl protection group is recommended; it can be removed easily with commercially available acylases (e. ...
... Because omniligase-1 has such a broad specificity, the acyl donor (ester) fragment normally requires N-terminal protection to prevent formation of cyclic peptides or polymers. The use of a phenylacetyl protection group is recommended; it can be removed easily with commercially available acylases (e. ...
Characteristics of Life Notes
... Autotrophs- make their own food through photosynthesis, such as plants. Chemoautotrophs- make their own food through chemicals / chemosynthesis. Heterotrophs- rely on others for food. Where do we get our energy from? i. Indirectly from photosynthesis and directly from cellular respiration, i ...
... Autotrophs- make their own food through photosynthesis, such as plants. Chemoautotrophs- make their own food through chemicals / chemosynthesis. Heterotrophs- rely on others for food. Where do we get our energy from? i. Indirectly from photosynthesis and directly from cellular respiration, i ...
Unit 1: Building Blocks Homework
... 9) Urea is a chemical which is present in urine. Urea has the formula H2NCONH2. An adult male, on average, excretes 30g of urea each day. How many moles are there in 30g of urea? ...
... 9) Urea is a chemical which is present in urine. Urea has the formula H2NCONH2. An adult male, on average, excretes 30g of urea each day. How many moles are there in 30g of urea? ...
1.2b Cells
... dissolve bacteria. When a bacterium is discovered within a cell, a lysosome bubble will fuse onto it and release its contents in an effort to dissolve the invader. If there was a defect in the lysosome of a white blood cell, the bacteria could accumulate within the cell and kill a person by ...
... dissolve bacteria. When a bacterium is discovered within a cell, a lysosome bubble will fuse onto it and release its contents in an effort to dissolve the invader. If there was a defect in the lysosome of a white blood cell, the bacteria could accumulate within the cell and kill a person by ...
HORMONE OF MIDDLE LOBE OF PITUITARY MELANOCYTE
... Pre-pro PTH: consisting of 115 amino acids is first formed in polysomes adhering on the rough ER membrane Pro-PTH: before the formation of Pre-pro PTH is completed its N-terminal end protrudes into the lumen of rough ER and a signal peptidase of rER membrane hydrolyzes the molecules to split off 25 ...
... Pre-pro PTH: consisting of 115 amino acids is first formed in polysomes adhering on the rough ER membrane Pro-PTH: before the formation of Pre-pro PTH is completed its N-terminal end protrudes into the lumen of rough ER and a signal peptidase of rER membrane hydrolyzes the molecules to split off 25 ...
Unit 4 Photosynthesis
... Named in order discovered Regions of Concentrated Chlorophyll What is evidence that red and blue light is absorbed in plants? In absorbing light, what change does this cause? Energized electrons leave chlorophyll Move down proteins in thylakoid membrane ...
... Named in order discovered Regions of Concentrated Chlorophyll What is evidence that red and blue light is absorbed in plants? In absorbing light, what change does this cause? Energized electrons leave chlorophyll Move down proteins in thylakoid membrane ...
A2 2, Analytical, Transition Metals, Electrochemistry and
... Answer all ten questions in Section A. Record your answers by marking the appropriate letter on the answer sheet provided. Use only the spaces numbered 1 to 10. Keep in sequence when answering. Answer all seven questions in Section B. Write your answers in the spaces provided in this question paper. ...
... Answer all ten questions in Section A. Record your answers by marking the appropriate letter on the answer sheet provided. Use only the spaces numbered 1 to 10. Keep in sequence when answering. Answer all seven questions in Section B. Write your answers in the spaces provided in this question paper. ...
Metabolic pathways File
... The chart used today is built on many years’ work. The current chart, at the time of writing, is the 22nd edition published in 2003. The chart is largely the work of one man, Donald Nicholson. Born in 1916, Donald Nicholson graduated in chemistry in 1936. In 1946, after working for a large pharmaceu ...
... The chart used today is built on many years’ work. The current chart, at the time of writing, is the 22nd edition published in 2003. The chart is largely the work of one man, Donald Nicholson. Born in 1916, Donald Nicholson graduated in chemistry in 1936. In 1946, after working for a large pharmaceu ...
AP Biology Discussion Notes Thursday 121516
... • Catabolic pathways funnel electrons from many kinds of organic molecules into cellular respiration • Glycolysis accepts a wide range of carbohydrates • Proteins must be digested to amino acids; amino groups can feed glycolysis or the citric acid cycle ...
... • Catabolic pathways funnel electrons from many kinds of organic molecules into cellular respiration • Glycolysis accepts a wide range of carbohydrates • Proteins must be digested to amino acids; amino groups can feed glycolysis or the citric acid cycle ...
DNA, RNA and Protein
... At the ribosome, codons in mRNA are recognized by tRNA anticodons to place amino acids in the specific sequence determined by the DNA. Three Stages of Translation: Initiation- assemble components to start process Elongation- add amino acids in repeated cycles ...
... At the ribosome, codons in mRNA are recognized by tRNA anticodons to place amino acids in the specific sequence determined by the DNA. Three Stages of Translation: Initiation- assemble components to start process Elongation- add amino acids in repeated cycles ...
Respiratory System Review
... 9. What structure is responsible for the gas exchange of carbon dioxide with oxygen? 10. Put the following in order from largest in structure to smallest. Capillary, Artery, Arteriole 11. When oxygen and carbon dioxide is exchanged in the alveoli, in what vessel does this exchange occur? a. Artery b ...
... 9. What structure is responsible for the gas exchange of carbon dioxide with oxygen? 10. Put the following in order from largest in structure to smallest. Capillary, Artery, Arteriole 11. When oxygen and carbon dioxide is exchanged in the alveoli, in what vessel does this exchange occur? a. Artery b ...
Cell organelles III. Cytoplasm, nucleus, nucleolus, SER, RER
... Pinocytosis: uptake of fluids Receptor mediated endocytosis: uptake of specific molecules ...
... Pinocytosis: uptake of fluids Receptor mediated endocytosis: uptake of specific molecules ...
Sequence and Structural Similarities Between Glyceraldehyde
... Substrate-binding proteins are components of ATP-binding cassette transporters which capture their substrates in the periplasm of bacteria. These proteins subsequently deliver their bound ligands to membrane components of the transporters. Bacterial periplasmic substrate-binding proteins are charact ...
... Substrate-binding proteins are components of ATP-binding cassette transporters which capture their substrates in the periplasm of bacteria. These proteins subsequently deliver their bound ligands to membrane components of the transporters. Bacterial periplasmic substrate-binding proteins are charact ...
Chapter 3 Extra Questions
... 16. What is meant by the term nutrient sink? Name two sinks for carbon and two sinks for nitrogen. 17. Bacteria are key participants in the carbon and nitrogen biogeochemical cycles. Briefly describe the role of bacteria in each. 18. Briefly explain how the production of dimethyl sulfide can support ...
... 16. What is meant by the term nutrient sink? Name two sinks for carbon and two sinks for nitrogen. 17. Bacteria are key participants in the carbon and nitrogen biogeochemical cycles. Briefly describe the role of bacteria in each. 18. Briefly explain how the production of dimethyl sulfide can support ...
Lecture 13: Fighting Entropy II: Respiration
... • Both processes use glycolysis to oxidize glucose and other organic fuels to pyruvate • However, the processes have different final electron acceptors: an organic molecule (such as pyruvate or acetaldehyde) in fermentation and O2 in cellular respiration • Cellular respiration produces 38 ATP per gl ...
... • Both processes use glycolysis to oxidize glucose and other organic fuels to pyruvate • However, the processes have different final electron acceptors: an organic molecule (such as pyruvate or acetaldehyde) in fermentation and O2 in cellular respiration • Cellular respiration produces 38 ATP per gl ...
Anti-c-myc antibody 9E10 - Protein Engineering, Design and Selection
... signal similar to the wild-type, QLISEEDL with a somewhat lower binding signal and KLISEDEL with no binding signal at all. The Kd values obtained (Table I) reflect the results from the binding studies of substitutional analysis very well. The substitutional analysis of the shortened peptide KLISEEDL ...
... signal similar to the wild-type, QLISEEDL with a somewhat lower binding signal and KLISEDEL with no binding signal at all. The Kd values obtained (Table I) reflect the results from the binding studies of substitutional analysis very well. The substitutional analysis of the shortened peptide KLISEEDL ...
PyMOL tutorial
... (Select the sheet using the sequence display. It should be easy because the sequence is colored the same as the structure, so just select all the yellow residues). 2. Show only the β sheet: (1X1R) hide -> everything (sheet) show -> as -> cartoon Notice that the β-sheet is mostly parallel, except for ...
... (Select the sheet using the sequence display. It should be easy because the sequence is colored the same as the structure, so just select all the yellow residues). 2. Show only the β sheet: (1X1R) hide -> everything (sheet) show -> as -> cartoon Notice that the β-sheet is mostly parallel, except for ...
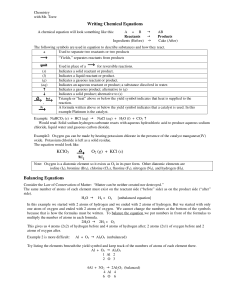
Writing Chemical Equations KClO3 O2 (g) + KCl (s) Balancing
... chloride, liquid water and gaseous carbon dioxide. Example2: Oxygen gas can be made by heating potassium chlorate in the presence of the catalyst manganese(IV) oxide. Potassium chloride is left as a solid residue. The equation would look like: ...
... chloride, liquid water and gaseous carbon dioxide. Example2: Oxygen gas can be made by heating potassium chlorate in the presence of the catalyst manganese(IV) oxide. Potassium chloride is left as a solid residue. The equation would look like: ...
Microbiology Of Fermented Foods and Beverages by momina
... Play a role in spoilage of fermented as well as non-fermented foods. Optimum temperature for growth varies from 30oC to 45oC. High tolerance to salt, low water activity and osmotic pressure. Many strains grow in acidic environments. Some show tolerance against ethanol and bile. Require nutrient rich ...
... Play a role in spoilage of fermented as well as non-fermented foods. Optimum temperature for growth varies from 30oC to 45oC. High tolerance to salt, low water activity and osmotic pressure. Many strains grow in acidic environments. Some show tolerance against ethanol and bile. Require nutrient rich ...
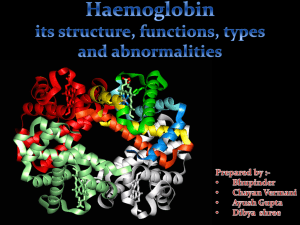
Haemoglobin (Roll no. 22
... molecule is an assembly of four globular protein subunits. Each subunit is composed of a protein chain tightly associated with a non-protein heme group. Each protein chain arranges into a set of alpha-helix , structural segments connected together in a globin fold arrangement. This folding pattern c ...
... molecule is an assembly of four globular protein subunits. Each subunit is composed of a protein chain tightly associated with a non-protein heme group. Each protein chain arranges into a set of alpha-helix , structural segments connected together in a globin fold arrangement. This folding pattern c ...
ANN 303 PRINCIPLES OF ANIMAL NUTRITION (A)
... The study of plant nutrition is important because animals depends on them for survival. Plants are capable to synthesize complex food materials using simple substances such as CO2 from the air and water and inorganic elements from the soil by means of photosynthesis. The greatest part of the energy ...
... The study of plant nutrition is important because animals depends on them for survival. Plants are capable to synthesize complex food materials using simple substances such as CO2 from the air and water and inorganic elements from the soil by means of photosynthesis. The greatest part of the energy ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.