DNA: Information Molecule
... Bacteria can take in pieces of DNA from their environment. This process is called transformation because in Griffith’s experiment the R strain was transformed into an S strain by taking in DNA from the dead molecules. ...
... Bacteria can take in pieces of DNA from their environment. This process is called transformation because in Griffith’s experiment the R strain was transformed into an S strain by taking in DNA from the dead molecules. ...
CST REVIEW Percent Error 1. 2. What is the formula for density?
... 23. If 85% of the isotopes of an element have a mass of 44.0 amu and 15% of the isotopes have a mass of 47 amu, what is the atomic mass of the element? Show work 24. Atoms combine to form molecules by electrons to form covalent bonds or by exchanging/transferring electrons to form bonds. 25. Are the ...
... 23. If 85% of the isotopes of an element have a mass of 44.0 amu and 15% of the isotopes have a mass of 47 amu, what is the atomic mass of the element? Show work 24. Atoms combine to form molecules by electrons to form covalent bonds or by exchanging/transferring electrons to form bonds. 25. Are the ...
Chapter 13 Organic Chemistry
... carbon atom because the two molecules can be interchanged by a simple rotation. We conclude that Figure 13.7 shows only two isomers of C4H8 (Figures 13.7a and 13.7c). Alkenes with several double bonds are called polyenes, and polyenes with alternating single and double bonds have delocalized π syste ...
... carbon atom because the two molecules can be interchanged by a simple rotation. We conclude that Figure 13.7 shows only two isomers of C4H8 (Figures 13.7a and 13.7c). Alkenes with several double bonds are called polyenes, and polyenes with alternating single and double bonds have delocalized π syste ...
Enzyme Mechanisms - Illinois Institute of Technology
... Homologous enzymes catalyze related reactions; this is how trp and his biosynthesis enzymes seem to have evolved Variant: recruit some enzymes from another pathway without duplicating the whole thing (example: ubiquitination) ...
... Homologous enzymes catalyze related reactions; this is how trp and his biosynthesis enzymes seem to have evolved Variant: recruit some enzymes from another pathway without duplicating the whole thing (example: ubiquitination) ...
Document
... Homologous enzymes catalyze related reactions; this is how trp and his biosynthesis enzymes seem to have evolved Variant: recruit some enzymes from another pathway without duplicating the whole thing (example: ubiquitination) ...
... Homologous enzymes catalyze related reactions; this is how trp and his biosynthesis enzymes seem to have evolved Variant: recruit some enzymes from another pathway without duplicating the whole thing (example: ubiquitination) ...
dna TRANSCRIPTION AND tRANSLATION
... bases is what determines how things are made in the human body. The sequence of DNA within an individual is like a very large book, and every single person has a unique sequence that sets them apart. Our genome, or our complete set of DNA, is located within the nucleus of all the cells within our bo ...
... bases is what determines how things are made in the human body. The sequence of DNA within an individual is like a very large book, and every single person has a unique sequence that sets them apart. Our genome, or our complete set of DNA, is located within the nucleus of all the cells within our bo ...
MIDTERM REVIEW UNIT 1: Mass/Measurement
... 9. Each chemistry teacher provides 6 test tubes to each lab group. In each class there are 12 lab groups, and the teacher has four classes. There are a total of 5 chemistry teachers. ...
... 9. Each chemistry teacher provides 6 test tubes to each lab group. In each class there are 12 lab groups, and the teacher has four classes. There are a total of 5 chemistry teachers. ...
The Respiratory System
... Minute ventilation is the volume of air you breathe in one minute. (VE) You can calculate a person’s minute ventilation by multiplying the volume of air they breathe in one breath, by their respiratory (breathing) rate. VE = TV x f If you breathe 14 times in one minute (respiratory rate) and you bre ...
... Minute ventilation is the volume of air you breathe in one minute. (VE) You can calculate a person’s minute ventilation by multiplying the volume of air they breathe in one breath, by their respiratory (breathing) rate. VE = TV x f If you breathe 14 times in one minute (respiratory rate) and you bre ...
Flexibility in energy metabolism supports hypoxia tolerance in
... Flexibility in energy metabolism supports hypoxia tolerance in Drosophila flight muscle: metabolomic and computational systems analysis Jacob Feala1,2 Laurence Coquin, PhD2 Andrew McCulloch, PhD1 Giovanni Paternostro, PhD1,2 1) UCSD Bioengineering 2) Burnham Institute for Medical Research ...
... Flexibility in energy metabolism supports hypoxia tolerance in Drosophila flight muscle: metabolomic and computational systems analysis Jacob Feala1,2 Laurence Coquin, PhD2 Andrew McCulloch, PhD1 Giovanni Paternostro, PhD1,2 1) UCSD Bioengineering 2) Burnham Institute for Medical Research ...
Evolution of Enzymatic Activity in the Enolase Superfamily: Structural
... M., Rayment, I., and Gerlt, J. A. (2004) Biochemistry 42, 224-229]. Importantly, the protein forms specific favorable interactions with the hydrophobic amino acid side chain, R-carbon, carboxylate, and the polar components of the N-acyl linkage. Accommodation of the components of the N-acyl linkage ...
... M., Rayment, I., and Gerlt, J. A. (2004) Biochemistry 42, 224-229]. Importantly, the protein forms specific favorable interactions with the hydrophobic amino acid side chain, R-carbon, carboxylate, and the polar components of the N-acyl linkage. Accommodation of the components of the N-acyl linkage ...
File - Groby Bio Page
... Used to reduce NAD and FAD. Three reduced NAD are produced and 1 reduced FAD per cycle. NAD = Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide FAD = Flavine adenine dinucleotide ...
... Used to reduce NAD and FAD. Three reduced NAD are produced and 1 reduced FAD per cycle. NAD = Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide FAD = Flavine adenine dinucleotide ...
Gold Biotechnology Enzyme and Antibody Immobilization
... • Glyoxal Agarose Beads: Supports with an aldehyde group that covalently reacts with the lysine groups in the biomolecules. • Aminoethyl Agarose Beads: Supports with an amino group that covalently reacts with acidic amino acids like aspartic acid or glutamic acid. Both types of resins give the biomo ...
... • Glyoxal Agarose Beads: Supports with an aldehyde group that covalently reacts with the lysine groups in the biomolecules. • Aminoethyl Agarose Beads: Supports with an amino group that covalently reacts with acidic amino acids like aspartic acid or glutamic acid. Both types of resins give the biomo ...
Question Paper - Revision Science
... (b) Chloroethane can be produced in various ways as shown below. Identify, by name or formula, the reagent needed for each of these reactions. ...
... (b) Chloroethane can be produced in various ways as shown below. Identify, by name or formula, the reagent needed for each of these reactions. ...
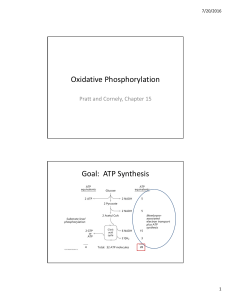
Oxidative Phosphorylation Goal: ATP Synthesis
... Through Q cycle Problem 10: An iron‐ sulfur protein in Complex III donates an electron to cytochrome c. Use the half reactions below to calculate the standard free energy change. How can you account for the fact that this process is spontaneous in the cell? ...
... Through Q cycle Problem 10: An iron‐ sulfur protein in Complex III donates an electron to cytochrome c. Use the half reactions below to calculate the standard free energy change. How can you account for the fact that this process is spontaneous in the cell? ...
4. Microbial Products
... Excessive pigment formation in D. salina is achieved by numerous stress factors like high temperature, lack of nitrogen and phosphate but excess of carbon, high light intensity, and high salt concentration, the latter two having the highest impact. ...
... Excessive pigment formation in D. salina is achieved by numerous stress factors like high temperature, lack of nitrogen and phosphate but excess of carbon, high light intensity, and high salt concentration, the latter two having the highest impact. ...
Biology and Its Themes
... DNA Structure and Function • Each chromosome has one long DNA molecule with hundreds or thousands of genes • Genes encode information for building proteins • DNA is inherited by offspring from their parents • DNA controls the development and maintenance of organisms ...
... DNA Structure and Function • Each chromosome has one long DNA molecule with hundreds or thousands of genes • Genes encode information for building proteins • DNA is inherited by offspring from their parents • DNA controls the development and maintenance of organisms ...
Biological membranes: the basics and why they are
... • Flexible phospholipid bilayer interspersed with protein molecules • Fluid – some parts move freely, if not anchored by other cell components • Mosaic – patchwork networks of proteins ...
... • Flexible phospholipid bilayer interspersed with protein molecules • Fluid – some parts move freely, if not anchored by other cell components • Mosaic – patchwork networks of proteins ...
Nucleic acids and their protein partners
... NMR and X-ray crystallography, bode well for structural snapshots along an RNA folding pathway. In the third review, we are aptly reminded that far from being dull, the classic RNA-recognition motif (RRM) continues to reveal new aspects of both form and function. Clery et al. point out that the abun ...
... NMR and X-ray crystallography, bode well for structural snapshots along an RNA folding pathway. In the third review, we are aptly reminded that far from being dull, the classic RNA-recognition motif (RRM) continues to reveal new aspects of both form and function. Clery et al. point out that the abun ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.