A and P lesson 4 - Calthorpe Park Moodle
... the capillaries, while carbon dioxide moves from the blood in the capillaries into the air in the alveoli. ...
... the capillaries, while carbon dioxide moves from the blood in the capillaries into the air in the alveoli. ...
video slide - Somers Public Schools
... NADH, forming lactate as an end product, with no release of CO2 • Lactic acid fermentation by some fungi and bacteria is used to make cheese and yogurt • Human muscle cells use lactic acid fermentation to generate ATP when O2 is scarce ...
... NADH, forming lactate as an end product, with no release of CO2 • Lactic acid fermentation by some fungi and bacteria is used to make cheese and yogurt • Human muscle cells use lactic acid fermentation to generate ATP when O2 is scarce ...
Chapter 9
... NADH, forming lactate as an end product, with no release of CO2 • Lactic acid fermentation by some fungi and bacteria is used to make cheese and yogurt • Human muscle cells use lactic acid fermentation to generate ATP when O2 is scarce ...
... NADH, forming lactate as an end product, with no release of CO2 • Lactic acid fermentation by some fungi and bacteria is used to make cheese and yogurt • Human muscle cells use lactic acid fermentation to generate ATP when O2 is scarce ...
Carboxylic Acids - BSAK Chemistry weebly
... • Acyl chlorides: These contain a -COCl group, e.g. ethanoyl chloride, CH3COCl, or benzoyl chloride, C6H5COCl • Alkyl chlorides: These have a chlorine attached to a carbon chain, e.g. chloroethane, C2H5Cl • Aryl chlorides: These have a chlorine attached directly to a benzene ring, e.g. chlorobenzen ...
... • Acyl chlorides: These contain a -COCl group, e.g. ethanoyl chloride, CH3COCl, or benzoyl chloride, C6H5COCl • Alkyl chlorides: These have a chlorine attached to a carbon chain, e.g. chloroethane, C2H5Cl • Aryl chlorides: These have a chlorine attached directly to a benzene ring, e.g. chlorobenzen ...
Introduction to enzymes
... 2. Kinetics alone will not give a chemical mechanism but combined with chemical and structural data mechanisms can be elucidated. 3. Kinetics help understand the enzymes role in metabolic pathways. 4. Under “proper” conditions rates are proportional to enzyme concentrations and these can be determin ...
... 2. Kinetics alone will not give a chemical mechanism but combined with chemical and structural data mechanisms can be elucidated. 3. Kinetics help understand the enzymes role in metabolic pathways. 4. Under “proper” conditions rates are proportional to enzyme concentrations and these can be determin ...
Lipid metabolism in the fowl under normal and abnormal
... indicated by an increase in the plasma free fatty acid level (Freeman, I 967; Braganza, Peterson & Candella, I 973). Since the injection of adrenocorticotrophic hormone (ACTH) also produces this response (Jaussi, Newcomer & Thayer, 1962), other stressors might be expected to have a similar effect. T ...
... indicated by an increase in the plasma free fatty acid level (Freeman, I 967; Braganza, Peterson & Candella, I 973). Since the injection of adrenocorticotrophic hormone (ACTH) also produces this response (Jaussi, Newcomer & Thayer, 1962), other stressors might be expected to have a similar effect. T ...
Designing Minor Groove Binding Drugs
... poison..“catalytic inhibitors,” such as coumermycin, inhibit essential ATP hydrolysis needed for topoisomerase function.3 ...
... poison..“catalytic inhibitors,” such as coumermycin, inhibit essential ATP hydrolysis needed for topoisomerase function.3 ...
Incorporation of radioactive citrate into fatty acids
... BRADY AND GURIN1 and DITURI AND GURIN2 were the first to show that soluble enzymes of pigeon liver could synthesize long-chain fatty acids from acetate and that citrate stimulated this process. These results were confirmed and extended to a number of other tissues by other workers and purification o ...
... BRADY AND GURIN1 and DITURI AND GURIN2 were the first to show that soluble enzymes of pigeon liver could synthesize long-chain fatty acids from acetate and that citrate stimulated this process. These results were confirmed and extended to a number of other tissues by other workers and purification o ...
respiration - Learn Biology
... because glucose (C6H12O6) is only partially broken down. When glucose is only partially broken down another waste product is made – Lactic acid! ...
... because glucose (C6H12O6) is only partially broken down. When glucose is only partially broken down another waste product is made – Lactic acid! ...
Cellular Energetics: Thermodynamics, ATP, Cellular
... D) bonds form between inhibitor and enzyme. E) None of the choices are correct. ...
... D) bonds form between inhibitor and enzyme. E) None of the choices are correct. ...
Open - Cherry Hill Tuition
... Mark ticks only. Ignore anything else if different symbols such as crosses are used as well. If crosses are used instead of ticks allow cross as equivalent to a tick. ...
... Mark ticks only. Ignore anything else if different symbols such as crosses are used as well. If crosses are used instead of ticks allow cross as equivalent to a tick. ...
Simple Models of Protein Folding
... approach to modeling protein folding involves using molecular dynamics simulations. Current advances in computing technologies have allowed all-atom simulations to probe several microseconds over a folding trajectory [11]. With the three aforementioned techniques in mind, the following methods secti ...
... approach to modeling protein folding involves using molecular dynamics simulations. Current advances in computing technologies have allowed all-atom simulations to probe several microseconds over a folding trajectory [11]. With the three aforementioned techniques in mind, the following methods secti ...
Origins of Sugars in the Prebiotic World
... • If the nucleophile is the 3’-OH group of another NTP, then a nucleic acid is generated: polymer of nucleotides – Oligomers (“oligos”) short length (DNA/RNA polymers of long ...
... • If the nucleophile is the 3’-OH group of another NTP, then a nucleic acid is generated: polymer of nucleotides – Oligomers (“oligos”) short length (DNA/RNA polymers of long ...
gfp_exercise_ver5
... Ribbons box. Alternatively, you can click on All Ribbons within the Show Ribbons box to view all structures at the same time. Answer ...
... Ribbons box. Alternatively, you can click on All Ribbons within the Show Ribbons box to view all structures at the same time. Answer ...
Are You Justifying Your Post-Workout Carbs
... studies suggest that high-carb diets induce lipogenic enzymes.(9) One can crack open any modern biochemistry text to see this. Carbs may also induce sleepiness if consumed too far ahead of a workout, if you are anything like me. Insulin is part of the effect and it’s a real Jekyll and Hyde hormone – ...
... studies suggest that high-carb diets induce lipogenic enzymes.(9) One can crack open any modern biochemistry text to see this. Carbs may also induce sleepiness if consumed too far ahead of a workout, if you are anything like me. Insulin is part of the effect and it’s a real Jekyll and Hyde hormone – ...
Creation/Evolution - Geoscience Research Institute
... Are Codons The Language of God? The genetic code appears to be non-random in nature and designed with considerable safeguards against harmful point mutations An evolutionary model suggests at least at some level of randomness in assignment of amino acids to codons No mechanism exists for genetic cod ...
... Are Codons The Language of God? The genetic code appears to be non-random in nature and designed with considerable safeguards against harmful point mutations An evolutionary model suggests at least at some level of randomness in assignment of amino acids to codons No mechanism exists for genetic cod ...
Introduction to Chemistry and Measurement
... The components of dyes such as ink may be separated by paper chromatography. ...
... The components of dyes such as ink may be separated by paper chromatography. ...
N-Terminal Intramolecularly Conserved Histidines of Three Domains
... full-length luciferase cDNA (4037 bp) has an open reading frame (ORF) of 3723 bp and encodes the 136 994 Da luciferase molecule (5). The ORF (Figure 1) contains an N-terminal sequence of 111 amino acids, which is homologous to the N-terminal region of the substrate-binding protein, LBP. This is foll ...
... full-length luciferase cDNA (4037 bp) has an open reading frame (ORF) of 3723 bp and encodes the 136 994 Da luciferase molecule (5). The ORF (Figure 1) contains an N-terminal sequence of 111 amino acids, which is homologous to the N-terminal region of the substrate-binding protein, LBP. This is foll ...
Document
... • These noncoding regions are called intervening sequences, or ____________ • The other regions are called ____________ because they are eventually expressed, usually translated into amino acid sequences • _____________________removes introns and joins exons, creating an mRNA molecule with a ...
... • These noncoding regions are called intervening sequences, or ____________ • The other regions are called ____________ because they are eventually expressed, usually translated into amino acid sequences • _____________________removes introns and joins exons, creating an mRNA molecule with a ...
Diversity in the Structure and Function of Amylase
... • Students enrolled in Principles of Biology I (BI 107) and II (BI 108) • Human salivary amylase: used in one of our lab modules, so students are familiar with this enzyme and its function ...
... • Students enrolled in Principles of Biology I (BI 107) and II (BI 108) • Human salivary amylase: used in one of our lab modules, so students are familiar with this enzyme and its function ...
RevisionResource
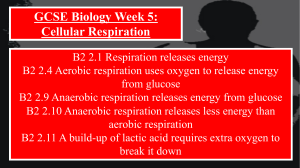
... Respiration is the release of energy from glucose in the muscles. When the body is at rest this is aerobic respiration. As you exercise you breathe harder and deeper and the heart beats faster to get oxygen to the muscles. Glucose + oxygen → energy + water + carbon dioxide ...
... Respiration is the release of energy from glucose in the muscles. When the body is at rest this is aerobic respiration. As you exercise you breathe harder and deeper and the heart beats faster to get oxygen to the muscles. Glucose + oxygen → energy + water + carbon dioxide ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.