Chapter 8
... one nucleotide is incorrect, this could affect the whole protein! • The genetic code is shared by almost all organisms. • For example: UUU codes for Phenylalanine in humans, a cactus, yeast, or an armadillo. ...
... one nucleotide is incorrect, this could affect the whole protein! • The genetic code is shared by almost all organisms. • For example: UUU codes for Phenylalanine in humans, a cactus, yeast, or an armadillo. ...
Rapid communication: Nucleotide sequence of red seabream
... amino acids and 14 amino acids from gilthead seabream and red seabream β-actin amino acid sequences, respectively (Figure 1). The amino acid sequences of red seabream β-actin differed from those of β-actin of gilthead seabream, which belongs to the same family as red seabream, by 16 amino acids out ...
... amino acids and 14 amino acids from gilthead seabream and red seabream β-actin amino acid sequences, respectively (Figure 1). The amino acid sequences of red seabream β-actin differed from those of β-actin of gilthead seabream, which belongs to the same family as red seabream, by 16 amino acids out ...
File
... – Many factors influence the rate of respiration, but the pathways are poorly understood. ...
... – Many factors influence the rate of respiration, but the pathways are poorly understood. ...
Water
... ④ Dipole-dipole interactions are not an alternative to dispersion forces. - They occur in addition to them. ...
... ④ Dipole-dipole interactions are not an alternative to dispersion forces. - They occur in addition to them. ...
Class 9 CBSE Test paper Solved Chapter 3: Atoms and...
... Ans: the valency of the element X is 1. The formula of the compounds formed by combination of X with hydrogen is XH and X with oxygen is X2O 9. Q. Atomic number of an element is 3. What would be the valency of the element? Also name the element. Ans: valency = 1 , Lithium 10.Q. Mention two advantage ...
... Ans: the valency of the element X is 1. The formula of the compounds formed by combination of X with hydrogen is XH and X with oxygen is X2O 9. Q. Atomic number of an element is 3. What would be the valency of the element? Also name the element. Ans: valency = 1 , Lithium 10.Q. Mention two advantage ...
Examples
... More active metals will replace less active metals from their compound in a solution A less active element will have no reaction when added to a more active element! Active metals replace hydrogen in water Active metals replace hydrogen in acids ...
... More active metals will replace less active metals from their compound in a solution A less active element will have no reaction when added to a more active element! Active metals replace hydrogen in water Active metals replace hydrogen in acids ...
DNA Sequencing:
... The gels must be quite large so that the molecules migrate further and are better resolved. Samples are denatured before they are loaded, and the gels must contain a high concentration of urea (7 to 8 molar) to prevent folding of the molecules and formation of secondary structures by hydrogen bondin ...
... The gels must be quite large so that the molecules migrate further and are better resolved. Samples are denatured before they are loaded, and the gels must contain a high concentration of urea (7 to 8 molar) to prevent folding of the molecules and formation of secondary structures by hydrogen bondin ...
Ch 4 - Department of Ecology and Evolution
... sReduction of activity and oxygen uptake when environmental oxygen is in low concentration(e.g., at time of low tide) sSpecies with higher activity have higher oxygen consumption rates, all other things being equal ...
... sReduction of activity and oxygen uptake when environmental oxygen is in low concentration(e.g., at time of low tide) sSpecies with higher activity have higher oxygen consumption rates, all other things being equal ...
2.2 PPT – Nutrient Cycles
... wind, water and freezing release the phosphates. Uptake: plants suck up PO43-, then are eaten by animals. Decomposition: Bacteria break down organic matter & phosphorous is returned to soil. Geologic Uplift: when rocks under the ground are pushed up mountains weathering. ...
... wind, water and freezing release the phosphates. Uptake: plants suck up PO43-, then are eaten by animals. Decomposition: Bacteria break down organic matter & phosphorous is returned to soil. Geologic Uplift: when rocks under the ground are pushed up mountains weathering. ...
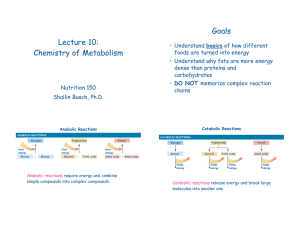
Lecture 10
... Anabolic reactions require energy and combine simple compounds into complex compounds. ...
... Anabolic reactions require energy and combine simple compounds into complex compounds. ...
Chapter 11
... Jerusalem artichokes and onions, store polymers of fructose. Sucrose, from photosynthesis, is the common starter molecule for respiration in most parts of a plant, but, as suggested, respiration may begin with starch in nongreen organs such as roots and stems. In other plants, or, more specifically, ...
... Jerusalem artichokes and onions, store polymers of fructose. Sucrose, from photosynthesis, is the common starter molecule for respiration in most parts of a plant, but, as suggested, respiration may begin with starch in nongreen organs such as roots and stems. In other plants, or, more specifically, ...
Lesson 1 - Working With Chemicals
... In the solid state ionic compounds are crystalline Ionic compounds have fairly high melting points In the solid form they do not conduct electricity In the aqueous (dissolved in water) form ionic compounds are electrolytes – they conduct ...
... In the solid state ionic compounds are crystalline Ionic compounds have fairly high melting points In the solid form they do not conduct electricity In the aqueous (dissolved in water) form ionic compounds are electrolytes – they conduct ...
Chemical Reactions Notes-1a-1
... Mg consists of closely packed atoms and O2 consists of dispersed molecules. ...
... Mg consists of closely packed atoms and O2 consists of dispersed molecules. ...
Molecular Mechanics
... • good geometries and relative energies of conformers of the same molecule (provided that electronic interactions are not important) • effect of substituents on geometry and strain energy • well parameterized for organics, less so for inorganics • specialty force fields available for proteins, DNA, ...
... • good geometries and relative energies of conformers of the same molecule (provided that electronic interactions are not important) • effect of substituents on geometry and strain energy • well parameterized for organics, less so for inorganics • specialty force fields available for proteins, DNA, ...
slides
... Glycolysis – Conversion of C6 sugars to CO2 and pyruvic acid Citric Acid Cycle (Kreb Cycle) – Oxydation of pyruvic acid to H+, eand CO2 (occurs in mitochondria) 3. The Q10 - The rate of respiration doubles when temperature rises 10 oC (18 oF) - Respiration can be reduced by lowering O2 and increasin ...
... Glycolysis – Conversion of C6 sugars to CO2 and pyruvic acid Citric Acid Cycle (Kreb Cycle) – Oxydation of pyruvic acid to H+, eand CO2 (occurs in mitochondria) 3. The Q10 - The rate of respiration doubles when temperature rises 10 oC (18 oF) - Respiration can be reduced by lowering O2 and increasin ...
File
... 45. Acetylene gas (C2H2) and Calcium hydroxide are produced by adding water to calcium carbide (CaC2). Write the balanced chemical equation. How many grams of acetylene are produced by adding excess water to 5.00 grams of calcium carbide? 46. Using the equation you balanced in the problem above, det ...
... 45. Acetylene gas (C2H2) and Calcium hydroxide are produced by adding water to calcium carbide (CaC2). Write the balanced chemical equation. How many grams of acetylene are produced by adding excess water to 5.00 grams of calcium carbide? 46. Using the equation you balanced in the problem above, det ...
HiPer® Protein Estimation Teaching Kit (Qualitative)
... To 1 ml of each standard and protein sample, add 1 ml of concentrated Nitric acid and boil for1 minute and allow it to cool to room temperature. To the above solution add few drops (0.2 ml) of 1 M NaOH. ...
... To 1 ml of each standard and protein sample, add 1 ml of concentrated Nitric acid and boil for1 minute and allow it to cool to room temperature. To the above solution add few drops (0.2 ml) of 1 M NaOH. ...
Click here for powerpoint
... How does mRNA code for proteins mRNA leaves nucleus mRNA goes to ribosomes in cytoplasm Proteins built from instructions on mRNA ...
... How does mRNA code for proteins mRNA leaves nucleus mRNA goes to ribosomes in cytoplasm Proteins built from instructions on mRNA ...
Selective toxicity of antibiotics
... All microorganisms require elemental oxygen to build their biochemical components, but not all of them require atmospheric oxygen. Most heterotrophic bacteria obtain oxygen from the same molecule that serves as a carbon source (CH2O). Autotrophs obtain oxygen from CO2. Most aerobic bacteria have an ...
... All microorganisms require elemental oxygen to build their biochemical components, but not all of them require atmospheric oxygen. Most heterotrophic bacteria obtain oxygen from the same molecule that serves as a carbon source (CH2O). Autotrophs obtain oxygen from CO2. Most aerobic bacteria have an ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.