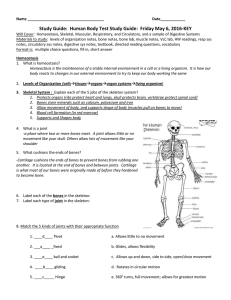
Homeostasis, Levels of Organization of Living Things, Skeletal
... 18. List and explain the 5 jobs of the circulatory system (2 points each) 1. Blood carries food, water, and oxygen to all of the cells in the body. 2. Blood removes waste from all of the cells of the body. 3. Blood helps to maintain our body temperature. 4. White blood cells in blood helps to fight ...
... 18. List and explain the 5 jobs of the circulatory system (2 points each) 1. Blood carries food, water, and oxygen to all of the cells in the body. 2. Blood removes waste from all of the cells of the body. 3. Blood helps to maintain our body temperature. 4. White blood cells in blood helps to fight ...
Pathobiochemistry of Ammonia in the Internal Environment of Fish
... The main purpose of food proteins is to provide the fish organism with necessary amino acids, important energy sources in tissues after deamination and decarboxylation. The majority of the absorbed amino acids proceed to the portal venous blood and is transported to the liver. The only exception is ...
... The main purpose of food proteins is to provide the fish organism with necessary amino acids, important energy sources in tissues after deamination and decarboxylation. The majority of the absorbed amino acids proceed to the portal venous blood and is transported to the liver. The only exception is ...
Dissecting the protein–RNA interface
... As of 11 November 2010, the PDB listed 824 structures of protein–RNA complexes that had been solved using X-ray crystallography (5). From this data set, 344 complexes were selected based on the following criteria: (i) structural resolution better than 3.0 Å and (ii) polypeptides and polyribonucleot ...
... As of 11 November 2010, the PDB listed 824 structures of protein–RNA complexes that had been solved using X-ray crystallography (5). From this data set, 344 complexes were selected based on the following criteria: (i) structural resolution better than 3.0 Å and (ii) polypeptides and polyribonucleot ...
Chemical Reactions
... • Product – what is made during the chemical reaction • Law of conservation of mass (or matter)- mass is neither created or destroyed in ordinary chemical or physical changes • Subscript - number (representing atoms) written below and to the right of a chemical symbol ...
... • Product – what is made during the chemical reaction • Law of conservation of mass (or matter)- mass is neither created or destroyed in ordinary chemical or physical changes • Subscript - number (representing atoms) written below and to the right of a chemical symbol ...
Oxidation - medscistudents
... 1. Once the activated FA enter the mitochondria, flavoprotein linked acyl CoA dehydrogenase (DH) removes two hydrogen atoms from the , position, forming ,- unsaturated fatty acyl CoA. This contains a double bond at and position. 2. Enoyl CoA hydratase adds a molecule of water at the double ...
... 1. Once the activated FA enter the mitochondria, flavoprotein linked acyl CoA dehydrogenase (DH) removes two hydrogen atoms from the , position, forming ,- unsaturated fatty acyl CoA. This contains a double bond at and position. 2. Enoyl CoA hydratase adds a molecule of water at the double ...
medical chemistry and biochemistry
... Amino acids: disposal of nitrogen Describe protein turnover and indicate the role of ubiquitin in protein degradation. Indicate how the ultimate end products of nitrogen catabolism in mammals differ from those in birds and in fish. Illustrate the central roles of transaminases (aminotranferases), of ...
... Amino acids: disposal of nitrogen Describe protein turnover and indicate the role of ubiquitin in protein degradation. Indicate how the ultimate end products of nitrogen catabolism in mammals differ from those in birds and in fish. Illustrate the central roles of transaminases (aminotranferases), of ...
Chapter 2 - Trimble County Schools
... • An element is a substance that cannot be broken down to other substances by chemical reactions • A compound is a substance consisting of two or more elements in a fixed ratio • A compound has characteristics different from those of its elements ...
... • An element is a substance that cannot be broken down to other substances by chemical reactions • A compound is a substance consisting of two or more elements in a fixed ratio • A compound has characteristics different from those of its elements ...
IB Chemistry Review. Unit I. Topics 2
... 5. What happens when magnesium metal reacts with chlorine gas? A. Each magnesium atom loses two electrons and each chlorine atom gains two electrons. B. Each magnesium atom gains one electron and each chlorine atom loses one electron. C. Each magnesium atom loses two electrons and each chlorine atom ...
... 5. What happens when magnesium metal reacts with chlorine gas? A. Each magnesium atom loses two electrons and each chlorine atom gains two electrons. B. Each magnesium atom gains one electron and each chlorine atom loses one electron. C. Each magnesium atom loses two electrons and each chlorine atom ...
MEDICAL BIOCHEMISTRY Lectures 35-36 Chp. 26
... glycolipids and glycoproteins found in most cell membranes. Those located on red blood cells have been studied extensively. A single genetic locus with two alleles determines an individual's blood type. These genes encode glycosyltransferases involved in the synthesis of the oligosaccharides of the ...
... glycolipids and glycoproteins found in most cell membranes. Those located on red blood cells have been studied extensively. A single genetic locus with two alleles determines an individual's blood type. These genes encode glycosyltransferases involved in the synthesis of the oligosaccharides of the ...
Topic 1 Review - Capital High School
... 5. What happens when magnesium metal reacts with chlorine gas? A. Each magnesium atom loses two electrons and each chlorine atom gains two electrons. B. Each magnesium atom gains one electron and each chlorine atom loses one electron. C. Each magnesium atom loses two electrons and each chlorine atom ...
... 5. What happens when magnesium metal reacts with chlorine gas? A. Each magnesium atom loses two electrons and each chlorine atom gains two electrons. B. Each magnesium atom gains one electron and each chlorine atom loses one electron. C. Each magnesium atom loses two electrons and each chlorine atom ...
Molecular Interactions of Collagen-binding Proteins
... proteins. The most abundant structural fiber is collagen. A collagen-fiber is comprised of bundles of collagen-fibrils, which again are comprised of individual collagen-molecules that are bundled together in a process called fibrillogenesis (Figure 1) [1, 2]. The fibrillogenesis of collagen is a hig ...
... proteins. The most abundant structural fiber is collagen. A collagen-fiber is comprised of bundles of collagen-fibrils, which again are comprised of individual collagen-molecules that are bundled together in a process called fibrillogenesis (Figure 1) [1, 2]. The fibrillogenesis of collagen is a hig ...
File ch 14 ppt1
... • A Lewis acid is an atom, ion, or molecule that accepts an electron pair to form a covalent bond. • The Lewis definition is the broadest of the three acid definitions. • A bare proton (hydrogen ion) is a Lewis acid H (aq ) + : NH3 (aq ) [H — NH3 ] (aq ) or [NH4 ] (aq ) ...
... • A Lewis acid is an atom, ion, or molecule that accepts an electron pair to form a covalent bond. • The Lewis definition is the broadest of the three acid definitions. • A bare proton (hydrogen ion) is a Lewis acid H (aq ) + : NH3 (aq ) [H — NH3 ] (aq ) or [NH4 ] (aq ) ...
CHEMISTRY 1710 - Practice Exam #2 (KATZ)
... water bath at 99°C. The barometric pressure is 753 torr. If the mass of the liquid retained in the flask is 1.362 g, what is its molar mass? a. ...
... water bath at 99°C. The barometric pressure is 753 torr. If the mass of the liquid retained in the flask is 1.362 g, what is its molar mass? a. ...
Improving Food Nutritional Quality and Productivity through Genetic
... content, enhanced rate of photosynthesis along with increase in total biomass and a moderate increase in tuber yield was observed [7]. It was found to be non-allergenic and safe for consumption suitable for commercial cultivation on the basis of field performance and biosafety assessment [7]. Legume ...
... content, enhanced rate of photosynthesis along with increase in total biomass and a moderate increase in tuber yield was observed [7]. It was found to be non-allergenic and safe for consumption suitable for commercial cultivation on the basis of field performance and biosafety assessment [7]. Legume ...
Fall.2008.Week9.Lesson.2 - reich
... • HCl + NaOH ____ + ____ • The “metals” swithc places. So H and Na will switch. Na will be with Cl, and H will be with OH • HCl + NaOH NaCl + H2O ...
... • HCl + NaOH ____ + ____ • The “metals” swithc places. So H and Na will switch. Na will be with Cl, and H will be with OH • HCl + NaOH NaCl + H2O ...
ALE 8 - Biol 100
... Outline the flow of genetic information from DNA to the production of proteins: DNA RNA Protein. For each step indicate where it takes place in the cell, the name of each process involved, what is needed for each process to occur, the names of the major enzymes involved, etc. DNA mRNA Protei ...
... Outline the flow of genetic information from DNA to the production of proteins: DNA RNA Protein. For each step indicate where it takes place in the cell, the name of each process involved, what is needed for each process to occur, the names of the major enzymes involved, etc. DNA mRNA Protei ...
D-Ribose Powder - Professional Complementary Health Formulas
... The body has the ability to make D–Ribose naturally from glucose; however, the metabolic process is slow and limited by glucose6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G-6-PDH), an enzyme typically in short supply. When D-Ribose is restricted or when nucleotides are decreased after intense exercise, ATP synthesis ...
... The body has the ability to make D–Ribose naturally from glucose; however, the metabolic process is slow and limited by glucose6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G-6-PDH), an enzyme typically in short supply. When D-Ribose is restricted or when nucleotides are decreased after intense exercise, ATP synthesis ...
Supplementary Figure Legend (doc 33K)
... condensation without cell membrane permeabilization (as evaluated with HO and PI staining) in VSMC exposed to 0.5 ml of: normal medium (N); serum starvation in RPMI (SS) for 24 h or incubated with either ZVAD-FMK (SS-ZVAD) or vehicle (SS-DMSO) prior to SS for 24 h. * = p = 0.02 vs. SS-DMSO, n = 6. L ...
... condensation without cell membrane permeabilization (as evaluated with HO and PI staining) in VSMC exposed to 0.5 ml of: normal medium (N); serum starvation in RPMI (SS) for 24 h or incubated with either ZVAD-FMK (SS-ZVAD) or vehicle (SS-DMSO) prior to SS for 24 h. * = p = 0.02 vs. SS-DMSO, n = 6. L ...
template
... Proteins are large molecules that are vital for all living organisms and they are essential components of many industrial products. The process of binding a protein to another is called protein-protein docking. Many automated algorithms have been proposed to find docking configurations that might yi ...
... Proteins are large molecules that are vital for all living organisms and they are essential components of many industrial products. The process of binding a protein to another is called protein-protein docking. Many automated algorithms have been proposed to find docking configurations that might yi ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.























