Effect of Zinc on Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle Intermediates and
... at -20 "C until used. The mycelium (500 mg) was ground with acid-washed sea sand in a precooled mortar (4 "C) containing 5 ml 8 % (w/v) perchloric acid in 40% (v/v) ethanol. The homogenate was centrifuged a t 25 ooo g for I o min, and the supernatant was decanted and stored at o to 4 "C. The residue ...
... at -20 "C until used. The mycelium (500 mg) was ground with acid-washed sea sand in a precooled mortar (4 "C) containing 5 ml 8 % (w/v) perchloric acid in 40% (v/v) ethanol. The homogenate was centrifuged a t 25 ooo g for I o min, and the supernatant was decanted and stored at o to 4 "C. The residue ...
1 Enzyme Mechanisms Topics: TIM, Chymotrypsin, Rate
... A. Orientation An experiment to support the importance of orientation for catalytic efficiency (that is, for rate enhancement), is shown on p5 of the handout, Figure B. Here positioning the reactive groups more closely can speed up the rate by 5 x 104 times. This shows that orientation alone is also ...
... A. Orientation An experiment to support the importance of orientation for catalytic efficiency (that is, for rate enhancement), is shown on p5 of the handout, Figure B. Here positioning the reactive groups more closely can speed up the rate by 5 x 104 times. This shows that orientation alone is also ...
Sample Chapters - Pearson Canada
... polymers and complex lipids with monomeric intermediates; stage 2, the interconversion of monomeric sugars, amino acids, and lipids with still simpler organic compounds; and stage 3, the ultimate degradation to, or synthesis from, inorganic compounds, including CO2, H2O, and NH3 (Figure 12.1b). As w ...
... polymers and complex lipids with monomeric intermediates; stage 2, the interconversion of monomeric sugars, amino acids, and lipids with still simpler organic compounds; and stage 3, the ultimate degradation to, or synthesis from, inorganic compounds, including CO2, H2O, and NH3 (Figure 12.1b). As w ...
Events of The Krebs Cycle
... This type of fat stimulates the liver to make cholesterol for storage in body tissues and to inhibit the release of cholesterol from the body. In terms of good nutrition it is recommended that unsaturated fats be substituted for saturated fats a high percentage of the time in the diet. Unit 8 - Obje ...
... This type of fat stimulates the liver to make cholesterol for storage in body tissues and to inhibit the release of cholesterol from the body. In terms of good nutrition it is recommended that unsaturated fats be substituted for saturated fats a high percentage of the time in the diet. Unit 8 - Obje ...
Supplementary Materials and Methods
... enriched in LSGs, protein "signatures" in all Arabidopsis protein coding genes were identified using InterProScan and associated databases [13]. Comparing the distribution of LSG and non-LSG protein signatures using hypergeometric tests identified enrichment for particular classes of protein signatu ...
... enriched in LSGs, protein "signatures" in all Arabidopsis protein coding genes were identified using InterProScan and associated databases [13]. Comparing the distribution of LSG and non-LSG protein signatures using hypergeometric tests identified enrichment for particular classes of protein signatu ...
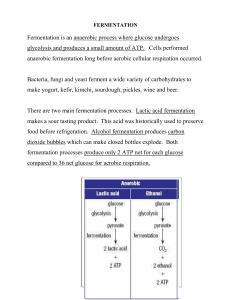
FERMENTATION
... FERMENTATION Fermentation is an __________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________. Cells performed anaerobic fermentation long before aerobic cellular respiration occurred. ...
... FERMENTATION Fermentation is an __________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________. Cells performed anaerobic fermentation long before aerobic cellular respiration occurred. ...
Document
... result in the production of unusual proteins as introns may still be present in some of the RNAs, and code for additional amino acids or aberrant terminations. c) Normally, a cell only exports mature or fully processed mRNA out of the nucleus. However, we learned in lecture that HIV can co-opt the c ...
... result in the production of unusual proteins as introns may still be present in some of the RNAs, and code for additional amino acids or aberrant terminations. c) Normally, a cell only exports mature or fully processed mRNA out of the nucleus. However, we learned in lecture that HIV can co-opt the c ...
File
... possesses because of its location or structure – CHEMICAL energy is potential energy available for release in a chemical reaction ...
... possesses because of its location or structure – CHEMICAL energy is potential energy available for release in a chemical reaction ...
Functional dissection of the baculovirus late expression factor
... approximate position of the LEF-8 region H homologous motif. N and C indicate the N- and C-termini of LEF-8, respectively. The next two lines represent N-terminal deletions of 66 and 134 amino acids, respectively. N-terminal deletions retain the initiation methionine codon as well as in-frame HA and ...
... approximate position of the LEF-8 region H homologous motif. N and C indicate the N- and C-termini of LEF-8, respectively. The next two lines represent N-terminal deletions of 66 and 134 amino acids, respectively. N-terminal deletions retain the initiation methionine codon as well as in-frame HA and ...
Amines and Amides
... • Fourth most common atom in living systems. • Important component of the structure of nucleic acids, DNA, and RNA • Essential to the structure and function of proteins – enzymes and antibodies ...
... • Fourth most common atom in living systems. • Important component of the structure of nucleic acids, DNA, and RNA • Essential to the structure and function of proteins – enzymes and antibodies ...
Respiratory Physiology
... Occurs when a person breathes shallowly, or gas exchange is hampered by diseases such as pneumonia, cystic fibrosis, or emphysema Respiratory alkalosis is a common result of hyperventilation Breathing deeply and rapidly, lowering pCO2 levels to <35 mm Hg Defined as a rate of Pulmonary Ventilation th ...
... Occurs when a person breathes shallowly, or gas exchange is hampered by diseases such as pneumonia, cystic fibrosis, or emphysema Respiratory alkalosis is a common result of hyperventilation Breathing deeply and rapidly, lowering pCO2 levels to <35 mm Hg Defined as a rate of Pulmonary Ventilation th ...
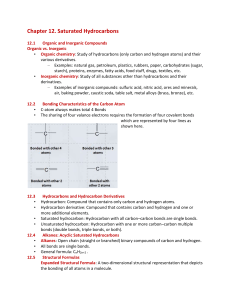
Notes-C12-121
... Different conformational structures result from C-C single bond rotation, but no breaking of bonds takes place. Different structural isomers result from different connectivity of atoms, which requires breaking and making of bonds in the same molecule. ...
... Different conformational structures result from C-C single bond rotation, but no breaking of bonds takes place. Different structural isomers result from different connectivity of atoms, which requires breaking and making of bonds in the same molecule. ...
Supplementary Figure 1: Gene/Protein restrictions selection. First
... into account all known stimulus (inputs) that may affect our group of proteins (136 ...
... into account all known stimulus (inputs) that may affect our group of proteins (136 ...
Ans8. Anaerobic Respiration/ Fermentation
... separate DNA or RNA fragments by size and reactivity. Nucleic acid molecules which are to be analyzed are set upon a viscous medium, the gel, where an electric field induces the nucleic acids to migrate toward the anode, due to the net negative charge of the sugar-phosphate backbone of the nucleic a ...
... separate DNA or RNA fragments by size and reactivity. Nucleic acid molecules which are to be analyzed are set upon a viscous medium, the gel, where an electric field induces the nucleic acids to migrate toward the anode, due to the net negative charge of the sugar-phosphate backbone of the nucleic a ...
Exam 2
... D. The elements were arranged into vertical groups of elements with similar chemical properties. Question 16 In which of the following sets are all the compounds likely to be coloured? A. KClO4, FeCl2, NH4VO3 B. Ca3(PO4)2, NH4VO3, MgBr2 C. FeCl2, NiCl2, K2CrO4 D. KClO4, MgBr2, Ca3(PO4)2 Questions 17 ...
... D. The elements were arranged into vertical groups of elements with similar chemical properties. Question 16 In which of the following sets are all the compounds likely to be coloured? A. KClO4, FeCl2, NH4VO3 B. Ca3(PO4)2, NH4VO3, MgBr2 C. FeCl2, NiCl2, K2CrO4 D. KClO4, MgBr2, Ca3(PO4)2 Questions 17 ...
VITAMINS-6
... • Also known as Folic acid, Folate, general term for Vitamin B9 • Folate is a naturally occurring form of the vitamin, found in food, while folic acid is synthetically produced • Folate refers to the various tetrahydrofolate derivatives naturally found in food ...
... • Also known as Folic acid, Folate, general term for Vitamin B9 • Folate is a naturally occurring form of the vitamin, found in food, while folic acid is synthetically produced • Folate refers to the various tetrahydrofolate derivatives naturally found in food ...
Alice and Lewis Carroll
... Alone in his study, the aged Dr. Faust despairs that his lifelong search for a solution to the riddle of life has been in vain. Twice he raises a goblet of poison to his lips but falters when the songs of young men and women outside his window re-awaken the unfulfilled passions and desires of his y ...
... Alone in his study, the aged Dr. Faust despairs that his lifelong search for a solution to the riddle of life has been in vain. Twice he raises a goblet of poison to his lips but falters when the songs of young men and women outside his window re-awaken the unfulfilled passions and desires of his y ...
Measurements/Unit Cancellation/Significant Figures 1. When
... 40. Write a balanced equation for the complete combustion of glucose (C6H12O6)... if 72.0 g glucose combusts with excess O2, what is mass of CO2 formed? More Stoichiometry questions 41. What is the percent by mass of oxygen in Fe2O3? ...
... 40. Write a balanced equation for the complete combustion of glucose (C6H12O6)... if 72.0 g glucose combusts with excess O2, what is mass of CO2 formed? More Stoichiometry questions 41. What is the percent by mass of oxygen in Fe2O3? ...
Diabetes? - H and N Herbs
... Lack of fiber in the American diet is thought to contribute to the development of Type II diabetes. Barley or fiber can help maintain glucose control in diabetes. It is best when taken with meals because the fiber prevents the absorption of some carbohydrates and allows more effective use of carbohy ...
... Lack of fiber in the American diet is thought to contribute to the development of Type II diabetes. Barley or fiber can help maintain glucose control in diabetes. It is best when taken with meals because the fiber prevents the absorption of some carbohydrates and allows more effective use of carbohy ...
Glucose Homeostasis
... Adipose Tissue They play an important role in glucose homeostatic mechanisms. If blood glucose level increases, decreases it through The uptake of glucose by tissues Glucose oxidation ...
... Adipose Tissue They play an important role in glucose homeostatic mechanisms. If blood glucose level increases, decreases it through The uptake of glucose by tissues Glucose oxidation ...
Ch. 10 ppt
... • Vaccines against the flu are the best way to protect public health. • Because flu viruses mutate quickly, new vaccines must be created every year. ...
... • Vaccines against the flu are the best way to protect public health. • Because flu viruses mutate quickly, new vaccines must be created every year. ...
AP Biology
... levels, or shells, of the atom. Chemical behavior depends on the number of valence electrons, those in the outermost shell. An atom with an incomplete valence shell is reactive. Electrons move within orbitals, three-dimensional spaces with specific shapes located within successive shells. Web/CD Act ...
... levels, or shells, of the atom. Chemical behavior depends on the number of valence electrons, those in the outermost shell. An atom with an incomplete valence shell is reactive. Electrons move within orbitals, three-dimensional spaces with specific shapes located within successive shells. Web/CD Act ...
ppt - University of Illinois Urbana
... Characterizing a Family - Compare the sequence and structure patterns of the family members to reveal shared characteristics that potentially describe common biological properties – Multiple sequence alignment – Motif/Domain - sequence and/or structure patterns common to protein family members (a tr ...
... Characterizing a Family - Compare the sequence and structure patterns of the family members to reveal shared characteristics that potentially describe common biological properties – Multiple sequence alignment – Motif/Domain - sequence and/or structure patterns common to protein family members (a tr ...
Final b
... 9. (10 pts) Draw the reactions for activation of a monomer and its use in glycogen synthesis. Explain the seemingly unusual feature of the thermodynamics associated with this reaction. ...
... 9. (10 pts) Draw the reactions for activation of a monomer and its use in glycogen synthesis. Explain the seemingly unusual feature of the thermodynamics associated with this reaction. ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.