answer key - chem.uwec.edu
... • Describe some of the activated carriers that we have encountered so far, including ATP, NADH, FADH2, FMNH2, CoenzymeA, Lipoamide and Biotin. (Question 3) • Describe why the stability of activated carriers is important. • Classify reactions according to reaction type: oxidation/reduction, ligation, ...
... • Describe some of the activated carriers that we have encountered so far, including ATP, NADH, FADH2, FMNH2, CoenzymeA, Lipoamide and Biotin. (Question 3) • Describe why the stability of activated carriers is important. • Classify reactions according to reaction type: oxidation/reduction, ligation, ...
投影片 1
... sequences as cues for its removal. Splicing enzyme: snRNPs, which usually assemble when catalysis begins. With different splicing method, different mRNA forms. This gene recombination provides evolutionary flexibility. Also, the life time of eucaryotic mRNA varies. ...
... sequences as cues for its removal. Splicing enzyme: snRNPs, which usually assemble when catalysis begins. With different splicing method, different mRNA forms. This gene recombination provides evolutionary flexibility. Also, the life time of eucaryotic mRNA varies. ...
genetics ch 7 [10-31
... Metabolic disorders classified based on pathological effects of pathway blocked (absence of end product, accumulation of substrate), different functional classes of proteins (receptors, hormones), associated cofactors (metals, vitamins), and pathways affected (glycolysis, citric acid cycle) o Clas ...
... Metabolic disorders classified based on pathological effects of pathway blocked (absence of end product, accumulation of substrate), different functional classes of proteins (receptors, hormones), associated cofactors (metals, vitamins), and pathways affected (glycolysis, citric acid cycle) o Clas ...
13C analysis of amino acids in human hair using trimethylsilyl
... human hair by gas chromatography/combustion/isotope ratio mass spectrometry (GC/C/IRMS). N,O-Bis (trimethylsilyl)trifluoroacetamide (BSTFA) derivatization is already widely used outside the IRMS community, is applicable to a variety of functional groups, and provides products that are common entries ...
... human hair by gas chromatography/combustion/isotope ratio mass spectrometry (GC/C/IRMS). N,O-Bis (trimethylsilyl)trifluoroacetamide (BSTFA) derivatization is already widely used outside the IRMS community, is applicable to a variety of functional groups, and provides products that are common entries ...
Two Perspectives on the Origin of the Standard Genetic Code
... mechanism for producing ordered, functional sequences of amino acids. However, the origin of the SGC remains one of the most challenging problems in molecular evolution. The SGC provides a recipe for synthesizing proteins from DNA sequences. But the pattern of associations between codons and amino a ...
... mechanism for producing ordered, functional sequences of amino acids. However, the origin of the SGC remains one of the most challenging problems in molecular evolution. The SGC provides a recipe for synthesizing proteins from DNA sequences. But the pattern of associations between codons and amino a ...
Chapter 16 - HCC Learning Web
... Archibald Garrod (1909) He was a physician who studied inborn errors in metabolism. He suggested that genes dictate phenotypes through enzymes that catalyze specific chemical reactions in cells. B. Nutritional Mutants in Neurospora. George Beadle and Edward Tatum using a bread mold (Neurospora crass ...
... Archibald Garrod (1909) He was a physician who studied inborn errors in metabolism. He suggested that genes dictate phenotypes through enzymes that catalyze specific chemical reactions in cells. B. Nutritional Mutants in Neurospora. George Beadle and Edward Tatum using a bread mold (Neurospora crass ...
Chapter 6. Metabolism & Enzymes
... active site binds substrate & puts stress on bonds that must be broken, making it easier to separate molecules ...
... active site binds substrate & puts stress on bonds that must be broken, making it easier to separate molecules ...
Chapter 4
... Book Example • More complicated problem on page 159 • TIP pg. 160: The first step in the analysis of a complex solution is to write down the components and focus on the chemistry of each one. When a strong electrolyte is present, write it as separated ions. ...
... Book Example • More complicated problem on page 159 • TIP pg. 160: The first step in the analysis of a complex solution is to write down the components and focus on the chemistry of each one. When a strong electrolyte is present, write it as separated ions. ...
boc-saq-compilation 272 kb boc-saq
... What is the difference between the way beta hairpins and alpha hairpins are held together? ...
... What is the difference between the way beta hairpins and alpha hairpins are held together? ...
12 Enzymes 9 28 05
... The lower the Km the better the enzyme recognizes substrate “finds it at low conc” ...
... The lower the Km the better the enzyme recognizes substrate “finds it at low conc” ...
PROTEINS
... Protein quality is a measure of the usefulness of a protein food for various purposes, including the growth, maintenance, repair of tissues, formation of new tissue and production of egg, wool and milk. Protein quality of food: There are two factors which determine the protein quality of food: i) Ho ...
... Protein quality is a measure of the usefulness of a protein food for various purposes, including the growth, maintenance, repair of tissues, formation of new tissue and production of egg, wool and milk. Protein quality of food: There are two factors which determine the protein quality of food: i) Ho ...
Basics on Protein Structure Building Blocks: Amino Acids
... 1. Find H bonds (just by electrostatic definition) 2. Compare hydrogen bonding pattern at each residue with known patterns ...
... 1. Find H bonds (just by electrostatic definition) 2. Compare hydrogen bonding pattern at each residue with known patterns ...
MC - Questions
... c) The kidney eliminates most of the urea dissolved in the blood. d) All of the above. 38. Which statement about renal dialysis is correct? a) Renal dialysis involves passive and active transport. b) Renal dialysis involves passive transport only. c) Renal dialysis involves active transport only. d) ...
... c) The kidney eliminates most of the urea dissolved in the blood. d) All of the above. 38. Which statement about renal dialysis is correct? a) Renal dialysis involves passive and active transport. b) Renal dialysis involves passive transport only. c) Renal dialysis involves active transport only. d) ...
enhanced rate of ethanol elimination from blood after intravenous
... Abstract — Aims: To investigate the effect of an amino acid mixture given intravenously (i.v.) on the rate of ethanol elimination from blood compared with equicaloric glucose and Ringer’s acetate as control treatments. Methods: In a randomized cross-over study, six healthy men (mean age 23 years) fa ...
... Abstract — Aims: To investigate the effect of an amino acid mixture given intravenously (i.v.) on the rate of ethanol elimination from blood compared with equicaloric glucose and Ringer’s acetate as control treatments. Methods: In a randomized cross-over study, six healthy men (mean age 23 years) fa ...
Metal Ion Transport and Storage
... Calcium--Storage • CaCO3 in a protein matrix makes up egg shells and coral skeletons • Calcium Hydroxyapatite in a collagen framework is the stored form of Ca2+ in bones and teeth: Ca10(PO4)6(OH)2 – Collagen: triple helix fibrous protein – Hydroxyapatite crystallizes around the collagen – Replaceme ...
... Calcium--Storage • CaCO3 in a protein matrix makes up egg shells and coral skeletons • Calcium Hydroxyapatite in a collagen framework is the stored form of Ca2+ in bones and teeth: Ca10(PO4)6(OH)2 – Collagen: triple helix fibrous protein – Hydroxyapatite crystallizes around the collagen – Replaceme ...
Costs of life - Dynamics of the protein inventory of
... to oxygen starvation, from signal transduction pathways to gene expression pattern, from metabolic reorganization after oxygen depletion to beginning cell death and lysis after glucose exhaustion. This experimental approach can be considered as a proof of principle how to combine cell physiology wit ...
... to oxygen starvation, from signal transduction pathways to gene expression pattern, from metabolic reorganization after oxygen depletion to beginning cell death and lysis after glucose exhaustion. This experimental approach can be considered as a proof of principle how to combine cell physiology wit ...
Document
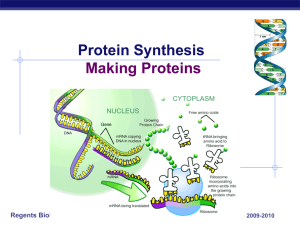
... Passing on DNA information Need to get DNA gene information from nucleus to cytoplasm ...
... Passing on DNA information Need to get DNA gene information from nucleus to cytoplasm ...
Chapter 14 – The Origin of Life
... Both of these form spontaneously in certain kinds of solutions. Microspheres can bud to form smaller microspheres, while cocervates can grow These cell-like structures are NOT alive and also lack hereditary characteristics ...
... Both of these form spontaneously in certain kinds of solutions. Microspheres can bud to form smaller microspheres, while cocervates can grow These cell-like structures are NOT alive and also lack hereditary characteristics ...
Document
... Homologous enzymes catalyze related reactions; this is how trp and his biosynthesis enzymes seem to have evolved Variant: recruit some enzymes from another pathway without duplicating the whole thing (example: ubiquitination) ...
... Homologous enzymes catalyze related reactions; this is how trp and his biosynthesis enzymes seem to have evolved Variant: recruit some enzymes from another pathway without duplicating the whole thing (example: ubiquitination) ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.