chapter 2 biochemistry
... Examples of Compounds: H2O - water contains H and O in a definite proportion (2 to 1) This is the formula for ...
... Examples of Compounds: H2O - water contains H and O in a definite proportion (2 to 1) This is the formula for ...
Making Proteins
... the active I am going tomore try rate ofyou a chemical reaction ready for some rememberbindsI am a product, too. The substrate convert you.substrate sucrose! – Build up me? ortobreak down to me. I am a fructose now. • Fit together with its substrate like a “lock” and a I am now“key” a product. In ad ...
... the active I am going tomore try rate ofyou a chemical reaction ready for some rememberbindsI am a product, too. The substrate convert you.substrate sucrose! – Build up me? ortobreak down to me. I am a fructose now. • Fit together with its substrate like a “lock” and a I am now“key” a product. In ad ...
Bioc 3111 - Faculty Web Pages
... molecules: proteins, nucleic acids, lipids, carbohydrates, and metabolic intermediates. As you have discovered, chemistry deals with many different aspects of matter, e.g. structure, physical properties, and chemical properties,including reaction rates, mechanism, etc. Biochemistry is no exception. ...
... molecules: proteins, nucleic acids, lipids, carbohydrates, and metabolic intermediates. As you have discovered, chemistry deals with many different aspects of matter, e.g. structure, physical properties, and chemical properties,including reaction rates, mechanism, etc. Biochemistry is no exception. ...
Chemical Reactions in Living Things
... Examples of anabolic reactions include building up starch molecules from individual glucose molecules or building up proteins from amino acids. A very important CATABOLIC reaction is respiration when glucose is oxidised to release CO2, H2O and E (ATP). ENZYMES control all these chemical reactions. E ...
... Examples of anabolic reactions include building up starch molecules from individual glucose molecules or building up proteins from amino acids. A very important CATABOLIC reaction is respiration when glucose is oxidised to release CO2, H2O and E (ATP). ENZYMES control all these chemical reactions. E ...
Chem of Life_Bio
... most living things and include sugars, like glucose and sucrose, and starches. – Starches are long chains of sugars. ...
... most living things and include sugars, like glucose and sucrose, and starches. – Starches are long chains of sugars. ...
aerobic vs anerobic ws - Hicksville Public Schools
... 17. Energy is released from ATP when the bond is broken between a. two phosphate groups c. ribose and a phosphate group b. adenine and ribose d. adenine and a phosphate group ...
... 17. Energy is released from ATP when the bond is broken between a. two phosphate groups c. ribose and a phosphate group b. adenine and ribose d. adenine and a phosphate group ...
Chapter 3 Everyday Chemistry of Life Chemistry is crucial Biology
... o Some chemical reactions release energy o Other reactions require energy to form bonds o Energy can be stored in these bonds o That stored energy will be released when the bonds are broken Acids and bases o Acids are substances that dissociate and release hydrogen ions o Bases are substances that t ...
... o Some chemical reactions release energy o Other reactions require energy to form bonds o Energy can be stored in these bonds o That stored energy will be released when the bonds are broken Acids and bases o Acids are substances that dissociate and release hydrogen ions o Bases are substances that t ...
Cellular Respiration
... cells can extract energy from fats and proteins breakdown of fat and proteins creates products that can be fed into the enzyme pathways of respiration Fats starts with hydrolysis into glycerol and fatty acids glycerol is converted into G3P and enters pathway fatty acids are converted into acetyl-CoA ...
... cells can extract energy from fats and proteins breakdown of fat and proteins creates products that can be fed into the enzyme pathways of respiration Fats starts with hydrolysis into glycerol and fatty acids glycerol is converted into G3P and enters pathway fatty acids are converted into acetyl-CoA ...
Food Chemistry
... There are three different groups of carbohydrates. They are called monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides. “Saccharide” means sugar. Monosaccharides (single molecule sugars) A single molecule sugar is called a monosaccharide. The prefix “mono” means one. However, the one molecule can ha ...
... There are three different groups of carbohydrates. They are called monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides. “Saccharide” means sugar. Monosaccharides (single molecule sugars) A single molecule sugar is called a monosaccharide. The prefix “mono” means one. However, the one molecule can ha ...
The Chemical Building Blocks of Life
... 2. Side groups determine type. 3. Sterols are most abundant and have one polar hydroxyl group. 4. Mostly hydrophobic with hydroxyl giving slight hydrophobic property a. Cholesterol: found in membranes to stabilize the membrane fluidity b. Steroid hormones: control development, behavior, and more c. ...
... 2. Side groups determine type. 3. Sterols are most abundant and have one polar hydroxyl group. 4. Mostly hydrophobic with hydroxyl giving slight hydrophobic property a. Cholesterol: found in membranes to stabilize the membrane fluidity b. Steroid hormones: control development, behavior, and more c. ...
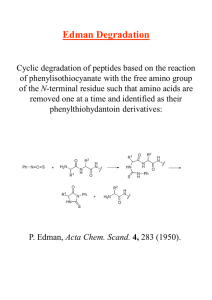
Edman Degradation
... Edman Degradation Cyclic degradation of peptides based on the reaction of phenylisothiocyanate with the free amino group of the N-terminal residue such that amino acids are removed one at a time and identified as their phenylthiohydantoin derivatives: ...
... Edman Degradation Cyclic degradation of peptides based on the reaction of phenylisothiocyanate with the free amino group of the N-terminal residue such that amino acids are removed one at a time and identified as their phenylthiohydantoin derivatives: ...
Cockayne syndrome
... Acid-base titration curve of amino acid and proteins o Protons will dissociate from weak acids at a certain pH, depending on the strength of the bond of the dissociable hydrogen. This pH is called the pKa of the acid. The Henderson-Hasselbach equation relates the relative amount of acid and base at ...
... Acid-base titration curve of amino acid and proteins o Protons will dissociate from weak acids at a certain pH, depending on the strength of the bond of the dissociable hydrogen. This pH is called the pKa of the acid. The Henderson-Hasselbach equation relates the relative amount of acid and base at ...
Sample exam 2
... The NH3 group is converted to Urea The NH3 group is converted to Acetyl-CoA The carbon skeleton is converted to Glucose The carbon skeleton is converted to Urea The carbon skeleton is converted to Ketone bodies ...
... The NH3 group is converted to Urea The NH3 group is converted to Acetyl-CoA The carbon skeleton is converted to Glucose The carbon skeleton is converted to Urea The carbon skeleton is converted to Ketone bodies ...
Chapter 2 Biochemistry Practice test
... 1. What are the three subatomic particles and their charges? a. Protons (+) b. Neutrons (0) c. Electrons (-) 2. What are the four organic compounds found in living things and what do they do? a. Carbohydrates – Main source of energy b. Lipids – Store energy c. Proteins – Chemical messengers d. Nucle ...
... 1. What are the three subatomic particles and their charges? a. Protons (+) b. Neutrons (0) c. Electrons (-) 2. What are the four organic compounds found in living things and what do they do? a. Carbohydrates – Main source of energy b. Lipids – Store energy c. Proteins – Chemical messengers d. Nucle ...
Why should we take care of our bodies?
... are made up of long chains of amino acids. It’s kind of like a really long pearl necklace. Each pearl is an amino acid held by a tight bond (called a peptide bond) between each one. ...
... are made up of long chains of amino acids. It’s kind of like a really long pearl necklace. Each pearl is an amino acid held by a tight bond (called a peptide bond) between each one. ...
Aquaporin IDI Prelab
... a. Why are the new water channels being developed referred to as biomimetic? ...
... a. Why are the new water channels being developed referred to as biomimetic? ...
Structural Biochemistry/Metabolism
... a. phospholipids consist of a glycerol, two fatty acid and a phosphate group attaching to an alcohol group b. phospholipids consist of hydrophilic head and hydrophobic tail c. phospholipids made up the cell membranes' bilayer 1) hydrophobic tails dislike water and try to get away by getting as close ...
... a. phospholipids consist of a glycerol, two fatty acid and a phosphate group attaching to an alcohol group b. phospholipids consist of hydrophilic head and hydrophobic tail c. phospholipids made up the cell membranes' bilayer 1) hydrophobic tails dislike water and try to get away by getting as close ...
Lecture 19
... (C•H2O)n Where n=3 or greater. A single saccharide is called a monosaccharide. Oligosaccharide is a few linked monosaccharides and are at time associated with proteins (glycoproteins) or lipids (glycolipids) Polysaccharides consist of many monosaccharides i.e. cellulose or glycogen ...
... (C•H2O)n Where n=3 or greater. A single saccharide is called a monosaccharide. Oligosaccharide is a few linked monosaccharides and are at time associated with proteins (glycoproteins) or lipids (glycolipids) Polysaccharides consist of many monosaccharides i.e. cellulose or glycogen ...
Fibrous proteins are especially abundant outside the cell, where
... For most animal and plant cells, glycolysis is only a prelude to the third and final stage of the breakdown of food molecules. In these cells, pyruvate formed at the end of glycolysis is rapidly transported into the mitochondria, completely oxidized to CO2 and H20. But for many anaerobic organisms, ...
... For most animal and plant cells, glycolysis is only a prelude to the third and final stage of the breakdown of food molecules. In these cells, pyruvate formed at the end of glycolysis is rapidly transported into the mitochondria, completely oxidized to CO2 and H20. But for many anaerobic organisms, ...
Faculty of Science Department of science Chemistry of
... to the steroid ring system. Examples of some chemical transformations with emphasis on Regio- and stereoselectivity. ■Nucleic acids (6) Structure of nucleic acids DNA and RNA. Biological function in relation to structure. Nucleosides and nucleotides. Transcription and protein synthesis. Synthesis of ...
... to the steroid ring system. Examples of some chemical transformations with emphasis on Regio- and stereoselectivity. ■Nucleic acids (6) Structure of nucleic acids DNA and RNA. Biological function in relation to structure. Nucleosides and nucleotides. Transcription and protein synthesis. Synthesis of ...
CHEMISTRY LIST OF TOPICS 1. Nature of chemistry (matter, mass
... 11. Heterocyclic compounds (nomenclature, nonaromatic heterocycles, aromatic heterocycles, five and six- membered ring containing heterocycles with one and more heteroatom(s), heterocycle derivatives);. 12. Carbohydrates (monosaccharides, disaccharides and polysaccharides); 13. Lipids (simple and co ...
... 11. Heterocyclic compounds (nomenclature, nonaromatic heterocycles, aromatic heterocycles, five and six- membered ring containing heterocycles with one and more heteroatom(s), heterocycle derivatives);. 12. Carbohydrates (monosaccharides, disaccharides and polysaccharides); 13. Lipids (simple and co ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.