MedBiochem Exam 1, 1998
... 33. When dinitrophenol is added to mitochondria, it A. decreases the flow of electrons through cytochrome oxidase. B. results in an increase in the intramitochondrial ratio of ATP/ADP. C. uncouples oxidative phosphorylation. D. increases the rate of ATP formation. ...
... 33. When dinitrophenol is added to mitochondria, it A. decreases the flow of electrons through cytochrome oxidase. B. results in an increase in the intramitochondrial ratio of ATP/ADP. C. uncouples oxidative phosphorylation. D. increases the rate of ATP formation. ...
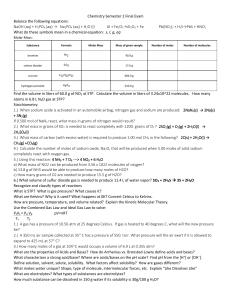
Chemistry Semester 2 Final Exam Chemistry Semester 2 Final Exam
... 2.) What mass in grams of SO2 is needed to react completely with 1200. grams of O2 ? 2SO2(g) + O2(g) + 2H2O(l) → 2H2SO4(l) 4805 g 3.) What mass of carbon (with excess water) is required to produce 1.00 mol CH4 in the following? 2C(s) + 2H2O(l) → CH4(g) +CO2(g) 24.02 g 4.) Calculate the number of mol ...
... 2.) What mass in grams of SO2 is needed to react completely with 1200. grams of O2 ? 2SO2(g) + O2(g) + 2H2O(l) → 2H2SO4(l) 4805 g 3.) What mass of carbon (with excess water) is required to produce 1.00 mol CH4 in the following? 2C(s) + 2H2O(l) → CH4(g) +CO2(g) 24.02 g 4.) Calculate the number of mol ...
Resume - TILT - Colorado State University
... generated a library of molecules based on the 4-alkoxydiphenylmethanones which contain tertiary, secondary amines and hydrazines. Regioselective alkylations of the hydrazine derivatives are achieved by using the (2,6-dichloro-4-methoxyphenyl)(2,4dichlorophenyl)methoxycarboxyl resin. Heterocycles 200 ...
... generated a library of molecules based on the 4-alkoxydiphenylmethanones which contain tertiary, secondary amines and hydrazines. Regioselective alkylations of the hydrazine derivatives are achieved by using the (2,6-dichloro-4-methoxyphenyl)(2,4dichlorophenyl)methoxycarboxyl resin. Heterocycles 200 ...
Biological membranes: the basics and why they are
... • Flexible phospholipid bilayer interspersed with protein molecules • Fluid – some parts move freely, if not anchored by other cell components • Mosaic – patchwork networks of proteins ...
... • Flexible phospholipid bilayer interspersed with protein molecules • Fluid – some parts move freely, if not anchored by other cell components • Mosaic – patchwork networks of proteins ...
Central Dogma Mini-Book Instructions
... DNA is the directions to build our bodies. The only problem is, DNA is locked inside the nucleus of a cell and can’t get out. To solve this problem, copies of the DNA are made in a form called mRNA. The process of making mRNA from DNA is called transcription. After transcription, the mRNA copies lea ...
... DNA is the directions to build our bodies. The only problem is, DNA is locked inside the nucleus of a cell and can’t get out. To solve this problem, copies of the DNA are made in a form called mRNA. The process of making mRNA from DNA is called transcription. After transcription, the mRNA copies lea ...
hydrogen ions
... The hydrogen ion is highly reactive and will combine with bases or negatively charged ions at very low concentrations. ...
... The hydrogen ion is highly reactive and will combine with bases or negatively charged ions at very low concentrations. ...
HUMAN BIOLOGY CHAPTER 2: The Chemistry of Living Things 2.2
... Carbon (koolstof) = common building block of all organic molecules o More stable when its second shell is filled with eight electrons o Natural tendency to form 4 covalent bonds with other molecules o Almost no limit to the size of organic molecules derived from carbon Macromolecules = consist of th ...
... Carbon (koolstof) = common building block of all organic molecules o More stable when its second shell is filled with eight electrons o Natural tendency to form 4 covalent bonds with other molecules o Almost no limit to the size of organic molecules derived from carbon Macromolecules = consist of th ...
Modelling the Protein and Amino Acid
... Abstract: Protein and amino acid requirements of the Greater rhea (Rhea americana) have been estimated from growth data available for this species, and assumptions derived with other closely related species. Differences in body weight and growth pattern caused considerable higher protein and amino a ...
... Abstract: Protein and amino acid requirements of the Greater rhea (Rhea americana) have been estimated from growth data available for this species, and assumptions derived with other closely related species. Differences in body weight and growth pattern caused considerable higher protein and amino a ...
Document
... increased product will slow reaction (known as negative feedback) Concentration of enzyme Increasing concentration increases enzyme activity up to a point ...
... increased product will slow reaction (known as negative feedback) Concentration of enzyme Increasing concentration increases enzyme activity up to a point ...
Worked solutions to textbook questions 1 Chapter 14 From organic
... molecular structure that is common to all three drugs. How does the structure of these molecules differ? ...
... molecular structure that is common to all three drugs. How does the structure of these molecules differ? ...
Document
... Enzymes are biological catalysts. They help the reactions that occur in our bodies by controlling the rate of reaction. An enzyme is basically a protein molecule made up of long chains of amino acids. These molecules are then “folded” to create a certain shape. Proteins are used in DNA replication, ...
... Enzymes are biological catalysts. They help the reactions that occur in our bodies by controlling the rate of reaction. An enzyme is basically a protein molecule made up of long chains of amino acids. These molecules are then “folded” to create a certain shape. Proteins are used in DNA replication, ...
Lecture: 27 Fatty acid and triacyl glycerol biosynthesis Biosynthesis
... The unsaturated fatty acids, linoleate, 18:2 (Δ9,12) and α-linolenate, 18:3 (Δ9,12,15) cannot be synthesised by mammals; but plants can synthesise both. The desaturases responsible for synthesis of both the above fatty acids are present in endoplasmic reticulum of plants. The plant ...
... The unsaturated fatty acids, linoleate, 18:2 (Δ9,12) and α-linolenate, 18:3 (Δ9,12,15) cannot be synthesised by mammals; but plants can synthesise both. The desaturases responsible for synthesis of both the above fatty acids are present in endoplasmic reticulum of plants. The plant ...
CELLS AND HEREDITY
... There are six elements that are especially important to life: carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, phosphorus, and sulfur (CHNOPS). There are about twenty others that play lesser roles. Iron, iodine and other trace elements make up less than 0.1% of the human body, but must be present for the body to ...
... There are six elements that are especially important to life: carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, phosphorus, and sulfur (CHNOPS). There are about twenty others that play lesser roles. Iron, iodine and other trace elements make up less than 0.1% of the human body, but must be present for the body to ...
Mitochondrium
... • O2 producing bacteria – early phase of phylogeny • the O2 is toxic to other cells/organisms ...
... • O2 producing bacteria – early phase of phylogeny • the O2 is toxic to other cells/organisms ...
Unit B2 - The Components of Life
... Enzymes are biological catalysts. They help the reactions that occur in our bodies by controlling the rate of reaction. An enzyme is basically a protein molecule made up of long chains of amino acids. These molecules are then “folded” to create a certain shape. Proteins are used in DNA replication, ...
... Enzymes are biological catalysts. They help the reactions that occur in our bodies by controlling the rate of reaction. An enzyme is basically a protein molecule made up of long chains of amino acids. These molecules are then “folded” to create a certain shape. Proteins are used in DNA replication, ...
26. oxidation of amino acids
... a small fraction of their energy needs from this source. Most microorganisms can scavenge amino acids from their environment if they are available; these can be oxidized as fuel when the metabolic conditions so demand. Photosynthetic plants, on the contrary, rarely oxidize amino acids to provide ene ...
... a small fraction of their energy needs from this source. Most microorganisms can scavenge amino acids from their environment if they are available; these can be oxidized as fuel when the metabolic conditions so demand. Photosynthetic plants, on the contrary, rarely oxidize amino acids to provide ene ...
Waves - members.iinet.com.au
... column of the periodic table are very reactive with other substances because they have a single electron in their outermost shell, just waiting to be stripped off to form a complete shell in some other atom. All the alkali metals have to be stored under oil except lithium as they react quickly with ...
... column of the periodic table are very reactive with other substances because they have a single electron in their outermost shell, just waiting to be stripped off to form a complete shell in some other atom. All the alkali metals have to be stored under oil except lithium as they react quickly with ...
Fundamental of Organic chemistry
... Organic compounds are extremely important as they are found in living things. Many products and materials are also organic products. Naturally occurring Synthetic Fuels (e.g. coal crude oil) in living orgainisms Carbohydrates plastics gasoline proteins cosmetics, perfumes kerosene fats and oils anae ...
... Organic compounds are extremely important as they are found in living things. Many products and materials are also organic products. Naturally occurring Synthetic Fuels (e.g. coal crude oil) in living orgainisms Carbohydrates plastics gasoline proteins cosmetics, perfumes kerosene fats and oils anae ...
Document
... Reagents = small carbon-based molecules (e.g. amino acids, carbohydrates) Catalysts = enzymes, proteins that bind and then catalyze chemical reaction ...
... Reagents = small carbon-based molecules (e.g. amino acids, carbohydrates) Catalysts = enzymes, proteins that bind and then catalyze chemical reaction ...
Functional lipidomics of oxidized products from polyunsaturated fatty
... discussed in relation with their biological relevance. 1. Autooxidation of PUFA It is well known that the autooxidation of PUFA leads to many metabolites that have been used as markers of the process (Catala, 2009). The mostly used one is malondialdehyde (MDA), which can also be produced through the ...
... discussed in relation with their biological relevance. 1. Autooxidation of PUFA It is well known that the autooxidation of PUFA leads to many metabolites that have been used as markers of the process (Catala, 2009). The mostly used one is malondialdehyde (MDA), which can also be produced through the ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.